Abstract
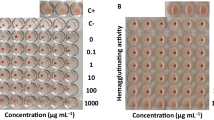
Five strains ofAeromonas hydrophila were studied for production of haemolysin specific for erythrocytes of various animal species using three cultural methods. All the strains produced haemolysin for all the erythrocyte species when the organisms were cultured on blood agar.
Using cellophane overlay method, all the strains produced haemolysin for fish erythrocytes and variable activity to mammalian erythrocytes. Only one strain produced haemolytic activity for various though not all of the erythrocyte species when grown in brain heart infusion broth.
Data suggest thatA. hydrophila produces multiple haemolysins with specificities for erythrocytes of different animals. This was confirmed for trout and horse erythrocyte targeted haemolysins, by using iso-electric focussing separation and by measuring the effect of addition of ammonium sulphate to the growth medium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan BJ & Stevenson RMW (1981) Extracellular virulence factors ofAeromonas hydrophila in fish infestions. Can. J. Microbiol. 27: 1114–1122
Asao T, Kozaki S, Keito K, Keiji KYO, Uemura T & Sakaguchi G (1986) Purification and characterization of anAeromonas hydrophila haemolysin. J. Clin. Microbiol. 24: 228–232
Bernheimer AW & Avigad L (1974) Partial characterization of Aerolysin, a lytic exotoxin fromAeromonas hydrophila. Infection and Immunity 9: 1016–1021
Boulanger Y, Lallier R & Cousineau G (1977) Isolation of enterotoxigenicAeromonas from fish. Can. J. Microbiol. 22: 1161–1164
Burke V, Robinson J, Gracey M, Peterson D, Meyer N & Halen V (1984) Isolation ofAeromonas spp. from an unchlorinated domestic water supply. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 48: 367–370
Cipriano RC, Bullock GL & Pule SW (1984)Aeromonas hydrophila and motile aeromonad septicaemias of fish. In: Fish Diseases, Leaflet, 68 p, US Dept of the Interior, Fish Wildlife Services, Division of Fishery Research, Washington
Lallier R & Higgins R (1988) Biochemical and toxigenic characteristics ofAeromonas spp. isolated from diseased mammals, moribund and healthy fish. Vet. Microbiol. 18: 63–71
Ljungh A, Wretlind B & Mollby R (1981) Separation and characterization of enterotoxin and two haemolysins fromAeromonas hydrophila. Acts. Path. Microbiol. Scand. 89: 387–397
Nieto TP & Ellis AE (1986) Characterization of extracellular metallo- and serine proteases ofAeromonas hydrophila. J. Gen. Microbiol. 132: 1975–1979
Popoff M (1984) Genus III,Aeromonas Kluyver and Van Niel 1936. In: Krieg NR (Ed) Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Vol I (pp 545–548). Baltimore, Williams and Wilkins
Rahim Z, Sanyl SC, Aziz KNS, Huo MI & Chowdhury AA (1984) Isolation of enterotoxigenic haemolytic and antibioticresistantAeromonas hydrophila strains from infected fish in Bangladesh. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 48: 865–867
Santos Y, Bandin I, Nieto RP, Nunez S & Toranzo A (1989) Haemolytic and agglutinating activities of motileAeromonas from fish culture systems. Bull. Eur. Ass. of Fish Path. 9(2): 31–34
Thune RL, Johnson MC, Graham TE & Amborski RL (1986)Aeromonas hydrophila B-haemolysins: Purification and examination of its role in virulence in O-group channel catfishIctalurus punctatus (Rafinesque). J. Fish Dis. 9: 55–61
Wretlind B, Mollby R & Wadstrom T (1971) Separation of two haemolysins fromAeromonas hydrophila by isoelectric focussing. Infection and Immun. 4: 503–505
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nzeako, B.C., Hastings, T.S. & Ellis, A.E. Cultural conditions forAeromonas hydrophila affect the production of haemolysins with differing host specificities. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 60, 67–72 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00572694
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00572694