Abstract
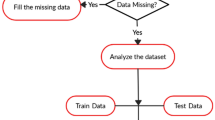
The key focus of this venture is to evaluate the calibration of classifiers built on rules, trees, and functions by exploring the uncertain information that exists in the Cardiotocography (CTG) dataset. Classification is imperative in diagnosing the health of the foetus and new born specifically in critical cases. It facilitates the obstetricians in acquiring the information of foetal well-being in pregnancy, substantially for the woman with complications. The research aims to classify the CTG data points into normal, suspicious and pathologic. Rules, trees, and function-based classifiers are applied in machine learning for predicting the health of the new born. Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) is used in pre-processing for selecting the relevant features. Rough set approximations are exploited in extracting the uncertain information from the data set. The result reveals the importance of useful information present in the uncertain data during classification. In this paper, the overall highest accuracy is displayed by Random Forest classifier with 99.57% and a tree-based approach has shown its supremacy over other approaches.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afridi R, Iqbal Z, Khan M, Ahmad A, Naseem R (2019) Fetal heart rate classification and comparative analysis using cardiotocography data and known classifiers. Int J Grid Distrib Comput 12(1):31–42
Amin B, Gamal M, Salama AA, Mahfouz K, El-Henawy IM (2019) Classifying cardiotocography data based on rough neural network. Mach Learn 10:8
Anitha A, Kannan E (2014a) Isolating critical data points from boundary region with feature selection. In: 2014 IEEE international conference on computational intelligence and computing research, (pp 1–4), IEEE
Anitha A, Kannan E (2014b) A constructive distance-based boundary detection approach with numeric variables. J Theor Appl Inf Technol 67:3
Ayres-de-Campos D, Bernardes J, Garrido A, Marques-de-Sa J, Pereira-Leite L (2000) SisPorto 2.0: a program for automated analysis of cardiotocograms. J Maternal-Fetal Med 9(5):311–318
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45(1):5–32
Cesarelli M, Romano M, Bifulco P (2009) Comparison of short term variability indexes in cardiotocographic foetal monitoring. Comput Biol Med 39(2):106–118
Cömert Z, Şengür A, Budak Ü, Kocamaz AF (2019) Prediction of intrapartum fetal hypoxia considering feature selection algorithms and machine learning models. Health Inf Sci Syst 7(1):17
Das S, Roy K, Saha CK (2019) Establishment of automated technique of FHR baseline and variability detection using CTG: statistical comparison with expert’s analysis. Int J Inf Eng Electronic Business 11:1
Deng W, Yao R, Zhao H, Yang X, Li G (2019) A novel intelligent diagnosis method using optimal LS-SVM with improved PSO algorithm. Soft Comput 23(7):2445–2462
Devane D, Lalor JG, Daly S, McGuire W, Cuthbert A, Smith V (2017) Cardiotocography versus intermittent auscultation of fetal heart on admission to labour ward for assessment of fetal wellbeing. Cochrane Datab Syst Rev 2017:1
Fawcett T (2006) An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recogn Lett 27(8):861–874
Fergus P, Huang DS, Hamdan H (2016) Prediction of intrapartum hypoxia from cardiotocography data using machine learning. In: Applied computing in medicine and health (pp 125–146), Morgan Kaufmann
Frank E, Hall MA (2011) Data mining: practical machine learning tools and techniques. Morgan Kaufmann
Hall M, Frank E, Holmes G, Pfahringer B, Reutemann P, Witten IH (2009) The WEKA data mining software: an update. ACM SIGKDD Explor Newsl 11(1):10–18
Heidari E, Sobati MA, Movahedirad S (2016) Accurate prediction of nanofluid viscosity using a multilayer perceptron artificial neural network (MLP-ANN). Chemometr Intell Lab Syst 155:73–85
Karabulut EM, Ibrikci T (2014) Analysis of cardiotocogram data for fetal distress determination by decision tree based adaptive boosting approach. J Comput Commun 2(9):32–37
Kaur G, Chhabra A (2014) Improved J48 classification algorithm for the prediction of diabetes. Int J Comput Appl 98:22
Keddachi K, Theljani F (2016) Fetal risk classification based on cardiotocography data: a kernel-based approach. In: Proceedings of the Second International Afro-European Conference for Industrial Advancement AECIA 2015 (pp 327–337). Springer, Cham
Loh WY (2011) Classification and regression trees. Wiley Interdiscipl Rev Data Min Knowl Discov 1(1):14–23
Macones GA, Hankins GD, Spong CY, Hauth J, Moore T (2008) The 2008 National Institute of Child Health and Human Development workshop report on electronic fetal monitoring: update on definitions, interpretation, and research guidelines. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs 37(5):510–515
Mahajan A, Ganpati A (2014) Performance evaluation of rule based classification algorithms. Int J Adv Res Comput Eng Technol 3(10):3546–3550
Molla MI, Jui JJ, Bari BS, Rashid M, Hasan MJ (2019) Cardiotocogram Data Classification Using Random Forest Based Machine Learning Algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 11th national technical seminar on unmanned system technology 2019 (pp. 357–369). Springer, Singapore
Moradi P, Gholampour M (2016) A hybrid pa rticle swarm optimization for feature subset selection by integrating a novel local search strategy. Appl Soft Comput 43:117–130
Moslehi F, Haeri A (2019) An evolutionary computation-based approach for feature selection. J Ambient Intell Hum Comput 2019:1–13
Newman DJ, Hettich S, Blake CL, Merz CJ, Aha DW (1998) UCI repository of machine learning databases. In: Department of Information and Computer Science, University of California, Irvine, CA. In: 1998 of Conference, http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets.html
Pal M (2005) Random forest classifier for remote sensing classification. Int J Remote Sens 26(1):217–222
Patil TR, Sherekar SS (2013) Performance analysis of j48 and j48 classification algorithm for data classification. Int J Comput Sci Appl 6:2
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough sets. Int J Comput Inform Sci 11(5):341–356
Platt J (1998) Sequential minimal optimization: a fast algorithm for training support vector machines
Potharaju SP, Sreedevi M, Ande VK, Tirandasu RK (2019) Data mining approach for accelerating the classification accuracy of cardiotocography. Clin Epidemiol Glob Health 7(2):160–164
Rajathi GM (2020) Optimized radial basis neural network for classification of breast cancer images. J Ambient Intell Hum Comput 2020:1–13
Ravi RV, Subramaniam K, Roshini TV, Muthusamy SPB, Venkatesan GP (2019) Optimization algorithms, an effective tool for the design of digital filters; a review. J Ambient Intell Hum Comput 2019:1–17
Rezaeian A, Rezaeian M, Khatami SF, Khorashadizadeh F, Moghaddam FP (2020) Prediction of mortality of premature neonates using neural network and logistic regression. J Ambient Intell Hum Comput 2020:1–9
Sathiaraj D, Triantaphyllou E (2012) On identifying critical nuggets of information during classification tasks. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 25(6):1354–1367
Shah SAA, Aziz W, Arif M, Nadeem MSA (2015) Decision trees based classification of cardiotocograms using bagging approach. In: 2015 13th International Conference on Frontiers of Information Technology (FIT) (pp 12–17), IEEE
Shahzad W, Asad S, Khan MA (2013) Feature subset selection using association rule mining and JRip classifier. Int J Phys Sci 8(18):885–896
Shehadeh M, Ebrahimi N, Ochigbo A (2012) Predicting the type of nanostructure using data mining techniques and multinomial logistic regression. Procedia Comput Sci 12:392–397
Silwattananusarn T, Kanarkard W, Tuamsuk K (2016) Enhanced classification accuracy for cardiotocogram data with ensemble feature selection and classifier ensemble. J Comput Commun 4(4):20–35
Smith V, Begley C, Newell J, Higgins S, Murphy DJ, White MJ, Devane D (2019) Admission cardiotocography versus intermittent auscultation of the fetal heart in low-risk pregnancy during evaluation for possible labour admission—a multicentre randomised trial: the ADCAR trial. BJOG Int J Obstetr Gynaecol 126(1):114–121
Spilka J, Chudáček V, Janků P, Hruban L, Burša M, Huptych M, Lhotská L et al (2014) Analysis of obstetricians’ decision making on CTG recordings. J Biomed Inform 51:72–79
Subasi A, Kadasa B, Kremic E (2020) Classification of the cardiotocogram data for anticipation of fetal risks using bagging ensemble classifier. Procedia Comput Sci 168:34–39
Thangaraj M, Vijayalakshmi CR (2013) Performance study on rule-based classification techniques across multiple database relations. Int J Appl Inf Syst 5(4):1–7
Xue B, Zhang M, Browne WN (2014) Particle swarm optimisation for feature selection in classification: novel initialisation and updating mechanisms. Appl Soft Comput 18:261–276
Yao Y (2008) Probabilistic rough set approximations. Int J Approx Reason 49(2):255–271
Yılmaz E (2016) Fetal state assessment from cardiotocogram data using artificial neural networks. J Med Biol Eng 36(6):820–832
Zeng X, Luo G (2017) Progressive sampling-based Bayesian optimization for efficient and automatic machine learning model selection. Health Inf Sci Syst 5(1):2
Zhang Y, Zhao Z (2017) Fetal state assessment based on cardiotocography parameters using PCA and AdaBoost. In: 2017 10th international congress on image and signal processing, BioMedical Engineering and Informatics (CISP-BMEI) (pp 1–6), IEEE
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kannan, E., Ravikumar, S., Anitha, A. et al. Analyzing uncertainty in cardiotocogram data for the prediction of fetal risks based on machine learning techniques using rough set. J Ambient Intell Human Comput (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02803-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02803-4