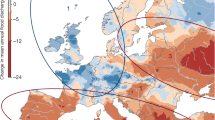
Abstract
In Central Europe, river flooding has been recently recognized as a major hazard, in particular after the 1997 Odra /Oder flood, the 2001 Vistula flood, and the most destructive 2002 deluge on the Labe/Elbe. Major recent floods in central Europe are put in perspective and their common elements are identified. Having observed that flood risk and vulnerability are likely to have grown in many areas, one is curious to understand the reasons for growth. These can be sought in socio-economic domain (humans encroaching into floodplain areas), terrestrial systems (land-cover changes – urbanization, deforestation, reduction of wetlands, river regulation), and climate system. The atmospheric capacity to absorb moisture, its potential water content, and thus potential for intense precipitation, are likely to increase in a warmer climate. The changes in intense precipitation and high flows are examined, based on observations and projections. Study of projected changes in intense precipitation, using climate models, for several areas of central Europe, and in particular, for drainage basins of the upper Labe/Elbe, Odra/Oder, and Vistula is reported. Significant changes have been identified between future projections and the reference period, of relevance to flood hazard in areas, which have experienced severe recent floodings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnell, N. and Liu, Chunzhen (Coordinating Lead Authors): 2001, Hydrology and water resources. Chapter 4 in: J. J. Mc Carthy, O. F. Canziani, N. A. Leary, D. J. Dokken and K. S. White (eds.), IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) Climate Change 2001: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of the Working Group II to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
A. Becker U. Grünewald (2003) ArticleTitleFlood risk in Central Europe Science 300 1099 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.1083624 Occurrence Handle12750504
S. Bergström A Forsman (1973) ArticleTitleDevelopment of a conceptual deterministic rainfall-runoff model Nord. Hydrol. 4 147–170
G. Berz (2001) Climatic change: effects on and possible responses by the insurance industry J. L. Lozán H. Graßl P. Hupfer (Eds) Climate of the 21st Century: Changes and Risks Wissenschaftliche Auswertungen Hamburg Germany Office 392–399
G. Bürger (2002) ArticleTitleSelected precipitation scenarios across Europe J. Hydrol. 262 99–110 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0022-1694(02)00014-8
J. H. Christensen O. B. Christensen (2003) ArticleTitleSevere summertime flooding in Europe Nature 421 805 Occurrence Handle10.1038/421805a Occurrence Handle12594501
O. B. Christensen J. H. Christensen B. Machenhauer M. Botzet (1998) ArticleTitleVery high-resolution regional climate simulations over Scandinavia – present climate J. Clim. 11 3204–3229 Occurrence Handle10.1175/1520-0442(1998)011<3204:VHRRCS>2.0.CO;2
M. Collins S. F. B. Tett C. Cooper (2001) ArticleTitleThe internal climate variability of HadCM3, a version of the Hadley Centre coupled model without flux adjustments Clim. Dynam. 17 61–81 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s003820000094
Gerstengarbe, F.-W. and Werner, P. C.: 1993, Katalog der Grosswetterlagen Europas nach Paul Hess und Helmuth Brezowski 1881–1992, Berichte des Deutschen Wetterdienstes Nr. 113, 4 Aufl., Selbstverlag des Deutschen Wetterdienst, Offenbach a. M., 249 pp.
Gerstengarbe, F.-W., Werner P. C. and Rüge, U.: 1999, Katalog der Grosswetterlagen Europas nach P. Hess und H. Brezowski 1881–1992, 5. Aufl. – Potsdam Institut für Klimafolgenforschung, Potsdam, Germany, 138 pp.
C. Gordon C. Cooper C. A. Senior H. T. Banks J. M. Gregory T. C. Johns J. F. B. Mitchell R. A. Wood (2000) ArticleTitleThe simulation of SST, sea ice extents and ocean heat transports in a version of the Hadley Centre coupled model without flux adjustment Clim. Dynam. 16 147–168 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s003820050010
D. Graczyk Z. W. Kundzewicz M. Szwed (2002) Zmienność przepływów rzeki Warty w Poznaniu, 1822–1994 (Variability of flow of the river Warta, 1822–1994) Z.W. Kundzewicz M. Radziejewski (Eds) Detekcja zmian klimatu i procesów hydrologicznych. (Detection of changes in climate and hydrological processes) Sorus Publishers Poznań 55–65
Grünewald, U. (ed.): 1998, Ursachen, Verlauf und Folgen des Sommer-Hochwassers 1997 an der Oder, sowie Aussagen zu bestehenden Risikopotentialen(Causes, course and consequences of the summer flood of 1997 on the Oder and assessment of existing risk potential; in German). Deutsche IDNDR Reihe 10a, Bonn, Germany.
Hess, P. and Brezowsky, H.: 1977, Katalog der Grosswetterlagen Europas. Berichte des Deutschen Wetterdienstes No. 113, Vol. 15, 2. Aufl. Selbstverlag des Deutschen Wetterdienstes, Offenbach a. M., 70 pp.
IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change): 2001a, Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis J. T. Houghton, Y. Ding, D. J. Griggs, M. Nouger, P. J. van der Linden, X. Dai, K. Maskell, and C. A. Johnson (eds.), Contribution of the Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change): 2001b, Climate Change 2001: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability J. J. McCarthy, O. F. Canziani, N. A. Leary, D. J. Dokken, and K. S. White (eds.), Contribution of the Working Group II to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, U.K.
IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change): 2001c, Climate Change 2001: Synthesis Report. Watson, R. T. and the Core Writing Team (eds.), Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
A. Krüger (2002) Statistische Regionalisierung des Niederschlags für Nordrhein-Westfalen auf Grundlage von Beobachtungsdaten und Klimaszenarien Mitteilungen aus dem Inst. für Geopysik und Meteorologie Universität zu Köln Köln, Germany 125
J. Kubát et al. (2003) Summary Report on Hydrometeorological Situation during the August 2002 Floods Czech Hydrometeorological Institute Prague Czech Republic
Z. W. Kundzewicz (2003) Extreme precipitation and floods in the changing world G. Blöschl S. Franks M. Kumagai K. Musiake D. Rosbjerg (Eds) Water Resources Systems – Hydrological Risk, Management and Development IAHS Press Wallingford 32–39
Z. W. Kundzewicz H.-J. Schellnhuber (2004) ArticleTitleFloods in the IPCC TAR perspective Nat. Hazards 31 IssueID1 111–128 Occurrence Handle10.1023/B:NHAZ.0000020257.09228.7b
Z. W. Kundzewicz K. Szamałek P. Kowalczak (1999) ArticleTitleThe Great Flood of 1997 in Poland Hydrol. Sci. J. 44 855–870
L. Menzel G. Bürger (2002) ArticleTitleClimate change scenarios and runoff response in the Mulde catchment (Southern Elbe, Germany) J. Hydrol. 267 53–64 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0022-1694(02)00139-7
M. Mudelsee M. Börngen G. Tetzlaff U. Grünewald (2003) ArticleTitleNo upward trends in the occurrence of extreme floods in central Europe Nature 421 166–169 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nature01928
Munich Re: 2003, Annual Review: Natural Catastrophes 2002. Topic 10.
R. J. Murray I. Simmonds (1991) ArticleTitleA numerical scheme for tracking cyclone centres from digital data. Part I: development and operation of the scheme Aust. Met. Magazine 39 155–166
N. Nakicenovic et al. (2000) IPCC Special Report on Emission Scenarios Cambridge University Press Cambridge, UK
Pinto, J. J. G.: 2002, Influence of Large-scale Atmospheric Circulation and Baroclinic Waves on the Variability of Mediterranean Rainfall. Mitteilungen aus dem Inst. für Geopysik und Meteorologie, Universität zu Köln, Köln, Germany, 134 pp.
V. D. Pope M. L. Gallani P. R. Rowntree R. A. Stratton (2000) ArticleTitleThe impact of new physical parametrizations in the Hadley Centre climate model – HadAM3 Clim Dynam. 16 123–146 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s003820050009
E. Roeckner K. Arpe L. Bengtsson L. Dümenil M. Esch E. Kirk F. Lunkeit M. Ponater B. Rockel R. Sausen U. Schlese S. Schubert M. Windelband (1992) Simulation of present-day climate with the ECHAM model: Impact of model physics and resolution Max-Planck-Institut für Meteorologie Hamburg
E. Roeckner K. Arpe L. Bengtsson M. Christoph M. Claussen L. Dümenil M. Esch M. Giorgetta U. Schlese U. Schulzweida (1996) The atmospheric general circulation model ECHAM4: Model description and simulation of present-day climate Max-Planck-Institut für Meteorologie Hamburg
Rudolf, B. and Simmer, C.: 2002, Niederschlag, Starkregen und Hochwasser. In: G. Tetzlaff (ed.), Wissenschaftliche Mitteilungen aus dem Institut für Meteorologie der Universität Leipzig. Sonderheft zum Jahr der Geowissenschaften – Atmosphäre November 2002, 28–43.
Rudolf, B. and Rapp, J.: 2003, The century flood of the River Elbe in August 2002: Synoptic weather development and climatological aspects, Quarterly Report of the Operational NWP-Models of the Deutscher Wetterdienst, Special Topic July 2002, Offenbach, Germany, 7–22.
U. Ulbrich T. Brücher A. H. Fink G. C. Leckebusch A Krüger J. G. Pinto (2003) ArticleTitleThe Central European Floods in August 2002, Part I: Rainfall periods and flood development Weather 58 371–376
U. Ulbrich T. Brücher A.H. Fink G.C. Leckebusch A. Krüger J.G. Pinto (2003) ArticleTitleThe Central European Floods in August 2002 , Part II: Synoptic causes and considerations with respect to climatic change Weather 58 434–441
W. J. Bebber Particlevan (1891) ArticleTitleDie Zugstraßen der barometrischen Minima nach den Bahnenkarten der Deutschen Seewarte für den Zeitraum von 1875–1890 Meteorol. Z. 8 361–366
P. C. Werner F.-W. Gerstengarbe (1997) ArticleTitleProposal for the development of climate scenarios Clim. Res. 8 171–182
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kundzewicz, Z.W., Ulbrich, U., brücher, T. et al. Summer Floods in Central Europe – Climate Change Track?. Nat Hazards 36, 165–189 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-004-4547-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-004-4547-6