Summary
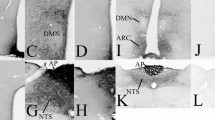
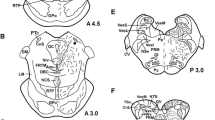
Glucagon- (GLU-IR), glicentin- (GLI-IR) and dopamine-beta-hydroxylase (DBH-IR) immunoreactive neurons were mapped in the medulla oblongata of colchicine pretreated guinea pigs. Numerous GLU-IR and GLI-IR perikarya are located in the area of the nucleus ambiguus, in the adjacent formatio reticularis, and less frequently in the nucleus reticularis lateralis, the nuclei raphe obscurus and commissuralis and the caudal part of the nucleus solitarius. In these nuclei, the coexistence of glicentin and glucagon within the same perikarya is demonstrated. DBH-IR is also found in neurons of the nuclei commissuralis, solitarius and reticularis lateralis (A1/A2 system of Dahlström and Fuxe 1964, 1965). However, a coexistence of GLU/GLI-IR and DBH-IR within the same neuron is not observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Colony PC, Helmstaedter V, Moody AJ, Garaud JC, Forssmann WG (1982) Glucagon and glicentin immunoreactive cells in human colon. Cell Tissue Res 221:483–491
Conlon JM, Samson WK, Dobbs RE, Orci L, Unger RH (1979) Glucagon-like polypeptides in canine brain. Diabetes 28:700–702
Dahlström A, Fuxe K (1964) Evidence for the existence of monoamine-containing neurons in the central nervous system. I. Demonstration of monoamines in the cell bodies of brain stem neurons. Acta Physiol Scand (Suppl. 232) 62:1–55
Dahlström A, Fuxe K (1965) Evidence for the existence of monoamine containing neurons in the CNS. II. Experimentelly induced changes in the intraneuronal amine levels of bulbospinal neuron systems. Acta Physiol Scand (Suppl. 247) 62:1–36
Dorn A, Bernstein H-G, Hahn H-J, Kostmann G, Ziegler M (1980) Regional distribution of glucagon-like immunoreactive material in the brain of rats and sand rats. An immunohistochemical investigation. Acta Histochem 66:269–272
Elger K-H (1983) Immunhistochemische Untersuchungen über das Vorkommen von glucagonartigen Peptiden im Zentralnervensystem des Meerschweinchens. Dissertation Heidelberg
Forssmann W-G, Pickel VM, Reinecke M, Hock D, Metz J (1981) Immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry of nervous tissue. In: Techniques in Neuroanatomical Research. Heym Ch, Forssmann W-G, (eds). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, pp 171–205
Garaud JC, Eloy R, Moody AJ, Stock C, Grenier JF (1980) Glucagon-and glicentin-immunoreactive cells in the human digestive tract. Cell Tissue Res 213:121–136
Guillemin R (1982) The brain as an endocrine organ — update 1981. Endocrinol Exp 16:151–162
Hamilton RB, Ellenberger H, Liskowsky D, Schneiderman N (1981) Parabrachial area as mediator of bradycardia in rabbits. J Autonom Nerv Syst 4:261–281
Hökfelt T, Fahrenkrug J, Tatemoto K, Mutt V, Werner S, Hulting A-L, Terenius L, Chang KJ (1983) The PHI (PHI-27)/corticotropin-releasing factor/enkephalin immunoreactive hypothalamic neuron: possible morphological basis for integrated control of prolactin, corticotropin, and growth hormone secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:895–898
Kalia M (1981) Brain stem localization of vagal preganglionic neurons. J Autonom Nerv Sys 3:451–481
Krieger DT (1983) Brain Peptides. What, where, and why? Science 222:975–985
Krieger DT, Liotta AS, Brownstein MJ, Zimmerman EA (1980) ACTH, β-Lipotropin, and related peptides in brain, pituitary and blood. Recent Prog Horm Res 36:277–336
Loewy AD, Wallach JH, McKellar S (1981) Efferent connections of the ventral medulla oblongata in the rat. Brain Res Rev 3:63–80
Matsushita M, Okado N (1981) Cells of origin of brainstem afferents to lobules I and II of the cerebellar anterior lobe in the cat. Neuroscience 6:2393–2405
Moody AJ, Sundby F (1980) Radioimmunoassay of gut-glucagon-like immunoreactants. In: Gastrointestinal hormones, Glass GBJ (ed). Raven Press, New York, pp 831–839
Moody AJ, Frandsen EK, Jacobsen H, Sundby F, Orci L (1976) The structural and immunologic relationship between gut GLIs and glucagon. Metabolism (Suppl. 1) 25:1336–1338
Moody AJ, Jacobsen H, Sundby F, Frandsen K, Beatens D, Orci L (1977) Heterogeneity of gut glucagon-like immunoreactivity (GLI). In: Glucagon: its role in physiology and clinical medicine. Foa PP, Bajaj JS (eds). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, pp 129–135
O'Donohue TL, Dorsa DM (1982) The opiomelanotropinergic neuronal and endocrine system. Peptides 3:353–395
Palkovits M, Jakobowitz DM (1974) Topographic atlas of catecholamine and acetyl-cholinesterase-containing neurons in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol 157:29–42
Pearson J, Goldstein M, Markey K, Brandeis L (1983) Human brainstem catecholamine neuronal anatomy as indicated by immunocytochemistry with antibodies to tyrosine hydroxylase. Neuroscience 8:3–32
Ravazzola M, Siperstein A, Moody AJ, Sundby F, Jacobsen H, Orci L (1979) Glicentin immunoreactive cells: their relationship to glucagon-producing cells. Endocrinology 105:499–508
Ravazzola M, Orci L (1980) Glucagon and glicentin immunoreactivity are topologically segregated in the granule of the human pancreatic. A cell. Nature 284:66–67
Saigal RP, Karamanlidis AN, Voogd J, Michaloudi H, Mangana O (1980) Cerebellar afferents from motor nuclei of cranial nerves, the nucleus of the solitary tract, and nuclei coeruleus and parabrachialis in sheep, demonstrated with retrograde transport of horseradish peroxidase. Brain Res 197:200–206
Sasaki H, Ebitani I, Tominaga M, Yamatani K, Yawata Y, Hara M (1980) Glucagon-like substance in the canine brain. Endocrinol Jpn 1:135–140
Somana R, Walberg F (1979) Cerebellar afferents from the nucleus of the solitary tract. Neurosci Lett 11:41–47
Sternberger LA (1979) Immunocytochemistry. Wiley, New York, pp 104–169
Tager H, Hohenboken M, Markese J, Dinerstein RJ (1980) Identification and localization of glucagon-related peptides in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:6229–6233
Thim L, Moody AJ (1981) The primary structure of porcine glicentin (proglucagon). Reg. Pept 2:139–150
Triepel J (1982) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) in the medulla oblongata of the guinea pig. Neurosci Lett 29:73–78
Triepel J, Elger KH, Thiekötter G, Marquard E, Forssmann W-G (1980) VIP- and glucagon-like immunoreactive neurons and axons in guinea pig brain. XI. Congreso internacional de Anatomia Ciudad de Mexico
Triepel J, Elger KH, Forssman WG (1982) Glicentin-immunoreactive perikarya and varicosities in the guinea pig central nervous system. Neurosci Lett 30:285–289
Vranic M, Engerman R, Doi K, Morita S, Yip CC (1976) Extrapancreatic glucagon and GLI. Extrapancreatic glucagon in the dog. Metabolism 25:1469–1473
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Carvas SFB 90
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Triepel, J., Elger, K.H., Mader, J. et al. Neurons of the A1/A2 region in the guinea pig medulla oblongata containing glucagon, glicentin, and dopamin-β-hydroxylase immunoreactivity. Anat Embryol 170, 239–245 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318727
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318727