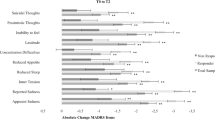
Summary
A study was carried out involving 134 neurotic-depressive inpatients (according to ICD-9) treated with cognitive behaviour therapy and in a subgroup additionally with antidepressants. Using standardized rating instruments, a large set of potential predictor variables was tested. After cross-validation according to the splithalf technique, only very few of these proved to be suitable as predictors for the main outcome criteria. These predictors included certain aspects of social functioning before index admission, intensity of depressive symptoms at admission and the degree of self-evaluated mood disturbances three weeks after admission. Several predictors known from the literature could not be reproduced in this study, demonstrating the well-known instability of most predictor findings. On the other side, the predictor profile of the neurotic-depressive patients was quite similar to that found in endogenous depressives, a result which might — together with other findings, such as the response of neurotic depressives to antidepressants — question the traditional subclassification of functional depressive states into these subgroups.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham HC, Kanter VB, Rosen I, Standen JL (1963) A controlled clinical trial of imipramine (Tofranil) with outpatients. Br J Psychiatry 109: 286–293
Ananth J (1978) Clinical prediction of antidepressant response. Int Pharmacopsychiatr 13: 69–93
Angst J (1965) Zur Prognose antidepressiver Behandlungen. Anglo-Germ Med Rev 2: 733–751
Avery DH, Wilson LG, Dunner DL (1983) Diagnostic subtypes of depression as predictors of therapeutic response. In: Clayton PJ, Barret JE (eds) Treatment of depression: old controversies and new approaches. Raven Press, New York, pp 193–205
Barthelmes H, Zerssen D v (1978) Das Münchner Psychiatrische Informationssystem (PSYCHIS München). In: Reichertz P, Schwarz E (eds) Informationssysteme in der medizinischen Versorgung. Ökologie der Systeme. Schattauer, Stuttgart, pp 138–145
Baumann U, Seidenstücker G (1977) Zur Taxonomie und Bewertung psychologischer Untersuchungsverfahren bei Psychopharmakaprüfungen. Pharmakopsychiatr 10: 291–331
Bielski RJ, Friedel O (1976) Prediction of tricyclic antidepressant response. A critical review. Arch. Gen Psychiatry 33: 1479–1489
Clancy J, Noyes R, Hoenk PR, Slymen DJ (1978) Secondary depression in anxiety neurosis. J Nerv Ment Dis, 166: 846–850
Conte HR, Plutchik R, Wild KV, Karasu TB (1986) Combined psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy for depression. A systematic analysis of the evidence. Arch Gen Psychiatry 43: 471–479
Covi L, Lipman RS, Derogatis LR, Smith III JE, Pattison JH (1974) Drugs and group psychotherapy in neurotic depression. Am J Psychiatry 131: 191–198
De Jong R (1986) Das Ansprechen auf verhaltenstherapeutisch-kognitive Behandlung bei Untergruppen depressiver Patienten mit einer ungünstigen Prognose. Verhaltensmodif 7: 152–168
De Jong R (1987) Neurotische Depression und psychologische Therapie. Lang, Frankfurt
De Jong R, Treiber R, Henrich G (1986) Effectiveness of two phsychological treatments for inpatients with severe and chronic depression. Cogn Ther Res 10: 645–663
Deykin EY, DiMascio A (1972) Relationship of patient background characteristics to efficacy of pharmacotherapy in depression. J Nerv Ment Dis 155: 209–215
Downing RW, Rickels K (1972) Predictors of amitriptyline response in outpatient depressives. J Nerv Ment Dis 154: 248–263
Ernst K, Ernst C (1968) Ergebnisse der Verlaufsforschung bei Neurosen. Eine vergleichende Literaturübersicht. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Fennell MJV, Teasdale JD (1982) Cognitive therapy with chronic, drug refractory depressed outpatients: A note of caution. Cogn Ther Res 6: 455–460
Friedman C, DeMowbray MS, Hamilton V (1961) Imipramine (Tofranil) in depressive states. J Ment Sci 107: 948–953
Gittelmann-Klein R, Klein D (1969) Premorbid asocial adjustment and prognosis in schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res 7: 35–53
Greer HS, Cawley RH (1966) Some observations on the natural history of neurotic illness. Archdall Medical Monograph, No 3. Australasian Medical Publishing, Sidney
Guy W (1976) Clinical Global Impressions (CGI). In: Guy W (ed) ECDEU assessment manual for psychopharmacology. Rockville, Maryland, pp 217–222
Harris JG (1975) An abbreviated form of the Phillips rating scale of premorbid adjustment in schizophrenia. J Abnorm Psychol 84: 129–137
Hiller W, v Zerssen D, Mombour W, Wittchen HU (1986) Die IMPS. Beltz, Weinheim
Kerr TA, Roth M, Schapira K, Gurney C (1972) The assessment and prediction of outcome in affective disorders. Br J Psychiatry 121: 167–174
Klerman GL, DiMascio A, Weissman M, Prusoff, B, Paykel ES (1974) Treatment of depression by drugs and psychotherapy. Am J Psychiatry 131: 186–191
Kiloh LG, Ball JR, Garside RF (1962) Prognostic factors in treatment of depressive states with imipramine. BMJ II: 1225–1227
Kupfer DJ, Spiker DG (1981) Refractory depression: prediction of non-response by clinical indicators. J Clin Psychiatry 42: 307–311
Lorr M (1974) Assessing psychotic behaviour by the IMPS. In: Pichot P, Olivier R (eds) Psychological measurement in psychopharmacology (Modern problems in pharmacopsychiatry, vol 7). Karger, Basel, pp 50–63
Möller HJ (1990) Möglichkeiten und Grenzen von Selbstbeurteilungsskalen zur Verlaufsbeurteilung depressiver Symptomatik im Rahmen der Therapie-Evaluation. In: Baumann U, Fähndrich E, Stieglitz R-D, Woggon B (eds) Veränderungsmessung in Psychiatrie und Psychologie. Theoretische, methodische und empirische Beiträge. Profil, München, pp 307–328
Möller HJ, Barthelmes H, Zerssen D v (1983) Forschungsmöglichkeiten auf der Grundlage einer routinemäßig durchgeführten psychiatrischen Basis- und Befunddokumentation. Psychiatr Clin 16: 45–61
Möller HJ, Fischer G, v Zerssen D (1987) Prediction of therapeutic response in acute treatment with antidepressants. Results of an empirical study involving 159 endogenous depressive inpatients. Eur Arch Psychiatr Neurol Sci 236: 349–357
Moore H, Kleining G (1960) Das soziale Selbstbild der Gesellschaftsschichten in Deutschland. Kölner Z Soziol Sozialpsychol 12: 86–119
Paykel ES, Prusoff BA, Klerman GI, Haskell D, DiMascio A (1973) Clinical responses to amitriptyline among depressed women. J Nerv Ment Dis 156: 149–165
Paykel ES, Freeling P, Hollyman JA (1988) Are tricyclic antidepressants useful for mild depression? A placebo controlled trial. Pharmacopsychiatry 21: 15–18
Prusoff BA, Weissman MM, Klerman GL, Rounsaville BJ (1980) Research diagnostic criteria. Subtypes of depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 37: 796–801
Raskin A, Crook TH (1976) The endogenous-neurotic distinction as a predictor of response to antidepressant drugs. Psychol Med 6: 59–70
Rose JT, Westhead TT (1967) Treatment of depression. A comparative trial of imipramine and desimipramine. Br J Psychiatry 113: 659–665
Strauss JS, Carpenter WT (1974) Prediction of outcome in schizophrenia. II. Relationship between predictor and outcome variables. Arch Gen Psychiatry 31: 37–42
Wechsler D (1964) Die Messung der Intelligenz Erwachsener. Hamburg-Wechsler-Intelligenz-Test für Erwachsene (HAWIE). 3. Aufl. Huber, Bern
Weissman MM, Prusoff MA, Klerman GL (1978) Personality and the prediction of long-term outcome of depression. Am J Psychiatry 135: 797–800
Wittenborn JR, Kiremitci N (1975) A comparison of antidepressant medications in neurotic and psychotic patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry 32: 1172–1176
Woggon B (1980) Veränderungen der psychopathologischen Symptomatik während 20tägiger antidepressiver oder neuroleptischer Behandlung. Psychiatr Clin 13: 150–164
Woggon B (1983) Prognose der Pharmakotherapie. Klinische Untersuchungen zur Voraussagbarkeit des Kurzzeittherapieer-folges von Neuroleptika und Antidepressiva Enke, Stuttgart
Zerssen D v (unter Mitarbeit von Koeller D-M) (1976) Klinische Selbstbeurteilungs-Skalen (KSb-S) aus dem Münchner Psychiatrischen Informationssystem (PSYCHIS München). a) Allgemeiner Teil; b) Paranoid-Depressivitäts-Skala; c) Befindlichkeits-Skala; d) Beschwerden-Liste. Beltz, Weinheim
Zerssen D v (1980) Psychopathometrische Verfahren und ihre Anwendung in der Psychiatrie. In: Peters U-H (ed) Die Psychologie des 20. Jahrhunderts, Bd X. Kindler, Zürich, pp 149–169
Zerssen D v (1982) Personality and affective disorders. In: Paykel ES (ed) Handbook of affective disorders. Livingston, Edinburgh, pp 212–228
Zerssen D v (1986) Clinical self-rating scales (CSRS) of the Munich psychiatric information system (PSYCHIS München). In: Sartorius N, Ban TA (eds) Assessment of depression. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 270–303
Zerssen D v, Cording C (1978) The measurement of change in endogenous affective disorders. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr 226: 95–112
Zerssen D v, Pfister H, Koeller D-M (1988) The Munich Personality Test (MPT) — a short questionnaire for self-rating and relatives' rating of personality traits: formal properties and clinical potential. Eur Arch Psychiatr Neurol Sci 238: 73–93
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Möller, H.J., Krokenberger, M. & v. Zerssen, D. Prediction of short-term outcome of neurotic-depressive inpatients. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Nuerosci 242, 301–309 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02190390
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02190390