Abstract
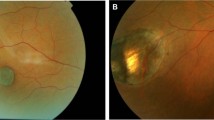
Of 51 infants and children who presented with visual impairment, developmental delays, and suspected brain abnormalities, 28 (55%) had clinical, electroretinographic, and cranial computed tomographic results indicative of cerebroretinal disorders. This report concentrates on the electroretinographic and psychophysical results from 12 patients who had evidence of progression of both brain and retinal disease. We believe these patients represent human cerebroretinal degenerative disorders that have yet to be completely characterized.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arden GB, Carter RM, Hogg CR, Powell DT, Ernst WJK, Clover GM, Lyness Al and Quinlan MP (1983) A modified ERG technique and the results obtained in X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Br J Ophthalmol 67:419–430
Foxman SG, Heckenlively JR and Wirtschafter J (1984) Classification of congenital and early onset retinitis pigmentosa. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 25 (Suppl), 128
Foxman SG, Wirtschafter JD and Letson RD (1983) Leber's congenital amaurosis and high hyperopia: a discrete entity. Proceedings of the International Congress of Ophthalmology. San Francisco, 1982, Acta XXIV, Vol. 1. Philadelphia, JB Lippincott, 55–58
Fulton AB and Hansen RM (1982) Background adaptation in human infants: Analysis of b-wave responses. Doc Ophthalmol Proc Ser 31:191–197
Fulton AB and Hansen RM (1983a) Retinal adaptation in infants and children with retinal degenerations. Ophthalmic Paediatr Genetics 2:167–179
Fulton AB and Hansen RM (1983b) Retinal sensitivity and adaptation in pediatric patients. Behavioural Brain Res 10:59–70
Fulton AB and Rushton WAH (1978) The human rod ERG: Correlation with psychophysical responses in light and dark adaptation. Vision Res 18:793–800
Fulton AB, Manning KA, Baker BN, Schukar SE and Bailey CJ (1982) Dark-adapted sensitivity, rhodopsin content, and background adaptation in ‘pcd/pcd’ mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 22:386–393
Geggel HS, Heckenlively JR, Martin Da, Ament ME and Kopple JD (1982) Human retinal dysfunction and taurine deficiency. Doc Ophthalmol Proc Ser 31:199–207
Mullen RJ and La Vail MM (1975) Two new types of retinal degeneration in cerebellar mutant mice. Nature 258:528–530
Nickel B and Hoyt CS (1982) Leber's congenital amaurosis; is mental retardation a frequent associated defect? Arch Ophthalmol 100:1089–1092
Noble KG and Carr RE (1978) Leber's congenital amaurosis, a retrospective study of 33 cases and a histopathological study of one case. Arch Ophthalmol 96:818–821
Perlman I (1983) Relationship between the amplitudes of the b-wave and a-wave as a useful index for evaluating the electroretinogram. Br J Ophthalmol 67:443–448
Robb RM, Dowton SB, Fulton AB and Levy HL (1984) Retinal degeneration in B12 disorder associated with methylmalonic aciduria and sulfur amino acid abnormalities. Am J Ophthalmol 97:691–696
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fulton, A.B., Hansen, R.M. & Harris, S.J. Retinal degenerations and brain abnormalities in infants and young children. Doc Ophthalmol 60, 133–140 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00158028
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00158028