Abstract
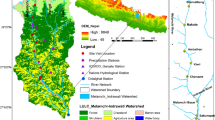
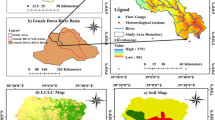
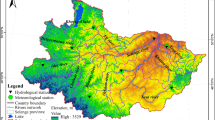
A catchment model coupled with a lake thermal model has been used to simulate the lake water balance of Lake Qinghai, a large inland lake on the northeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in China. The sensitivity analyses show that changes in precipitation will produce larger changes in runoff than temperature and cloudiness, whereas changes in lake level are equally sensitive to changes in temperature and precipitation. With a doubling of CO2 in the atmosphere, four GCMs experiments predict warmer and wetter conditions in the Qinghai region than at present. The total runoff in the lake basin and evaporation will, in most cases, increase as conditions become warmer and wetter. The lake level changes would remain uncertain because the effects of an increase in precipitation are countered by the rise of temperature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
An, Z., Wu, X., Wang, P., Wang, S., Dong, G., Sun, X., Zhang, D., Lu, Y., Zheng, S., and Zhan, S.: 1991a, ‘The Ancient Monsoon in China in the Last 130 ka - I. Records of Ancient Monsoon’, Sci. China 10, 1076-1081 (in Chinese).
An, Z., Wu, X., Wang, P., Wang, S., Dong, G., Sun, X., Zhang, D., Lu, Y., Zheng, S., and Zhan, S.: 1991b, ‘The Ancient Monsoon in China in the Last 130 ka - II. Variations of Ancient Monsoon’, Sci. China 11, 1209-1215 (in Chinese).
Bultot, F., Dupriez, G. L., and Gelleus, D.: 1988a, ‘Estimated Annual Regime of Energy-Balance Components, Evaportranspiration and Soil Moisture for a Drainage Basin in the Case of a CO2 Doubling’, Clim. Change 12, 39-56.
Bultot, F., Coppens, A., Dupriez, G. L., and Gelleus, D.: 1988b, ‘Repercussions of a CO2 Doubling on the Water Cycle and on the Water Balance - a Case Study for Belgium’, J. Hydrol. 99, 319-347.
Chen, K., Bowler, J. M., and Kelts K.: 1990, ‘Palaeoclimatic Evolution Within the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau in the Last 40,000 Years’, Quat. Sci.bf 1, 21-31 (in Chinese).
Cohen, S. J.: 1986, ‘Impacts of CO2 - Induced Climatic Change on Water Resources in the Great Lake Basin’, Clim. Change 8, 135-153.
Cohen, S. J.: 1991, ‘Possible Impacts of Climatic Warming Scenarios on Water Resources in the Saskatchewan River Sub-Basin, Canada’, Clim. Change 19, 291-317.
COHMAP Members: 1988, ‘Climatic Changes of the Last 18,000 Years: Observations and Model Simulations’, Science 241,1043-1052.
Croley II, T. E.: 1990, ‘Laurentian Great Lakes Double-CO2 Climate Change Hydrological Impacts’, Clim. Change 17, 27-47.
De Bruin, H. A. R. and Wessels, H. R. A.: 1988, ‘A Model for the Formation and Melting of Ice on Surface Waters’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 27, 164-173.
Fang, J.-Q.: 1991, ‘Lake Evolution During the Past 30,000 years in China, and Its Implications for Environmental Change’, Quat. Res. 36, 37-60.
Flaschka, J. M., Stockton, C., and Boggess, W.: 1987, ‘Climatic Variation and Surface Water Resources in the Great Basin Region’, Water Resour. Bull. 23, 47-57.
Glazovsky, N. F.: 1990, ‘A Concept on the Resolving of the Aral Crisis’, Proceeding of the U.S.S.R. Academy of Sciences (Geographical Series), 4, 28-41 (in Russian).
Gleick, P. H.: 1986, ‘Methods for Evaluating the Regional Hydrologic Impacts of Global Climatic Changes’, J. Hydrol. 88, 97-116.
Gleick, P. H.: 1987, ‘The Development and Testing of a Water Balance Model for Climate Impact Assessment: Modeling the Sacramento Basin’, Water Resour. Res. 23, 1049-1061.
Hansen, J., Russell, Rind, D., Stone, P., Lacis, A., Lebedeff, S., Ruedy, R., and Travis, L.: 1983, ‘Efficient Three-Dimensional Global Models for Climate Studies: Model I and II’, Mon. Wea. Rev. 111, 609-662.
Harrison, S. P., Yu, G., and Tarasov, P. E.: 1996, ‘Late Quaternary Lake-level Record from Northern Eurasia’, Quat. Res. 45, 138-159.
Hartmann, H. C.: 1990, ‘Climate Change Impacts on Laurentian Great Lakes Levels’, Clim. Change 17, 49-67.
Hostetler, S. W. and Bartlein, P. J.: 1990, ‘Simulation of Lake Evaporation with Application to Modeling Lake Level Variations of Harney-Malheur Lake, Oregon’, Water Resour. Res. 26, 2603-2612.
Hostetler, S. W. and Giorgi, F.: 1995, ‘Effects of a 2 × CO2 Climate on Two Large Lake Systems: Pyramid Lake, Nevada, and Yellowstone Lake, Wyoming’, Glob. Planet. Change 10, 43-54.
IPCC (Intergovenmental Panel on Climate Change): 1992, in Houghton, J. T., Callander, B. A., and Varney, S. K. (eds.), Climate Change 1992: The Supplementary Report to the IPCC Scientific Assessment, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, U.K.
Kong, Z., Du, N., Shan, F., Tong, G., Luo, S., and Fan, S.: 1990, ‘Vegetation and Climatic Changes in the Last 11000 Years in Qinghai Lake - Numerical Analysis Based on Palynology in Core QH85-18C’, Marine Geol. Quat. Geol. 10, 79-80 (in Chinese).
Kwadjik, J. and Rotmans, J.: ‘The Impact of Climate Change on the River Rhine: A Scenarios Study’, Clim. Change 30: 397-425.
Leontyev, O. K.: 1986, ‘The Problem of the Aral Sea’, J. Moscow Univ. (Geogr. Ser.) 5, 46-51 (in Russian).
Manabe, S. and Wetherald, R. T.: 1987, ‘Large-Scale Changes in SoilWetness Induced by an Increase in Carbon Dioxide’, J. Atmos. Sci. 44, 1211-1235.
Mimikou, M. A. and Kouvopoulos, Y. S.: 1991, ‘Regional Climatic Change Impacts: An Impacts on Water Resources’, Hydrol. Sci. J. 36(3), 247-270.
Mitchell, J. F. B.: 1983, ‘The Seasonal Response of a General Circulation Model to Changes in CO2and Sea Temperatures’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 109, 113-152.
Nash, L. L. and Gleick, P. H.: 1991, ‘Sensitivity of Streamflow in the Corolado Basin to Climatic Change’, J. Hydrol. 125, 225-241.
Nemec, J. and Schaake, J.: 1982, ‘Sensitivity of Water Resource Systems to Climatic Variation’, Hydrol. Sci. 27, 327-343.
Panagoulia, D.: 1992, ‘Impacts of GISS-Modeled Climate Changes on Catchment Hydrology’, Hydrol. Sci. J. 37(2), 141-163.
Penman, H. L.: 1948, ‘Natural Evaporation from Open Water, Bare Soil and Grass’, Proc. Roy. Soc. London A193, 120-146.
Prell, W. and Kutzbach, J.: 1987, ‘Monsoon Variability over the Past 150,000 Years’, J. Geophys. Res. 92, 8411-8425.
Qin, B.: 1993a, ‘The Hydrological Characteristics and Water Budget of Qinghai Lake Drainage Basin’, Chinese J. Oceanogr. Limnol. 11(4), 314-320.
Qin, B.: 1993b, ‘The Responses of Inland Lakes to Climate Change in Central Asia’, J. Lake Sci. 5, 118-127 (in Chinese).
Qin, B.: 1993c, ‘Estimates Water Balance of Paleolake Qinghai in Stable Wet and Warm Period of Holocene’, Adv. Water Sci. 5, 24-30 (in Chinese).
Qin, B. and Yu, G.: 1998, ‘The Implication of Inland Lake Level Variations at 6 kaBP and 18 kaBP in Mainland Asia’, Glob. Planet. Change(in press).
Rao, Y. P.: 1981, ‘The Climate of the Indian Subcontinent’, in Arakawa, H. (ed.), World Survey of Climatology, Vol. 9, Elsevier, Amsterdam/London/New York, pp. 67-75.
Revelle, R. and Waggoner, P.: 1983, ‘Effects of Carbon-Dioxide-Induced Climatic Change on Water Supplies in the Western United States’, Clim. Change, National Academy of Sciences, National Academy Press, Washington, pp. 419-432.
Richards, J. M.: 1971, ‘Simple Expression for the Saturation Vapor Pressure of Water in the Range -50° to 140 °C’, Brit. J. Appl. Phys. 4, L15-L18.
Ripley, E. A.: 1987, ‘Climate Change and the Hydrological Regime’, in Healey, M. and Wallace, R. (eds.), Canadian Aquatic Resources, Canadian Bulletin of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 215, Dept. of Fisheries and Oceans, pp. 137-178.
Robock, A., Turco, R. P., Harwell, M. A., Ackerman, T. P., Andressen, R., Chang, H.-S., and Sivakumar, V. K.: 1993, ‘Use of General Circulation Model Output in the Creation of Climate Change Scenarios for Impact Analysis’, Clim. Change 23, 293-335.
Sanderson, M. and Wong, L.: 1987, ‘Climatic Change and Great Lake Water Levels’, in Solomon, S. (ed.), The Influence of Climate Change and Climatic Variability on the Hydrologic Regime and Water Resources, IAHS Publication No. 168.
Schaake, J. C.: 1990, ‘From Climate to Flow’, in Waggoner, P. E. (ed.), Climate Change and U.S. Water Resources, John Wiley, pp. 177-206.
Schlesinger, M. E. and Zhao, Z.: 1989, ‘Seasonal Climatic Changes Induced by Doubled CO2 as Simulated by the OSU Atmospheric GCM/Mixed-Layer Ocean Model’, J. Clim. 2, 459-495.
Schneider, S. H., Gleick, P. H., and Mearns, L. O.: 1990, ‘Prospects for Climate Change’, in Waggoner, P. E. (ed.), Climate Change and U.S. Water Resources, John Wiley, pp. 41-74.
Schwarz, H. E.: 1979, ‘Climatic Change and Water Supply: How Sensitive Is the Northeast?’, Climate, Climatic Change and Water Supply, National Academy of Sciences, Washington D.C.
Sevastyanov, D. V. and Smirnova, N. P., 1986, Issyk-Kul Lake and the Tendency of Its Natural Development, Leningrad, Nauka, p. 256 (in Russian).
Shi, Yafeng, Kong, Zhaozheng, Wang, Sumin, Tang, Lingyu, Wang, Fubao, Yao, Tandong, Zhao, Xitao, Zhang, Peiyuan, and Shi, Shaohua.: 1993, ‘Mid-Holocene Climates and Environments in China’, Glob. Planet. Change 7, 219-234.
Shi, C., Bian, Y., and Zhu, X.: 1984, ‘Models of Estimation of Evaporation from Water Surface’, Scientia Geographica Sinica 4, 1-10 (in Chinese).
Shiklomanov, I. A.: 1989, ‘Anthropogenic Change of Climate, Water Resources and Water Management Problems’, Proc. Conference on Climate and Water, Helsinki.
Shuttleworth, W. J., Gash, J. H. C., Lloyd, C. R., McNeil, D. D., Moore, C. J., and Wallace, J. S.: 1988, ‘An Integrated Micrometeorological System for Evaporation Measurement’, Agric. For. Meteorol. 43, 295-317.
Shuttleworth, W. J. and Wallace, J. S.: 1984, ‘Evaporation from Sparse Crops - An Energy Combination Theory’, Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 111, 839-855. @@@
Singh, B.: 1987, ‘The Impacts of CO2-Induced Climate Change on Hydro-Electric Generation Potential in the James Bay Territory of Quebec’, in Solomon, S. et al. (eds.), The Influence of Climate Change and Climatic Variability on the Hydrologic Regime and Water Resources, IAHS Publication No. 168, pp. 403-418.
Stockton, C. W. and Roggess, W. R.: 1979, ‘Geohydrological Implications of Climate Change on Water Resources Development’, U.S. ACRE Institute for Water Resources, Fort Belvoir,VA.
U.S. EPA: 1984, ‘Potential Climate Impacts of Increasing Atmospheric CO2 the Emphasis on Water Availability and Hydrology in the United States’, Office of Policy Analysis, Washington, D.C.
Yu, G. and Qin, B.: 1997, ‘Holocene Temperature and Precipitation Reconstructions and Monsoonal Climates in Eastern China Using Pollen Data’, Palaeoclim.: Data Model. 2, 1-32.
Vassiljev, J., Harrison, S. P., and Haxeltine, A.: 1995, ‘Recent Lake-Level and Outflow Variations at Lake Viljandi, Estonia: Validation of Coupled Lake-Catchment Modeling Scheme for Climate Change Studies’, J. Hydrol. 170, 63-77.
Wang, S. and Li, J.: 1991, ‘Lake Sediments - An Effective Tool for Investigation Palaeoclimate Change - The Case Study in L. Qinghai and L. Daihai’, Chinese Sci. Bull. 36, 54-36 (in Chinese).
Wang, S. and Shi, Y.: 1992, ‘Analysis and Discussion of Lake Qinghai Evolution Since Late Quaternary’, J. Lake Sci. 4, 1-9 (in Chinese).
Wetherald, R. T. and Manabe, S.: 1986, ‘An Investigation of Cloud Cover Changes in Response to Thermal Forcing’, Clim. Change 8, 5-23.
Wilson, C. A. and Mitchell, J. F. B.: 1987, ‘A Doubling CO2 Climate Sensitivity Experiment with a Global Climate Model Including a Simple Ocean’, J. Geophys. Res. 92, 13315-13343.
Zhang, J., Zhu, B., Zhu, F., Wang, D., Sun, G., Lu, J., Peng, Y., and Wang, Y.: 1988, ‘Advances in the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau Meteorology, the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau Meteorological Experiment (1979) and Research’, Science Press, Beijing, pp. 14-16 (in Chinese).
Zhang, S.: 1983, ‘The Patterns of Dryness from Cold and Warm Decades in Historical Times of China’, Geograph. Res. 2, 32-39 (in Chinese).
Zhang, J.: 1991, ‘General Climate of China’, Meteorological Press House, Beijing, 430 pp. (in Chinese).
Zhao, R.: 1984, The Catchment Hydrological Models, Hydroelectric Press, Beijing, 214 pp. (in Chinese).
Zhao, R.: 1992, ‘The Xin’Anjiang Model Applied in China’, J. Hydrol. 135, 371-381. (Received 17 June, 1996; in revised form 15 January, 1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, B., Huang, Q. Evaluation of the Climatic Change Impacts on the Inland Lake – A Case Study of Lake Qinghai, China. Climatic Change 39, 695–714 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005319616456
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005319616456