Abstract
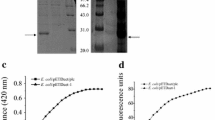
Twenty-two Bacillus cereus strains were screened for phospholipase C (PLC, EC 3.1.4.3) activity using p-nitrophenyl phosphorylcholine as a substrate. Two strains (B. cereus SBUG 318 and SBUG 516) showed high activity at elevated temperatures (>70°C) at acidic pH (pH 3.5–6) and were selected for cloning and functional expression using Bacillus subtilis. The genes were amplified from B. cereus DNA using primers based on a known PLC sequence and cloned into the expression vector pMSE3 followed by transformation into B. subtilis WB800. On the amino acid level, one protein (PLC318) was identical to a PLC described from B. cereus, whereas PLC516 contained an amino acid substitution (E173D). PLC production using the recombinant strains was performed by an acetoin-controlled expression system. For PLC516, 13.7 U g−1 wet cell weight was determined in the culture supernatant after 30 h cultivation time. Three purification steps resulted in pure PLC516 with a specific activity of 13,190 U mg−1 protein.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anthonsen T, D’Arrigo P, Pedrocchi-Fantoni G, Secundo F, Servi S, Sundby E (1999) Phospholipids hydrolysis in organic solvents catalysed by immobilised phospholipase C. J Mol Catal B Enzym 6:125–132
Durban M, Bornscheuer UT (2003) An assay system for the detection of phospholipase C activity. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 105:633–637
El-Sayed MY, Roberts MF (1985) Charged detergents enhance the activity of phospholipase C (Bacillus cereus) towards micellar short-chain phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta 831:133–141
Garcia de Herreros A, Dominguez I, Diaz-Meco MT, Graziani G, Cornet ME, Guddal PH, Johansen T, Moscat J (1991) Requirement of phospholipase C-catalyzed hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine for maturation of Xenopus laevis oocytes in response to insulin and ras p21. J Biol Chem 266:6825–6829
Ghelardi E, Celandroni F, Salvetti S, Barsotti C, Baggiani A, Senesi S (2002) Identification and characterization of toxigenic Bacillus cereus isolates responsible for two food-poisoning outbreaks. FEMS Microbiol Lett 208:129–134
Guddal PH, Johansen T, Schulstad K, Little C (1989) Apparent phosphate retrieval system in Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol 171:5702–5706
Haftendorn R, Ulbrich-Hofmann R (2002) Activity of phospholipase C in two-phase systems. Anal Biochem 306:144–147
Hergenrother PJ, Spaller MR, Haas MK, Martin SF (1995) Chromogenic assay for phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. Anal Biochem 229:313–316
Johansen T, Holm T, Guddal PH, Sletten K, Haugli FB, Little C (1988) Cloning and sequencing of the gene encoding the phosphatidylcholine-preferring phospholipase C of Bacillus cereus. Gene 65:293–304
Kamberov E, Ivanov A (1990) Purification of phospholipase-C from Bacillus cereus by affinity chromatography on 2-(4-aminophenylsulphonyl)ethyl-cellulose. J Chromatogr 525:307–318
Kurioka S, Matsuda M (1976) Phospholipase C assay using p-nitrophenylphosphoryl-choline together with sorbitol and its application to studying the metal and detergent requirement of the enzyme. Anal Biochem 75:281–289
Little C, Otnaess A-B (1975) The metal ion dependence of phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. Biochim Biophys Acta 391:326–333
Martin SF, Hergenrother PJ (1998) General base catalysis by the phosphatidylcholine-preferring phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus: the role of Glu4 and Asp55. Biochemistry 37:5755–5760
Mulcahy LS, Smith MR, Stacey DW (1985) Requirement for ras proto-oncogene function during serum-stimulated growth of NIH 3T3 cells. Nature 313:241–243
Notermans S, Batt CA (1998) A risk assessment approach for food-borne Bacillus cereus and its toxins. Symp Ser Soc Appl Microbiol 84:51–61
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Manniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press
Seo K-H, Rhee JI (2004) High-level expression of recombinant phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus in Pichia pastoris and its characterization. Biotechnol Lett 26:1475–1479
Silbersack J, Jürgen B, Hecker M, Schneidinger B, Schmuck R, Schweder T (2006) An acetoin-regulated expression system of Bacillus subtilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol (in press). DOI https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0549-5
Tan CA, Roberts MF (1998) Engineering of the nonspecific phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus: replacement of glutamic acid-4 by alanine results in loss of interfacial catalysis and enhanced phosphomonoesterase activity. Biochemistry 37:4275–4279
Tan CA, Hehir MJ, Roberts MF (1997) Cloning, overexpression, refolding, and purification of the nonspecific phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. Protein Expr Purif 10:365–372
Toora S, Singh G (1990) Factors affecting production and activity of phospholipase C by Yersinia enterocolitica. J Appl Bacteriol 69:113–118
Wu SC, Yeung JC, Duan Y, Ye R, Szarka SJ, Habibi HR, Wong SL (2002) Functional production and characterization of a fibrin-specific single-chain antibody fragment from Bacillus subtilis: effects of molecular chaperones and a wall-bound protease on antibody fragment production. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3261–3269
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Südchemie (München, Germany) for financial support and to Dr. Dirk Albrecht from the Division of Microbial Physiology and Molecular Biology of the Ernst-Moritz-Arndt-University Greifswald for the MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Durban, M.A., Silbersack, J., Schweder, T. et al. High level expression of a recombinant phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus in Bacillus subtilis . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74, 634–639 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0712-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0712-z