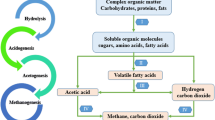
Abstract
Purpose
This study assessed the co-digestion of slaughterhouse wastewater (SWW) with Opuntia fícus-indica (OFI) under semi-continuous conditions.
Methods
Four different mixing ratios were studied at mesophilic temperature (38 ± 1°C): 100% SWW, 75% SWW/25% OFI, 25% SWW/75% OFI and 100% OFI. Process parameters such as biogas production, methane content, redox potential, pH, alkalinity, NH4-N, and VFA were used to infer differences in the bioreactors.
Results
Biodigester 2 (75% SWW and 25% OFI) presented the best cumulative biogas yield and methane content with 86 L and 57% (v/v), respectively. Inhibition of the biogas production process was observed in the remaining reactors.
Conclusion
The results showed that the co-digestion of SWW with OFI residues improved process performance in terms of biogas production. This improvement demonstrated that OFI could be applied as a novel co-substrate in systems digesting wastewaters that contain high levels of nitrogen compounds.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Júnior, L.J., Glbiatti, J.A., Ortolani, A.F.: Produção de biogás a partir de estrume de ruminantes e monogástricos com e sem inóculo (1987)
Ware, A., Power, N.: What is the effect of mandatory pasteurisation on the biogas transformation of solid slaughterhouse wastes? Waste Manag. 48, 503–512 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.10.013
Labatut, R.A., Angenent, L.T., Scott, N.R.: Biochemical methane potential and biodegradability of complex organic substrates. Bioresour. Technol. 102, 2255–2264 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.10.035
Palatsi, J., Viñas, M., Guivernau, M., Fernandez, B., Flotats, X.: Anaerobic digestion of slaughterhouse waste: main process limitations and microbial community interactions. Bioresour. Technol. 102, 2219–2227 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.09.121
Lienen, T., Kleyböcker, A., Verstraete, W., Würdemann, H.: Foam formation in a downstream digester of a cascade running full-scale biogas plant: influence of fat, oil and grease addition and abundance of the filamentous bacterium Microthrix parvicella. Bioresour. Technol. 153, 1–7 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.11.017
Bayr, S., Ojanperä, M., Kaparaju, P., Rintala, J.: Long-term thermophilic mono-digestion of rendering wastes and co-digestion with potato pulp. Waste Manag. 34, 1853–1859 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2014.06.005
Borowski, S., Kubacki, P.: Co-digestion of pig slaughterhouse waste with sewage sludge. Waste Manag. 40, 119–126 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.03.021
Edström, M., Nordberg, Å., Thyselius, L.: Anaerobic treatment of animal byproducts from slaughterhouses at laboratory and pilot scale. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. A 109, 127–138 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:109:1-3:127
Caldereiro, G.: Caracterização da digestão de resíduos agroindustriais em biodigestor de fluxo contínuo operado em escala real (2015)
Ramos-Suárez, J.L., Martínez, A., Carreras, N.: Optimization of the digestion process of Scenedesmus sp. and Opuntia maxima for biogas production. Energy Convers. Manag. 88, 1263–1270 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2014.02.064
Godoy, F.S.: Pontencial del Cultivo de la chumbera (Opuntia ficus-indica (L.)Miller) para la Obtención de Biocombustibles. 285 (2012)
Gebrekidan, T., Egigu, M.C., Muthuswamy, M.: Efficiency of biogas production from cactus fruit peel co-digestion with cow dung. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2, 916–923 (2014)
Vidal, J., Carvajal, A., Huiliñir, C., Salazar, R.: Slaughterhouse wastewater treatment by a combined anaerobic digestion/solar photoelectro-Fenton process performed in semicontinuous operation. Chem. Eng. J. 378, 122097 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122097
Páramo-Vargas, J., Granados, S.G., Maldonado-Rubio, M.I., Peralta-Hernández, J.M.: Up to 95 % reduction of chemical oxygen demand of slaughterhouse effluents using Fenton and photo-Fenton oxidation. Environ. Chem. Lett. 14, 149–154 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-015-0534-2
Jigar, E., Sulaiman, H., Asfaw, A., Bairu, A.: Study on renewable biogas energy production from cladodes of Opuntia ficus indica. Science (80-) 1, 44–48 (2011)
Rajagopal, R., Massé, D.I., Singh, G.: A critical review on inhibition of anaerobic digestion process by excess ammonia. Bioresour. Technol. 143, 632–641 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.06.030
Chen, C., Zheng, D., Liu, G.J., Deng, L.W., Long, Y., Fan, Z.H.: Continuous dry fermentation of swine manure for biogas production. Waste Manag. 38, 436–442 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2014.12.024
Pereira, E.L., Campos, C.M.M., Moterani, F.: Efeitos do pH, acidez e alcalinidade na microbiota de um reator anaeróbio de manta de lodo (UASB) tratando efluentes de suinocultura. Arq. Bras. Psicol. 66, 17–35 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4136/1980-993X
Leonardo, M.S.F.: Caracterização do Digestor Anaeróbio de Lamas Biológicas da ETAR do Choupal, em Coimbra (2012)
Belli Filho, P.: Stockage et odeur des dejections animales- cas du lisier de porc (1995)
Hunting, E.R., Kampfraath, A.A.: Contribution of bacteria to redox potential (Eh) measurements in sediments. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 10, 55–62 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-012-0080-4
de Oliveira, R.A., Foresti, E.: Balanço de massa de reatores anaeróbicos de fluxo ascendente com manta de lodo (UASB) tratando águas residuárias de suinocultura. Eng. Agrícola 24, 807–820 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-69162004000300035
Gerardi, M.H.: The Microbiology of Anaerobic Digesters. Wiley, Hoboken (2003)
Venkatesh, M.: Appraisal of the carbon to nitrogen (C/N) ratio in the bed sediment of the Betwa River, Peninsular India. Int. J. Sediment Res. (2019).https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsrc.2019.07.003
Xu, R., Zhang, K., Liu, P., Khan, A., Xiong, J., Tian, F., Li, X.: Bioresource Technology: a critical review on the interaction of substrate nutrient balance and microbial community structure and function in anaerobic co-digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 247, 1119–1127 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.095
Medri, W.: Modelagem e otimização de sistemas de estabilização para tratamento de dejetos de suínos. 230 (1997)
Eryuruk, K., Tezcan, U., Bak, U.: Electrochemical treatment of wastewaters from poultry slaughtering and processing by using iron electrodes. J. Clean. Prod. 172, 1089–1095 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.254
Reilly, M., Cooley, A.P., Tito, D., Tassou, S.A., Theodorou, M.K.: Electrocoagulation treatment of dairy processing and slaughterhouse wastewaters. Energy Procedia 161, 343–351 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2019.02.106
Kobya, M., Senturk, E., Bayramoglu, M.: Treatment of poultry slaughterhouse wastewaters by electrocoagulation. 133, 172–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.10.007
Chakchouk, I., Elloumi, N., Belaid, C., Mseddi, S., Chaari, L., Kallel, M.: A combined electrocoagulation–electrooxidation treatment for dairy wastewater. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 34, 109–117 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1590/0104-6632.20170341s20150040
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support given to the Project 0330_IDERCEXA_4_E-Renewable Investment, Development and Energy for the Improvement of the Entrepreneurial Fabric in the Region Centro, Estremadura and Alentejo co-financed by INTERREG-European Regional Development Fund through the FEDER. G. Lourinho also acknowledges FCT - Fundação para a Ciêcia e Tecnologia - for financial support under the Grant SFRH/BDE/111878/2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panizio, R.M., Calado, L.F.d., Lourinho, G. et al. Potential of Biogas Production in Anaerobic Co-digestion of Opuntia ficus-indica and Slaughterhouse Wastes. Waste Biomass Valor 11, 4639–4647 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-019-00835-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-019-00835-2