Abstract
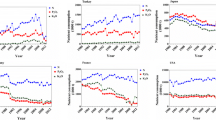
The growing world population is expected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, which will increase the present demand for food by ~ 70%. Consequently, to boost agrarian production and achieve food security, within limited arable land, the effective use of fertilizers becomes critical. However, the economic efficiency of mineral fertilizers has fallen dramatically as the price hike in fertilizers became dearer than food. The current winds of global climate change due to continued emissions of greenhouse gases from human activities have been posing unprecedented challenges before the agriculture sector and fertilizer industry. The limited geological resources of raw material for the manufacture of fertilizers and market fluctuations of fertilizer minerals initiate wide-reaching competition and raise challenge of food security. It is observed since the last century that the production of fertilizer minerals has risen almost constantly; however, consumption varied greatly from one region to another. It remained constant or declined in Western Europe and North America, but increased rapidly in East and South Asia especially in China and India. The Asian share of global fertilizer consumption is more than 60% and growing rapidly. This supply-demand pattern influences mineral fertilizers’ trade-flow and thereby global competition. Hence, there is a need to develop the fertilizer mineral sector and adopt policies and strategies to ensure materials security. The sustainable agricultural intensification and the agronomical proportions, timing, and placement with the right source are crucial factors which determine the sustainable utility of fertilizer minerals. In the wake of the above, we provide a critical appraisal of fertilizer minerals.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The planetary boundary (PB), a concept introduced in 2009, aimed to define the environmental limits within which humanity can safely operate (Steffen et al. 2015).
References
Abdulkarim AY, Abdulsalam S, Aliyu E-NU, Muhammad IM (2019) Bio-fertilizers via co-digestion: a review. Traektoriâ Nauki- Path Sci 5(6) ISSN 2413-9009
Arovuori K, Karikallio H (2009) Consumption patterns and competition in the world fertilizer markets. 19th Symposium of the International Food and Agribusiness Management Association, June 20–21, 2009, Budapest, Hungary pp 1–15. https://www.ifama.org/resources/files/2009-Symposium/1035_paper.pdf
Arslan A, McCarthy N, Lipper L, Asfaw S, Cattaneo A, Kokwe M (2015) Climate smart agriculture? Assessing the adaptation implications in Zambia. J Agric Econ 66(3):753–780
Baffes J, Koh WC (2018) Fertilizer prices to rise in 2019 on supportive fundamentals. https://blogs.worldbank.org/developmenttalk/fertilizer-prices-rise-2019-supportive-fundamentals. Accessed 20 Sep 2020
Baffes J, Koh WC (2020) Mixed results for fertilizers amid COVID-19 panic. https://blogs.worldbank.org/opendata/mixed-results-fertilizers-amid-covid-19-panic. Accessed 25 July 2020
Baffeswee J, Koh C (2019) Fertilizer market outlook: potash prices to rise in 2019 but urea and phosphates remain subdued. https://blogs.worldbank.org/developmenttalk/fertilizer-market-outlook-potash-prices-rise-2019-urea-and-phosphates-remain. Accessed 11 Mar 2020
Bindraban PS, Dimkpa CO, Pandey R (2020) Exploring phosphorus fertilizers and fertilization strategies for improved human and environmental health. Biol Fertil Soils 56:299–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-019-01430-2
Brentrup F (2009) The impact of mineral fertilizers on the carbon footprint of crop production. Conference paper. International Plant Nutrition Colloquium XVI, University of California, Davis/US
Brentrup F, Lammel J (2011) LCA to assess the environmental impact of different fertilisers and agricultural systems. Proc. Int. Fertiliser Society, April 14, York, UK
Brentrup F, Palliere C (2008) GHG emissions and energy efficiency in European nitrogen fertiliser production and use. Proc. International Fertiliser Society, December 11, York, UK
Business Wire (2019) India’s Fertilizer Market: 2019–2024 Analysis & Outlook with a CAGR Projection of 12.3% - ResearchAndMarkets.com. https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20190701005584/en/Indias-Fertilizer-Market-2019-2024-Analysis-Outlook-with-a-CAGR-Projection-of-12.3---ResearchAndMarkets.com#:~:text=com%20%7C%20Business%20Wire-,India's%20Fertilizer%20Market%3A%202019%2D2024%20Analysis%20%26%20Outlook%20with%20a,of%2012.3%25%20%2D%20ResearchAndMarkets.com&text=The%20Indian%20fertilizer%20market%20was,12.3%25%20during%202019%2D2024. Accessed 23 Sep 2020
Chand S (2016) Growth and distribution of fertilizers industry in India. www.yourarticlelibrary.com. Accessed 15 May 2019
Childers DL, Corman J, Edwards M, Elser JJ (2011) Sustainability challenges of phosphorus and food: solutions from closing the human phosphorus cycle. BioScience 61(2):117–124. https://doi.org/10.1525/bio.2011.61.2.6
Chun-Li W, Shiuan-Yuh C, Chiu-Chung Y (2010) Present situation and future perspective of bio-fertilizer for environmentally friendly agriculture. Environmental science. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Present-situation-and-future-perspectives-of-for-Chun-li-ShiuanYuh/74099737b73e45b3694018e7309d9238f703da3d
Cordell D, Drangert J-O, White S (2009) The story of phosphorus: global food security and food for thought. Glob Environ Chang 19:292–305
Datta PS, Deb DL, Tyagi SK (1997) Assessment of groundwater contamination from fertilizers in the Delhi area based on 18O, NO3- and K+ composition. J Contam Hydrol 27:249–262
Dawson CJ, Hilton J (2011) Fertilizer availability in a resource-limited world: production and recycling of nitrogen and phosphorus. Food Policy 36:14–22
Drescher A, Glaser R, Richert C, Nippes K (2011) Demand for key nutrients (NPK) in the year 2050: Draft Report. University of Freiburg. Department of Geography, pp 41–46. https://esdac.jrc.ec.europa.eu/projects/NPK/Documents/Freiburg_Demand_for_key_nutrients_in_2050_Drescher.pdf
ECOTECH Research and Consulting (2001) Final Report: Chapter 9: Fertilizer taxes. Study on Environmental Taxes and Charges in the EU. https://ec.europa.eu/environment/enveco/taxation/pdf/ch9_fertilisers.pdf. Accessed 17 July 2020
Factbook (2019) Nutrien Factbook 2019. https://www.nutrien.com/sites/default/files/uploads/2019-05/Nutrien%20Fact%20Book%202019.pdf. Accessed 20 September 2020
FAI (2016) Fertilizer Statistics 2015–2016. Fertilizer Association of India. http://www.krishijagran.com/farm-data/indian-fertilizer-sector-at-a-glance/. Accessed 17 February 2020
FAO (2005) The state of food and agriculture 2005. Food and Agriculture Organization of United Nations, Rome
FAO (2009) Resource STAT-Fertilizer. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. http://faostat.fao.org/site/575/DesktopDefault.aspx?PageID=575#ancor. Accessed 12 March 2009
FAO (2012) The state of food and agriculture 2012. Food and Agriculture Organization of United Nations, Rome, 165p
FAO (2016) World fertilizer trends and outlook to 2019. Food and Agriculture Organization of United Nations, Rome. https://www.fao.org/publication. Accessed 25 October 2020
FAO (2017) The future of food and agriculture trends and challenges. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Rome. p 163. http://www.fao.org/3/a-i6583e.pdf. Accessed 11 Oct 2020
FAO (2019) The state of food and agriculture 2019. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome. http://ww.fao.org/3/a-i6583e.pdf. Accessed 2 Nov 2020
FAO (2020a) World fertilizer trends and outlook to 2022. Food and Agriculture Organization of United Nations, Rome, 28p
FAO (2020b) Global trends, statistics and insights for fertilizer. Published by NationMaster. https://www.nationmaster.com/nmx/sector/fertilizer. Accessed 28 Sep 2020
Fertilizer Canada (2018) Annual Report Value Add+. https://fertilizercanada.ca/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/fc_annualreport2018_en_vf2-web.pdf. Accessed 20 Oct 2020
Garside M (2019) Distribution of global potash reserves by select country 2018. https://www.statista.com/statistics/604174/distribution-of-potash-reserves-worldwide-by-select-country/. Accessed 5 Sep 2020
Geissler B, Mew MC, Steiner G (2019) Phosphate supply security for importing countries: developments and the current situation. Sci Total Environ 677:511–523
Gilbert N (2009) The disappearing nutrient. Nature 461:716–718
Grand View Research (2019) Nitrogenous fertilizer market size, share and trends analysis report by product (urea, ammonium nitrate), by application (cereals and grains, oilseeds & pulses), by region, and segment forecasts, 2019–2025. https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/nitrogenous-fertilizer-market#:~:text=Some%20of%20the%20key%20market,Limited%2C%20and%20Coromandel%20International%20Ltd. Accessed 8 Oct 2020
Gupta U (2014) Fertilizer industry in India- challenges and way-forward. http://www.uttamgupta.com/fertilizers/fertilizer-industry-in-india-challenges-way-forward. Accessed 23 Mar 2020
Haldar SK (2018) Chapter 13 Mineral processing. In: Haldar SK (ed) Mineral exploration: Principles and Applications, Second edn. Elsevier, pp 259–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/C2017-0-00902-3
Hanlon MT, Ray S, Saengwilai P, Luthe D, Lynch JP, Brown KM (2018) Buffered delivery of phosphate to Arabidopsis alters responses to low phosphate. J Exp Bot 69(5):1207–1219. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erx454
IBM (2015a) Apatite and Rock Phosphate. 52nd Edition Potash (Advance Release) Ministry of Mines Govt. of India, Indian Bureau of Mines, Nagpur, p 21. http://ibm.nic.in/writereaddata/files/08172015131038Apatite%20and%20Rock%20Phosphate.pdf
IBM (2015b) Indian Minerals Yearbook 2013 (Part- III: Mineral Reviews) 52nd Edition Potash (Advance Release). Ministry of Mines Govt. of India, Indian Bureau of Mines, Nagpur p 5. www.ibm.gov.in. Accessed 17 Apr 2020
IBM (2017) Indian Minerals Yearbook 2017 (Part- III: Mineral Reviews) 56th Edition. Ministry of Mines Govt. of India, Indian Bureau of Mines, Nagpur. www.ibm.gov.in
IBM (2018) Indian minerals yearbook 2017 (part- III: mineral reviews) 56th Edition. Ministry of Mines Govt. of India, Indian Bureau of Mines, Nagpur. www.ibm.gov.in. Accessed 25 Oct 2020
IBM (2020) Indian minerals yearbook 2019 (part- III: mineral reviews) 58th Edition. Ministry of Mines Govt. of India, Indian Bureau of Mines, Nagpur. www.ibm.gov.in. Accessed 15 Oct 2020
IFA (2019) Fertilizer Outlook 2019–2023. Annual Conference, Montreal, 11–13 June 2019. PIT, Market Intelligence and Agriculture Services, IFA. https://api.ifastat.org/reports/download/12620. Accessed 24 Oct 2020
IFIA (2000) Mineral fertilizer use and the environment. International Fertilizer Industry Association. Revised edition, Paris 53p
Isherwood KF (2000) Fertilizer use and the environment. International Fertilizer Industry Association. Revised edition, Paris
Japan Fertilizer Ammonia Association (2003) Japan Fertilizer & Ammonia Producers Association. http://www.jaf.gr.jp/en.html. Accessed 9 Mar 2020
Kotschi J (2013) A soiled reputation: adverse impacts of mineral fertilizers in tropical agriculture. Heinrich Böll Foundation, WWF Germany 58p
Kotschi J (2015) Adverse impacts of mineral fertilizers in tropical agriculture, a soiled reputation. Heinrich Böll Foundation, Germany, pp 37–42
MacDonald GK, Bennett EM, Potter PA, Ramankutty N (2011) Agronomic phosphorus imbalances across the world’s croplands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(7):3086–3091. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1010808108
Mala P (2013) Fertilizer scenario in India. International Journal of Social Science & Interdisciplinary Research 2(1):62–72. https://dokumen.tips/documents/fertilizer-scenario-in-india-indian-journal-of-social-science-interdisciplinary.html. Accessed 19 Mar 2020
Mao H, Wang J, Wang Z, Zan Y, Lyons G, Zou C (2014) Using agronomic biofortification to boost zinc, selenium, and iodine concentrations of food crops grown on the loess plateau in China. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 14:459–470
Maximum Yield Inc (2018) What is a fertilizer? - definition from yield. https://www.maximumyield.com/definition/202/fertilizer. Accessed 19 Oct 2020
Mew MC (2016) Phosphate rock costs, prices and resources interaction. Sci Total Environ 542:1008–1012
Mew MC, Steiner G, Geissler B (2018) Phosphorus supply chain—scientific, technical, and economic foundations: a transdisciplinary orientation. Sustainability 2018(10):1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10041087
Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers (2015) Self sufficiency in fertilizer production. Press Info. Bureau, Govt. of India. http://pib.nic.in/newsite/PrintRelease.aspx?relid=121426. Accessed 8 Jan 2019
Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers (2019) Demand – production details of fertilizers. https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1595328. Accessed 25 Aug 2020
Moberg F, Höök K, Salomonsson L, Mastroianni K, Lundberg J, Karlberg L, Rundgren G (2015) How to feed nine billion within the planet’s boundaries: the need for an agroecological approach. Swedish International Agricultural network Initiative, Sweden. https://www.siani.se/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/siani_agroecology_brief_march_4.pdf. Accessed 22 Nov 2020
Mogollon JM, Beusen AHW, van Grinsven HJM, Westhoek H, Bouwman AF (2018) Future agricultural phosphorus demand according to the shared socioeconomic pathways. Glob Environ Chang 50:149–163
Nemecek T, Elie OH, Dubois D, Gaillard G, Schaller B, Chervet A (2011) Life cycle assessment of Swiss farming systems: II. Extensive and intensive production. Agric Syst 104:233–245
Nielsen, HØ (2010) Bounded rationality in decision-making: How cognitive shortcuts and professional values may interfere with market-based regulation. Manchester University Press, Mancheste, p 256
Oldham L (2019) Secondary plant nutrients: calcium, magnesium, and sulfur. Mississippi State University. http://extension.msstate.edu/sites/default/files/publications/information-sheets/is1039_web.pdf. Accessed 12 august 2020
Pistilli M (2020) 10 top phosphate countries by production. https://investingnews.com/daily/resource-investing/agriculture-investing/phosphate-investing/top-phosphate-countries-by-production/. Accessed 28 September 2020
Quinn R (2020) Global fertilizer outlook – 6 global fertilizer demand bright. https://www.dtnpf.com/agriculture/web/ag/crops/article/2020/01/03/global-fertilizer-demand-bright. Accessed 25 August 2020
Rajani A (2019) Complex fertilizers. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.30561.25446. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/335716743_COMPLEX_FERTILIZERS. Accessed 20 September 2020
Rakesh S, Juttu R, Jogula K, Raju B (2020) Glauconite: an indigenous and alternative source of potassium fertilizer for sustainable agriculture. Int J Bioresour Sci 7(1):17–19. https://doi.org/10.30954/2347-9655.01.2020.4
Reuters (2010) China needs to cut use of chemical fertilizers: research. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-china-agriculture-fertiliser/china-needs-to-cut-use-of-chemical-fertilizers-research-idUSTRE60D20T20100114. Accessed 12 march 2020
Roberts TL (1999) The role of fertilizer in growing the world’s food. https://www.topcropmanager.com/the-role-of-fertilizer-in-growing-the-worlds-food-10387/. Accessed 23 February 2020
Rockström J, Steffen W, Noone K, Persson Å, Chapin FS, Lambin E, Lenton TM, Scheffer M, Folke C, Schellnhuber H, Nykvist B, De Wit CA, Hughes T, van der Leeuw S, Rodhe H, Sörlin S, Snyder PK, Costanza R, Svedin U, Falkenmark M, Karlberg L, Corell RW, Fabry VJ, Hansen J, Walker B, Liverman D, Richardson K, Crutzen P, Foley J (2009) Planetary boundaries: exploring the safe operating space for humanity. Ecol Soc 14(2):32p
Roser Max (2020) Future population growth. Published online at https://OurWorldInData.org. Retrieved from: https://ourworldindata.org/future-population-growth (Online Resource). Accessed 18 Nov 2020
Savci S (2012) An agricultural pollutant: chemical fertilizer. Int J Environ Sci Dev 3(1):77–80
Savoy H (2012) Fertilizers and their uses. Agricultural Extension Service. http://www.utextension.utk.edu/ Accessed 21 Mar 2020
Scherer HW (2000) Fertilizers Ullmann’s encyclopedia of industrial chemistry 2000. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. https://doi.org/10.1002/14356007.a10_323.pub3
Schröder JJ (2014) The position of mineral nitrogen fertilizer in efficient use of nitrogen and land: a review. Nat Res Forum 5:936–948. https://www.mendeley.com/catalogue/3015ce1c-62a9-3429-a002-2ac7bf90b283/ Accessed 5 Oct 2020
Singh C (2017) Evaluation of soil fertility status in soils of Balodabazar Block under Balodabazar District of Chhattisgarh. Indira Gandhi Krishi Vishwavidhyalaya, Raipur 221p
Skowroñska M, Filipek T (2014) Life cycle assessment of fertilizers: a review. Int Agrophys 28:101–110. https://doi.org/10.2478/intag-2013-0032
Smil V (2004) Enriching the earth. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, p 135 ISBN 978-0-262-69313-4
Sönmez I, Kaplan M, Sönmez S (2007) An investigation of seasonal changes in nitrate contents of soils and irrigation waters in greenhouses located in antalya-demre region. Asian J Chem 19(7):5639–5646
Steffen W, Richardson K, Rockström J, Cornell SE, Fetzer I, Bennett EM, Biggs R, Carpenter SR, de Vries W, de Wit CA, Folke C, Gerten D, Heinke J, Mace G, Persson LM, Ramanathan V, Reyers B, Sörlin S (2015) Planetary boundaries: guiding human development on a changing planet. Science 347:1259855. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1259855
Tabatabai MA (1987) Physicochemical fate of sulfate in soils. JAPCA 37(1):34–38. https://doi.org/10.1080/08940630.1987.10466197
TFI (2018) 2018 state of the fertilizer industry. The Fertilizer Institute. p 54. https://www.tfi.org/sites/default/files/tfi-stateoftheindustry-2018.pdf. Accessed 15 Aug 2020
The Great Soviet Encyclopedia (1979) Mineral fertilizers. https://encyclopedia2.thefreedictionary.com/Mineral+Fertilizers. Accessed 28 August 2020
UN Industrial Development Organization (1998) Fertilizer manual (3rd ed). International Fertilizer Development Center (IFDC). Kluwer Academic, Boston, p 46
UNEP (2016a) Frontiers 2016 report: emerging issues of environmental concern. United Nations Environment Programme, Nairobi p 77. www.unep.org. Accessed 18 Oct 2020
UNEP (2016b) Food systems and natural resources. A report of the working group on food systems of the international resource panel Westhoek H, Ingram J, Van Berkum S, Özay L and Hajer M p 164. https://www.resourcepanel.org/sites/default/files/documents/document/media/food_systems_summary_report_english.pdf
UNEP/IFA (2001) Environmental aspects of phosphate and potash mining. United Nations Environment Programme and International Fertilizer Industry Association, Paris
USGS (2019) Mineral Commodity Summaries 2019. U.S. Geological Survey. https://prd-wret.s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/assets/palladium/production/atoms/files/mcs2019_all.pdf. Accessed 24 Feb 2020
USGS (2020) Mineral Commodity Summaries 2020. U.S. Geological Survey. https://doi.org/10.3133/mcs2020
Villalba G, Liu Y, Schroder H, Ayres RU (2008) Global phosphorus flows in the industrial economy from a production perspective. J Ind Ecol 12:557–569
Wakeel A, Farooq M, Qadir M, Schubert S (2011) Potassium substitution by sodium in plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 30(4):401–413. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352689.2011.587728
Williams J (2019) The worldwide fertilizer market to 2024. https://www.worldfertilizer.com/environment/21032019/the-worldwide-fertilizer-market-to-2024/. Accessed 20 July 2020
World Bank (2020) Fertilizer consumption (% of fertilizer production) https://datacatalog.worldbank.org/search?search_api_views_fulltext_op=AND&query=fertilizer&nid=&sort_by=search_api_relevance&sort_order=DESC. Accessed 28 Sep 2020
Youssef MMA, Eissa MFM (2014) Biofertilizers and their role in management of plant parasitic nematodes. A review. J Biotechnol Pharm Res 5(1):1–6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Randive, K., Raut, T. & Jawadand, S. An overview of the global fertilizer trends and India’s position in 2020. Miner Econ 34, 371–384 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13563-020-00246-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13563-020-00246-z