Abstract
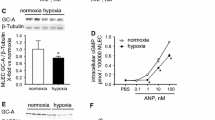
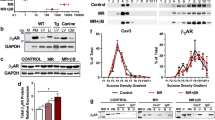
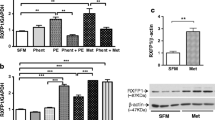
Adrenomedullin (AM) is a potent vasorelaxing peptide with natriuretic, diuretic, and growth inhibitory properties. Plasma concentrations and myocardial AM expression are increased in heart failure (HF). Since AM and AM binding sites are abundantly expressed in the lungs, we investigated to what extent pulmonary AM and AM receptor subtypes [CRLR/RAMP2 (AM1) and CRLR/RAMP3 (AM2)] are changed in HF and whether the lungs contribute to the increased plasma concentrations of AM reported in HF. Pulmonary AM mRNA and protein expression were increased by 2.8- and 2.6-fold, respectively, whereas mRNA expression of RAMP2 and CRLR was decreased in rats with HF 7 days after induction of MI compared to sham-operated rats (P < 0.05). Pulmonary AM receptor density was substantially decreased in HF rats compared to sham (3.7 ± 0.6 vs. 29.9 ± 1.1 fmol/mg membrane protein; P < 0.05). Immunoreactivities against AM and the AM receptor components CRLR, RAMP2, and RAMP3 in the pulmonary tissue were seen in vascular smooth muscle cells, vascular endothelial cells, and in alveolar macrophages. AM mRNA expression in alveolar macrophages obtained from HF rats by bronchoalveolar lavage was 2.9-fold higher than in sham-operated rats (P < 0.05). An even more substantial increase of AM mRNA expression was found in alveolar macrophages from patients with HF (10-fold, P < 0.05), and this increase displayed a negative correlation to left ventricular systolic function (P < 0.05). Furthermore, a net release of AM from the lungs into the circulation was only found in HF patients with the most severe left ventricular systolic dysfunction. Thus, our data demonstrate increased expression and decreased receptor binding of AM in the lungs in severe HF. Furthermore, our data indicate that alveolar macrophages are an important source of pulmonary AM in both experimental and clinical HF. Finally, a net release of AM from the lungs into the circulation was only found in patients with severe systolic dysfunction.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agorreta J, Zulueta JJ, Montuenga LM, Garayoa M (2005) Adrenomedullin expression in a rat model of acute lung injury induced by hypoxia and LPS. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 288:L536–L545
Alexis N, Soukup J, Ghio A, Becker S (2000) Sputum phagocytes from healthy individuals are functional and activated: a flow cytometric comparison with cells in bronchoalveolar lavage and peripheral blood. Clin Immunol 97:21–32
Burnett JC Jr, Kao PC, Hu DC, Heser DW, Heublein D, Granger JP, Opgenorth TJ, Reeder GS (1986) Atrial natriuretic peptide elevation in congestive heart failure in the human. Science 231:1145–1147
Calderone A, Thaik CM, Takahashi N, Chang DL, Colucci WS (1998) Nitric oxide, atrial natriuretic peptide, and cyclic GMP inhibit the growth-promoting effects of norepinephrine in cardiac myocytes and fibroblasts. J Clin Invest 101:812–818
Cheng D, Tian W, Chen W, Xiao X (2002) Expression of adrenomedullin and its receptor in lungs of rats with hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Chin Med J (Engl) 115:1806–1808
Cheung BMY, Hwang ISS, Li CYY OW-S, Tsang KWT, Leung RYH, Kumana CR, Tang F (2004) Increased adrenomedullin expression in lungs in endotoxaemia. J Endocrinol 181:339–345
Dschietzig T, Azad HA, Asswad L, Böhme C, Bartsch C, Baumann G, Stangl K (2002) The adrenomedullin receptor acts as clearance receptor in pulmonary circulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 294:315–318
Fujita M, Kuwaki T, Ando K, Fujita T (2005) Sympatico-inhibitory action of endogenous adrenomedullin through inhibition of oxidative stress in the brain. Hypertension 45:1165–1172
Gullestad L, Aukrust P (2001) The cytokine network in heart failure: pathogenetic importance and potential therapeutic targets. Heart fail Monit 2:8–13
Hirayama N, Kitamura K, Imamura T, Kato J, Koiwaya Y, Eto T (1999) Secretion and clearance of the mature form of adrenomedullin in humans. Life Sci 64:2505–2509
Kakishita M, Nishikimi T, Okano Y, Satoh T, Kyotani S, Nagaya N, Fukushima K, Nakanishi N, Takishita S, Miyata A, Kangawa K, Matsuo H, Kunieda T (1999) Increased plasma levels of adrenomedullin in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Clin Sci 96:33–39
Kamoi H, Kanazawa H, Hirata K, Kurihara N, Yano Y, Otani S (1995) Adrenomedullin inhibits the secretion of cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant, a member of the interleukin-8 family, from rat alveolar macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 211:1031–1035
Kishimoto I, Rossi K, Garbers DL (2001) A genetic model provides evidence that the receptor for atrial natriuretic peptide (guanylyl cyclase-A) inhibits cardiac ventricular myocyte hypertrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:2703–2706
Kitamura K, Kangawa K, Kawamoto M, Ichiki Y, Nakamura S, Matsuo H, Eto T (1993) Adrenomedullin: a novel hypotensive peptide isolated from human pheochromocytoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 192:553–560
Leeper-Woodford SK, Detmer K (1999) Acute hypoxia increases alveolar macrophage tumor necrosis factor activity and alters NF-kappaB expression. Am J Physiol 276:L909–L916
Lippton H, Chang JK, Hao Q, Summer W, Hyman A (1994) Adrenomedullin dilates the pulmonary vascular bed in vivo. J Appl Physiol 76:2154–2156
Mann D (1999) Mechanisms and models in heart failure: a combinatorial approach. Circulation 100:999–1008
McLatchie LM, Fraser NJ, Main MJ, Wise A, Brown J, Thompson N, Solari R, Lee MG, Foord SM (1998) RAMPs regulate the transport and ligand specificity of the calcitonin- receptor-like receptor. Nature 393:333–339
Mukoyama M, Nakao K, Hosoda K, Suga S, Saito Y, Ogawa Y, Shirakami G, Jougasaki M, Obata K, Yasue H, kambayashi Y, Inouye K, Imura H (1991) Brain natriuretic peptide as a novel cardiac hormone in humans. Evidence for an exquisite dual natriuretic peptide system, atrial natriuretic peptide and brain natriuretic peptide. J Clin Invest 87:1402–1412
Nagaya N, Satoh T, Nishikimi T, Uematsu M, Furuichi S, Sakamaki F, Oya H, Kyotani S, Nakanishi N, Goto Y, Masuda Y, Miyatake K, Kangawa K (2000) Hemodynamic, renal, and hormonal effects of adrenomedullin infusion in patients with congestive heart failure. Circulation 101:498–503
Nakamura R, Kato J, Kitamura K, Onitsuka H, Imamura T, Cao Y, Marutsuka K, Asada Y, Kangawa K, Eto T (2004) Adrenomedullin administration immediately after myocardial infarction ameliorates progression of heart failure in rats. Circulation 110:426–431
Nakayama M, Takahashi K, Murakami O, Yanai M, Sasaki H, Shirato K, Shibahara S (1999) Production and secretion of adrenomedullin in cultured human alveolar macrophages. Peptides 20:1123–1125
Nicholls DP, Onuoha GN, McDowell G, Elborn JS, Riley MS, Nugent AM, Steele IC, Shaw C, Buchanan KD (1996) Neuroendocrine changes in chronic cardiac failure. Basic Res Cardiol 91(Suppl 1):13–20
Nishikimi T, Horio T, Sasaki T, Yoshihara F, Takishita S, Miyata A, Matsuo H, Kangawa K (1997) Cardiac production and secretion of adrenomedullin are increased in heart failure. Hypertension 30:1369–1375
Nishikimi T, Matsuoka H, Shimada K, Matsuo H, Kangawa K (2000) Production and clearance sites of two molecular forms of adrenomedullin in human plasma. Am J Hypertens 13:1032–1034
Øie E, Vinge LE, Tønnessen T, Grøgaard HK, Kjekshus H, Christensen G, Smiseth OA, Attramadal H (1997) Transient, isopeptide-specific induction of myocardial endothelin-1 mRNA during congestive heart failure in rats. Am J Physiol 273:H1727–H1736
Øie E, Vinge LE, Yndestad A, Sandberg C, Grøgaard HK, Attramadal H (2000) Induction of a myocardial adrenomedullin signaling system during ischemic heart failure in rats. Circulation 101:415–422
Øie E, Vinge LE, Andersen GØ, Yndestad A, Krobert KA, Sandberg C, Ahmed MS, Haug T, Levy FO, Skomedal T, Attramadal H (2005) RAMP2 and RAMP3 mRNA levels are increased in failing rat cardiomyocytes and associated with increased responsiveness to adrenomedullin. J Mol Cell Cardiol 38:145–151
Owji AA, Smith DM, Coppock HA, Morgan DGA, Bhogal R, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR (1995) An abundant and specific binding site for the novel vasodilator adrenomedullin in the rat. Endocrinology 136:2127–2134
Poyner DR, Sexton PM, Marshall I, Smith DM, Quirion R, Born W, Muff R, Fischer JA, Foord SM (2002) International Union of Pharmacology. XXXII. The mammalian calcitonin gene-related peptides, adrenomedullin, amylin, and calcitonin receptors. Pharmacol Rev 54:233–246
Richards AM (2004) The natriuretic peptides in heart failure. Basic Res Cardiol 99:94–100
Sikkeland LI, Kongerud J, Stangeland AM, Haug T, Alexis NE (2007) Macrophage enrichment from induced sputum. Thorax 62:558–559
Stangl K, Dschietzig T, Richter C, Stangl V, Bartsch C, Zurbrügg HR, Pregla R, Baumann G, Felix SB, Laule M (2002) Cessation of pulmonary and coronary secretion of adrenomedullin peptides in the progression of human heart failure. Horm Metab Res 34:81–86
Stenmark KR, Davie NJ, Reeves JT, Frid MG (2005) Hypoxia, leukocytes, and the pulmonary circulation. J Appl Physiol 98:715–721
Swynghedauw B (1999) Molecular mechanisms of myocardial remodeling. Physiol Rev 79:215–262
Tamura N, Ogawa Y, Chusho H, Nakamura K, Nakao K, Suda M, Kasahara M, Hashimoto R, Katsuura G, Mukoyama M, Itoh H, Saito Y, Tanaka I, Otani H, Katsuki M, Nakao K (2000) Cardiac fibrosis in mice lacking brain natriuretic peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:4239–4244
von Lueder TG, Kjekshus H, Edvardsen T, Øie E, Urheim S, Vinge LE, Ahmed MS, Smiseth OA, Attramadal H (2004) Mechanisms of elevated plasma endothelin-1 in CHF: congestion increases pulmonary synthesis and secretion of endothelin-1. Cardiovasc Res 63:41–50
Xu P, Dai A, Zhou H, Shen H, Liu L, Song W (2003) Expression and role of adrenomedullin and its receptor in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Chin Med J (Engl) 116:863–867
Yndestad A, Holm AM, Müller F, Simonsen S, Frøland SS, Gullestad L, Aukrust P (2003) Enhanced expression of inflammatory cytokines and activation markers in T-cells from patients with chronic heart failure. Cardiovasc Res 60:141–146
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Øie, E., Ahmed, M.S., Ueland, T. et al. Adrenomedullin is increased in alveolar macrophages and released from the lungs into the circulation in severe heart failure. Basic Res Cardiol 105, 89–98 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-009-0070-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-009-0070-y