Abstract
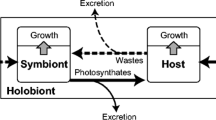
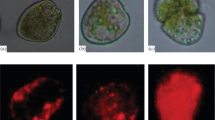
Laboratory experiments were carried out to determine the influence of symbiotic dinoflagellates (zooxanthellae) on the shell growth, longevity, and reproductive potential of Globigerinoides sacculifer (Brady). Its symbionts were eliminated by 72-h treatment with a photosynthetic inhibitor (DCMU). Symbiont elimination resulted in earlier gametogenesis (shortened survival time) and smaller shell sizes of G. sacculifer when compared to untreated foraminifera grown in sea water. Individuals kept in continuous darkness in untreated sea water also exhibited early gametogenesis, short survival times and small shell sizes. Aposymbiotic foraminifera formed on the average one or two chambers fewer per individual and their rate of shell size increase is slower than symbiont-bearing foraminifera. Symbionts were lysed within perialgal vacuoles of G. sacculifer when subjected to DCMU treatment or kept in continuous darkness. One DCMU-treated group was reinfected with symbionts from crushed G. sacculifer donors. Soon after reinfection, these foraminifera resumed a shell growth rate and exhibited developmental stages that were nearly equivalent to those of untreated individuals, as deduced from their shell size, frequency of sac-like chambers, rate of gametogenesis, and survival time. Our experiments indicate that the symbionts aid in calcification and that elimination of symbionts triggers gametogenesis, thus shortening the life span of the foraminiferal host. The results imply that shell growth in symbiont-bearing planktonic foraminifera occurs mainly in the euphotic zone and that they do not survive for long periods below it.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Alldredge, A. L. and B. M. Jones: Hastigerina pelagica: foraminiferal habitat for planktonic dinoflagellates. Mar. Biol. 22, 131–135 (1973)
Anderson, O. R.: Fine structure of a symbiont-bearing colonial Radiolarian, Collosphaera globularis, and 14C isotopic evidence for assimilation of organic substances from its zooxanthellae. J. Ultrastructure Res. 62, 181–189 (1978)
Anderson, O. R. and A. W. H. Bé: The ultrastructure of a planktonic foraminifer, Globigerinoides sacculifer (Brady) and its symbiotic dinoflagellates. J. Foram. Res. 6(1), 1–21 (1976)
Barnes, D. J. and D. L. Taylor: In situ studies of calcification and photosynthetic carbon fixation in the coral Montastrea annularis. Helgoländer wiss. Meeresunters. 24, 284–291 (1973)
Bé, A. W. H.: An ecological, zoogeographic and taxonomic review of Recent planktonic foraminifera. In: Oceanic micropaleontology, pp 1–100. Ed. by A. T. Ramsay. London: Academic Press 1977
Bé, A. W. H.: Gametogenic calcification in a spinose planktonic foraminifer, Globigerinoides sacculifer (Brady). Mar. Micropaleont. 5, 283–310 (1980)
Bé, A. W. H., D. A. Caron and O. R. Anderson: Effects of feeding frequency on life processes of the planktonic foraminifer Globigerinoides sacculifer (Brady) in laboratory culture. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 61(1), 257–277 (1981)
Bé, A. W. H., Chr. Hemleben, O. R. Anderson, M. Spindler, J. Hacunda and S. Tuntivate-Choy: Laboratory and field observations of living planktonic forminifera. Micropaleontology 23(2), 155–179 (1977)
Bé, A. W. H. and W. H. Hutson: Ecology of planktonic foraminifera and biogeographic patterns of life and fossil assemblages in the Indian Ocean. Micropaleontology 23(4), 369–414 (1977)
Bé, A. W. H. and H. J. Spero: Shell regeneration and biological recovery of planktonic foraminifera after physical injury induced in laboratory culture. Micropaleontology 27(3), 305–316 (1981)
Caron, D. A., A. W. H. Bé and O. R. Anderson: Effects of variations in light intensity on life processes of the planktonic foraminifer Globigerinoides sacculifer in laboratory culture. J. mar. biol. Ass. U. K. 62(2), 435–451 (1982)
Chalker, B. E.: Calcium transport during skeletogenesis in heramatypic corals. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 54a, 455–459 (1976)
Chalker, B. E. and D. L. Taylor: Light-enhanced calcification and the role of oxidative phosphorylation in calcafication of the coral Acropora cervicornis. Proc. R. Soc. London B 190, 323–331 (1975)
Dietz-Elbrächter, G.: Untersuchungen über die Zooxanthellen der Foraminifere Heterostegina depressa Orbigny, 1826. Meteor Forsch. Ergebn., Reihe C 6, 41–47 (1971)
Duguay, L. E. and D. L. Taylor: Primary production and calcification by the soritid foraminifer Archaias angulatus (Fichtel and Moll). J. Protozoology 25(3), 356–361 (1978)
Goreau, T. F.: Calcium carbonate deposition by coralline algae and corals in relation to their roles as reef builders. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 109, 127–167 (1963)
Hallock, P.: Trends in test shape with depth in large symbiontbearing foraminifera. J. Foram. Res. 9(1), 61–69 (1979)
Hottinger, L. and D. Dreher: Differentiation of protoplasm in Nummulitidae (Foraminifera) from Elat, Red Sea. Mar. Biol. 25, 41–61 (1974)
Kremer, B. P., R. Schmaljohann and R. Röttger: Features and nutritional significance of photosynthates produced by unicellular algae symbiontic with larger foraminifera. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2, 225–228 (1980)
Lee, J. J., H. D. Freudenthal, V. Kossoy and A. W. H. Bé: Cytological observations on two planktonic foraminifera, Globigerina, bulloides and Globigerinoides ruber. J. Protozoology 12(4), 531–542 (1965)
Lee, J. J. and W. Zucker: Algal flagellate symbiosis in the foraminifer Archaias. J. Protozoology 16, 71–81 (1969)
Lee, J. J. and W. D. Bock: The importance of feeding in 2 species of soritid foraminifera with algal symbionts. Bull. mar. Sci. 26(4), 530–537 (1977)
Lee, J. J., M. E. McEnery, E. G. Kahn and F. L. Schuster: Symbiosis and the evolution of larger foraminifera. Micropaleontology 25(2), 118–140 (1979)
Lee, J. J., M. E. McEnery, R. Röttger and Ch. W. Reimer: The isolation, culture and identification of endosymbiotic diatoms from Heterostegina depressa d'Orbigny and Amphistegina lessonii d'Orbigny (larger Foraminifera) from Hawaii. Bot. Mar. 23, 297–302 (1980)
Leutenegger, S.: Ultrastructure and motility of dinophyceans symbiotic with larger, imperforated foraminifera. Mar. Biol. 44, 157–164 (1977a)
Leutenegger, S.: Ultrastructure des foraminiferes perforés et imperforés ainsi que de leurs symbiotes. Cah. Micropaleont., Cent. Nat. R. S. Paris 3, 1–51 (1977b)
Müller-Merz, E. and J. J. Lee: Symbiosis in the larger foraminiferan Sorites marginalis (with notes on Archaias spp.). J. Protozoology 23(3), 390–396 (1976)
Murray, J.: On the distribution of the pelagic foraminifera at the surface and on the floor of the ocean. Nat. Sci. (ecology), 11, 17–27 (1897)
Muscatine, L.: Nutrition in corals. In: Biology and geology of coral reefs, Vol II, Biology I, pp 271–324. Ed. by O. A. Jones and R. Endean, New York: Academic Press 1973
Pearse, V. B. and L. Muscatine: Role of symbiotic algae (zooxanthellae) in coral calcification. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 141, 350–363 (1971)
Rahat, M. and O. Adar: Effect of symbiotic zooxanthellae and temperature on budding and strobilition in Cassiopeia andromeda. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 159, 394–401 (1980)
Rhumbler, L.: Die Foraminiferen (Thalamophoren) der Plankton-Expedition; Teil 1. Die allgemeinen Organisationsverhältnisse der Foraminiferen. Plankton-Exped. Humboldt-Stiftung, Ergebn., 3 L, C. I, 1–331 (1911)
Ross, C. A.: Biology and ecology of Marginopora vertebralis (Foraminiferida), Great Barrier Reef. J. Protozool. 19(1), 181–192 (1972)
Ross, C. A.: Evolutionary and ecological significance of large calcareous foraminiferida (protozoa), Great Barrier Reef. Proceedings of the Second International Coral Reef Symposium 1, 327–333 (1974)
Röttger, R.: Die Bedeutung der Symbiose von Heterostegina depressa (Foraminifera, Nummulitidae) für hohe Siedlungsdichte und Karbonatproduktion. Deutsch. zool. Gesell. Verh. 65, 42–47 (1972)
Smith, D. C., L. Muscatine and D. H. Lewis: Carbohydrate movement from autotrophs to heterotrophs in parasitic and mutualistic symbiosis. Biol. Rev. 44, 17–90 (1969)
Sournia, A.: Primary production of sands in the lagoon of an atoll and the role of foraminiferan symbionts. Mar. Biol. 37, 29–32 (1976)
Spindler, M. and Ch. Hemleben: Symbionts in planktonic foraminifera (Protozoa). In: Endocytobiology—endosymbiosis and cell biology, Vol. 1. pp 133–140. Ed. by W. Schwemmler and H. E. A. Schenk. New York, Berlin: Walter de Gruyter and Co 1980
Steele, R. D. and D. C. Smith: Factors affecting the reduction of algal symbiont populations in green hydra. J. Zool. Soc. London 193, 201–214 (1981)
Taylor, D. L.: On the symbiosis between Amphidinium klebsii (Dinophyceae) and Amphiscolops langerhansi (Turbellaria: Acoela). J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 51, 301–314 (1971)
Taylor, D. L.: Symbiotic marine algae: taxonomy and biological fitness. In: Symbiosis in the sea, pp 245–262. Ed. by W. B. Vernberg. Columbia, S.C.: University of South Carolina Press 1974
Tizard, T. H., H. N. Moseley, J. Y. Buchanan and J. Murray: Narrative of the cruise of H.M.S. “Challenger”, with a general account of the scientific results of the expedition. Sci. Res. H.M.S. “Challenger” 1873–1876, Rept. 1(2), 511–1110 (1885)
Trench, R. K.: The physiology and biochemistry of zooxanthellae symbiotic with marine coelenterates. I. The assimilation of photosynthetic products of zooxanthellae by two marine coelenterates. Proc. R. Soc. London B 177, 225–235 (1971a)
Trench, R. K.: The physiology and biochemistry of zooxanthellae symbiotic with marine coelenterates. II. Liberation of fixed 14C by zooxanthellae In vitro. Proc. R. Soc. London B 177, 237–250 (1971b)
Trench, R. K.: The physiology and biochemistry of zooxanthellae symbiotic with marine coelenterates. III. The effect of homogenates of host tissues on the excretion of photosynthetic products in vitro by zooxanthellae from two marine coelenterates. Proc. R. Soc. London B 177, 251–264 (1971c)
Vandermeulen, J. H., N. D. Davis and L. Muscatine: The effect of inhibitors of photosynthesis on zooxanthellae in corals and other marine invertebrates. Mar. Biol. 16, 185–191 (1972)
Zucker, W. H.: Fine structure of planktonic foraminifera and their endosymbiotic algae. Ph.D. Thesis, City University of New York, N.Y., 65 pp. 1973
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by S. K. Pierce, College Park
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bé, A.W.H., Spero, H.J. & Anderson, O.R. Effects of symbiont elimination and reinfection on the life processes of the planktonic foraminifer Globigerinoides sacculifer . Mar. Biol. 70, 73–86 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397298
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397298