Abstract
Research on aquatic ecosystems has shown the presence of diel (24 hour) variations of chlorophylla. In order to investigate this phenomenon in the Great Lakes, an IFYGL program was set up in which 8 cruises were made roughly monthly between April and October 1972. Two Lake Ontario Stations were chosen, one inshore near Oshawa, Ontario and the other mid-lake. Chlorophylla samples were taken approximately every two hours at depths of 1, 5 and 1o m at the inshore station and 1, 10 and 20 m at the mid-lake station.
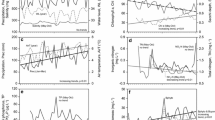
Chlorophylla concentrations at the 1 m depth were reduced during periods of high light intensities, but this phenomenon was observed only during the late June and July cruises at the near-shore station. Apparently, during most cruises, light intensities were too low to produce this effect. Coefficients of variation of chlorophylla concentrations as great as too% occurred at the deeper sampling depth during periods when the thermocline was well developed. This variability was associated with a thermocline motion in which the fixed depths sampled moved from the epilimnion into the thermocline or the hypolimnion and back again over the sampling period. When the lake was not thermally stratified, variability of chlorophylla concentrations was also observed with coefficients of variations between 20–3o%. Horizontal advection by currents, vertical turbulence, and presence of Langmuir cells were possible mechanisms causing such chlorophylla variability.
In light of these observations, caution must be used in interpreting spatial and temporal distributions of chlorophylla in lakes. Special care must be taken when sampling at depths near the thermocline due to movements that take place. For this reason, water samples taken from the epilimnion during periods of thermal stratification are recommended as opposed to fixed depth or integrated samples which could be affected by thermocline movements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bainbridge, R. 1957. The size, shape and density of marine phytoplankton concentrations. Biol. Rev. 32: 91–115.
Bennett, E. B. & Saylor, J. H. 1974. IFYGL Water Movement Program: a post field-work review. Paper presented at the 55th Annual Meeting, Amer. Geophysical Union, Washington, D.C. 8–12 April, 1974
Bernhard, M. & Rampi, L. 1965. Horizontal microdistribution of marine phytoplankton of the Ligurian Sea. Proc. 5th Mar. Biol. Sympos., Göteborg: 13–24.
Cassie, R. M. 1959. Microdistribution of plankton. N.Z. J. Sci. 2: 398–409.
Cassie, R. M. 1962. Microdistribution and other error components of C14 primary production estimates. Limnol. Oceanogr. 7:121–130.
Cassie, R. M. 1963. Microdistribution of plankton. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Ann. Rev. 1: 223–252.
Colebrook, J. M. 1960. Plankton and water movements in Windermere. J. Anim. Ecol. 29: 217–242.
Glooschenko, W. A., Curl, H. C. & Small, L. F. 1972a. Diel periodicity of chlorophyll a concentrations in Oregon Coastal Waters. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada. 29: 1253–1259
Glooschenko, W. A., Moore, J. E. & Vollenweider, R. A. 1972b. The seasonal cycle of pheo-pigments in Lake Ontario with particular emphasis on the role of zooplankton grazing. Limnol. Oceanogr. 17: 597–605.
Harris, G. P. & Lott, J. N. A. 1973. Observations of Langmuir circulations in Lake Ontario. Limnol. Oceanogr. 18: 584–6o9.
Hasle, G. R. 1954. The reliability of single observations in phytoplankton surveys. Nytt. Mag. Bot. 2: 121–137.
Ichimura, S. 1960. Diurnal fluctuation of chlorophyll content in Lake water. Bot. Mag. Tokyo 73: 217–224.
Kamykowski, D. 1974. Possible interactions between phytoplankton and semidiurnal internal tides. J. Mar. Res. 32:67–89.
Kramer, J. R., Allen, H. E., Baulne, G. W. & Burns, N. M. 1971. Lake Erie Time Study (LETS). Canada Centre for Inland Waters.
Mortimer, C. F. 1971. Large-scale oscillating motions and seasonal temperature changes in Lake Michigan and Lake Ontario. Special Report No. 12, Centre for Great Lakes Studies, University of Wisconsin, Milwaukee.
Platt, T. & Filion, C. 1973. Spatial variability of the productivity: biomass ratio for phytoplankton in a small marine basin. Limnol. Oceanogr. 18: 743–749
Platt, T., Dickie, L. M. & Trites, R. W. 1970. Spatial heterogeneity of phytoplankton in a near-shore environment. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada. 27: 1453–1473
Schröder, R. 1962. Vertikalverteilung des Zooplanktons und Thermokline. Arch. Hydrobiol. Suppl. Bd. 25: 401–410.
Schröder, R. 1969. Ein summierender Wasserschöpfer. Arch. Hydrobiol. 66: 241–243.
Small, L. F. 1963. Effect of wind on the distribution of chlorophyll a in Clear Lake, Iowa. Limnol. Oceanogr. 8:426–432.
Sournia, A. 1974. Circadian periodicities in natural populations of marine phytoplankton. Adv. Mar. Biol. 12: 325–389.
Verduin, J. 1951. A comparison of phytoplankton data obtained by a mobile sampling method with those obtained from a single station. Am. J. Bot. 38: 5–11.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was undertaken as part of the International Field Year for the Great Lakes, a joint Canadian-U.S. contribution to the International Hydrological Decade Program
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glooschenko, W.A., Blanton, J.O. Short-term variability of chlorophyll a concentrations in Lake Ontario. Hydrobiologia 53, 203–212 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00818542
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00818542