Abstract
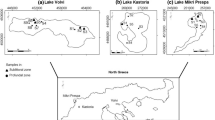
Many researchers have shown the importance of water chemistry and benthic habitat characteristics for the conservation of the freshwater macroinvertebrate biodiversity. However, few authors have examined the physical effect of extreme water-level fluctuations in lakes. The present study set out to determine, through a comparative study between a regulated lake (Laja Lake, LL) and an unregulated lake (Icalma Lake, IL) of the Andean zone of southern Chile, how man-made disturbances of the natural hydrological regime affect the structure of the benthic macroinvertebrate community. The results showed LL had very low values for species richness, density and biomass in comparison with IL, and the community was composed mainly of few individuals belonging to opportunistic taxa such as Chironomidae and Naididae. We suggest that the low values in the regulated lake are potentially explained by littoral zone factors driven by the water-level fluctuations such as: desiccation, freezing of the biota, removal of organic particles from the sediment and absence of aquatic macrophytes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan JD, Flecker AS (1993) Biodiversity conservation in running waters. BioScience 43:32–43
Batzer DP, Wissinger SA (1996) Ecology of insect communities on nontidal wetlands. Annu Rev Entomol 41:75–100
Bendell BE, McNicol DK (1987) Fish predation, lake acidity and the composition of aquatic insect assemblages. Hydrobiologia 150:193–202
Bendell BE, McNicol DK (1995) Lake acidity, fish predation and the distribution and abundance of some littoral insects. Hydrobiologia 302:133–145
Brodersen KP, Dall PC, Lindegaard C (1998) The invertebrate fauna in the upper stony littoral of Danish lakes: macroinvertebrates as trophic indicators. Freshw Biol 39:577–592
Bruguière JG (1789) Encyclopédie méthodique ou par ordre de mateières. Histoire naturelle des Vers, des Mollusques, Paris
Bryan SD, Hill TD, Lynott ST, Duffy WG (1995) The influence of changing water levels and temperatures on the food habits of walleye in Lake Oahe, South Dakota. J Freshwat Ecol 10:1–10
Buchanan JB (1984) Sediment analysis. In: McIntyre AD (ed) Methods for the study of marine benthos. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 41–65
CNE. (2006). Fijación de precios de nudo abril de 2006 sistema interconectado central (SIC). Technical report Comisión Nacional de Energía, Santiago de Chile
Colwell RK 1997. EstimateS: Statistical estimation of species richness and shared species from samples. Version 5. User’s Guide and application. Available via DIALOG. http://viceroy.eeb.uconn.edu/estimates. Cited 27 Jul 2006
Connell JH (1978) Diversity in tropical rain forest and coral reefs. Science 199:1302–1310
Connor EF, McCoy ED (1979) The statistics and biology of the species area relationship. Am Nat 113:791–833
D'Orbigny AD (1846) Voyage dans l'Amerique méridionale. 5, part. 3, Mollusques, Paris
Eadie JM, Keast A (1984) Resource heterogeneity and fish species diversity in lakes. Can J Zool 62:1689–1695
Fraser JC (1972) Water levels, fluctuation, and minimum pools in reservoirs for fish and other aquatic resources: an annotated bibiliography. FAO Fish Tech Pap 113:1–42
Friday LE (1987) The diversity of macroinvertebrate and macrophyte communities in ponds. Freshw Biol 18:87–104
Gaboury MN, Patalas JW (1984). Influence of water level drawdown on the fish populations of Cross Lake, Manitoba. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 41:118–125
Galat DL, Lipkin R (2000) Restoring the ecological integrity of great rivers: historical hydrographs aid in defining reference conditions for the Missouri River. Hydrobiologia 422/423:29–48
Gotelli N, Graves G (1996) Null models in ecology. Washington, Smithsonian Institution Press
Gray JE (1828) Spicilegia zoologica; or original figures and short systematic descriptions of new and unfigured animals, London
Hildrew AG, Townsend CR (1987) Organization in freshwater benthic communities. In: Gee JHR, Giller PS (eds) Organization of communities past and present. Blackwell, Oxford pp 347–371
Hill JL, Curran PJ, Foody GM (1994) The effect of sampling on the species-area curve. Global Ecol Biogeogr Lett 4:97–106
Hill NM, Keddy PA, Wisheu IC (1998) A hydrological model for predicting the effects of dams on the shoreline vegetation of lakes and reservoirs. Can J Bot 73:598–607
Hynes HB (1961) The effect of water-level fluctuations on littoral fauna. Verhandlungen Internationale Vereinigung Limnologie 14:652–656
Jeffries M (1989) Measuring Talling’s ‘element of chance’ in pond populations. Freshw Biol 21:383–393
Keddy PA, Reznicek AA (1986) Great Lakes vegetation dynamics: the role of fluctuating water levels and buried seeds. J Great Lakes Res 12:25–36
Lieffers VJ, Shay JM (1981) The effects of water level on the growth and reproduction of Scirpus maritimus var. paludosus. Can J Bot 59:118–121
MacArthur RJ, Wilson WO (1967) The Theory of island biogeography. Princeton University Press, New Jersey
Mardones M, Ugarte E, Rondanelli M, Rodríguez A and Barrientos C 1993. Planificación ecológica en el sector Icalma y Galletué (IX Región): Proposición de un método, v. 6. Concepción, Monografías Científicas EULA, Centro EULA-Chile, Universidad de Concepción
Mardones M, Vargas J (2005) Efectos hidrológicos de los usos eléctrico y agrícola en la cuenca del río Laja (Chile centro-sur). Revista de Geografía Norte Grande 33:89–102
Marklund H, Sandsten H, Hansson LS, Blindow I (2002) Effects of waterfowl and fish on submerged vegetation and macroinvertebrates. Freshw Biol 47:2049–2059
Muñoz S, Mendoza G, Valdovinos C (1999) Evaluación rápida de la biodiversidad de macroinvertebrados bentónicos en cinco lagos costeros de la VIII Región (Chile). Gayana (Zool) 62:86–91
Nardini A, Blanco H, Senior C (1997) Why didn’t EIA work in the chilean project canal Laja-Diguillín? Environ Impact Assess Rev 17:53–63
Palomäki R (1994) Response by macrozoobenthos biomass to water level regulation in some Finnish lake littoral zones. Hydrobiologia 286:17–26
Parra O, Vighi M, Valdovinos C, Urrutia R, Chuecas L, Campos H, Vismara R et al. (1993). Evaluación de la calidad del agua y ecología del sistema linético y fluvial del río Biobío: Monografías Científicas EULA, v. 12. Concepción, Centro EULA-Chile, Universidad de Concepción
Richter BD, Mathews R, Harrison DL, Wigington R (2003) Ecologically sustainable water management: managing river flows for ecological integrity. Ecol Appl 13:206–224
Robinson CLK, Tonn WM (1989) Influence of environmental factors and piscivory in structuring fish assemblages of small Alberta lakes. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 46:81–89
Rodríguez MA, Lewis WM (1997) Structure of fish assemblages along environmental gradients in floodplain lakes of the Orinoco River. Ecol Monogr 67:109–128
Scarsbrook MR, Townsend CR (1993) Stream community structure in relation to spatial and temporal variation: a habitat template stud of two contrasting New Zealand streams. Freshw Biol 29:395–410
Scasso F, Campos H (2000) Pelagic fish communities and eutrophication in lakes of an andean basin of central Chile. J Freshw Ecol 15:71–82
Tadeusz P, Miroslawa P, Bijok P (1999) Diversity of invertebrate fauna in littoral of shallow Myczkowce dam reservoir in comparison with a deep Solina dam reservoir. Hydrobiologia 408:203–210
Tonn WM, Magnuson JJ (1982) Patterns in the species composition and richness of fish assemblages in northern Wisconsin lakes. Ecology 63:1149–1166
Townsend CR, Scarsbrooke MR, Doledec S (1997) The intermediate disturbance hypothesis, refugia, and biodiversity in streams. Limnol Oceanogr 42:938–941
Valdovinos C (2006) Invertebrados dulceacuícolas, In: CONAMA (ed) Biodiversidad de Chile – patrimonio y desafíos. Santiago de Chile, Ocho Libros, pp 204–225
Vargas J, Alarcón B (2001) Aportes al balance hídrico de la cuenca del Laja XV Congreso Chileno de Ingeniería Hidráulica 1:125–132
Varrelman SK, Spencer CN (1991) Preliminary investigation of effects of water-level regulation on nearshore benthic invertebrates of Flathead Lake compared to Lake McDonald, northwest Montana. Proc Montana Acad Sci 51:85–102
Ward JV (1992) Aquatic insect ecology. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Ward JV (1998) Riverine landscapes: biodiversity patterns, disturbance regimes, and aquatic conservation. Biol Conserv 83:269–278
Wellborn GA, Skelly DK, Werner EW (1996) Mechanisms creating community structure across a freshwater habitat gradient. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 27:337–363
Wilcox DA (1993) Effects of water-level regulation on wetlands of the Great Lakes. Great Lakes Wetlands 4:1–2
Wilcox DA, Meeker JE (1991) Disturbance effects on aquatic vegetation in regulated and unregulated lakes in northern Minnesota. Can J Bot 69:1542–1551
Wilcox DA, Meeker JE (1992) Implications for faunal habitat related to altered macrophyte structure in regulated lakes in northern Minnesota. Wetlands 12:192–203
Zar JH (1999). Biostatistical analysis. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Drs. Lizandro Chuecas and Sergio Mancinelli (University of Concepcion, Chile) and for their helpful comments pertaining to the manuscripts. We also thank Alejandro Peña, Hector Alonso, Waldo San Martin, and Miguel Vilches, for their help in the field. This work was supported by the FONDECYT (Chile) Project 1000526, DIUC (University of Concepcion) 203.310.036–1.0 and the International Scientific Program CHL00/03 between CONICYT (Chile) and BMBF (Germany).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valdovinos, C., Moya, C., Olmos, V. et al. The importance of water-level fluctuation for the conservation of shallow water benthic macroinvertebrates: an example in the Andean zone of Chile. Biodivers Conserv 16, 3095–3109 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-007-9165-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-007-9165-7