Abstract
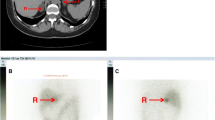
In primary aldosteronism the type of adrenal lesion was correctly identified in 28 of 40 patients (70%) by standard adrenal scintigraphy. Suppression scintigraphy did not improve the validity of the method. In all patients the diagnosis was confirmed by surgery (unilateral adenoma n=32; bilateral adrenal hyperplasia n=11). False classification of the adrenal lesion(s) by standard scintigraphy was mostly due to a bilateral adrenal isotopic uptake in patients with an unilateral aldosteronoma. However, a substantial number of these patients (6 of 11 patients) received long-term spironolactone treatment prior to the examination. Thus, in primary aldosteronism adrenal changes induced by chronic spironolactone administration are probably a major cause for incorrect differentiation between adenoma and hyperplasia by adrenal scintigraphy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beierwaltes WH, Lieberman LM, Ansari AN, Nishiyama H (1971) 131I-19-iodocholesterol in the diagnosis of adrenal disease. J Lab Clin Med 78:986–987
Conn JW, Hinerman DL (1977) Spironolactone-induced inhibition of aldosterone biosynthesis in primary aldosteronism: morphological and functional studies. Metabolism 26:1293–1307
Gaillard RC, Riondel AM, Chabert P, Vallotton MB (1980) Effect of spironolactone on aldosterone regulation in man. Clin Sci Mol Med 58:227–233
Kovacs K, Horvath F, Singer W (1973) Fine structure and morphogenesis of spironolactone bodies in the zona glomerulosa of the human adrenal cortex. J Clin Pathol 26:949–957
Lumb G, Newberne P, Rust JH, Wagner B (1978) Effects in animals of chronic administration of spironolactone — a review. J Environ Pathol Toxicol 1:647–660
Sundsfjord JA, Marton P, Jørgensen H, Aakvaag A (1973) Reduced aldosterone secretion during spironolactone treatment in primary aldosteronism: report of a case. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 39:734–739
Vetter H, Vetter W (1975) Control of plasma aldosterone in a patient with Conn's Syndrome before and during spironolactone medication. Klin Wochenschr 53:391–393
Vetter H, Appenheimer M, Lucas R, Weiand H, Herschbach ML, Glänzer K, Witassek F, Krück F (1977) Effect of spironolactone on plasma and urinary aldosterone in primary aldosteronism. Horm Res 8:23–28
Vetter H, Brecht G, Fischer M, Galanski M, Glänzer K, Cramer BM, Puoliadis G, Sialer G, Studer A, Tenschert W, Wollnik S, Zumkley H, Vetter W (1980) Laterization procedures in primary aldosteronism. Klin Wochenschr 58:1135–1141
Weinberger MH, Grim CE, Hollifield JW, Kem DC, Ganguly A, Kramer NJ, Yune HY, Wellman H, Donohuf JP (1979) Primary aldosteronism — diagnosis, localization, and treatment. Ann Intern Med 90:386–395
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fischer, M., Vetter, W., Winterg, B. et al. Adrenal scintigraphy in primary aldosteronism. Spironolactone as a cause of incorrect classification between adenoma and hyperplasia. Eur J Nucl Med 7, 222–224 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00256468
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00256468