Abstract
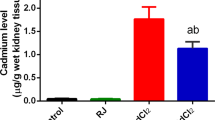
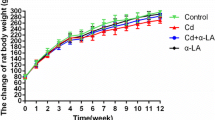
Oxidative stress is an important mechanism underlying toxicity induced by cadmium (Cd) exposure. However, there are significant differences of the antioxidant baseline in different populations. This means that different human has different intensity of oxidative stress in vivo after exposure to toxicants. LiasH/H mouse is a specific model which is created by genetically modifying the Lias 3′-untranslated region (3′-UTR). LiasH/H mice express high levels of LA and have high endogenous antioxidant capacity which is approximately 150% higher than wild-type C57BL/6 J mice (WT, Lias+/+). But more importantly, they have dual roles of metal chelator and antioxidant. Here, we applied this mouse model to evaluate the effect of endogenous antioxidant levels in the body on alleviating Cd-induced renal injury including Cd metabolism, oxidative stress, and inflammation. In the experiment, mice drank water containing Cd (50 mg/L), for 12 weeks. Many biomarkers of Cd metabolism, oxidative stress, inflammation, and major pathological changes in the kidney were examined. The results showed overexpression of the Lias gene decreased Cd burden in the body of mice, mitigated oxidative stress, attenuated the inflammatory response, and subsequent alleviated cadmium-induced kidney injury in mice.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data from the present study may be obtained from the corresponding author if the requirements are reasonable.
References
Turner A (2019) Cadmium pigments in consumer products and their health risks. Sci Total Environ 657:1409–1418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.096
Huang Y, Liu J, Yang L, Li X, Hu G, Wang G, Sun G, Li Z (2021) Fate of lead and cadmium in precalciner cement plants and their atmospheric releases. ACS Omega 6(33):21265–21275. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c01329
Jarup L (2003) Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br Med Bull 68:167–182. https://doi.org/10.1093/bmb/ldg032
Peana M, Pelucelli A, Chasapis CT, Perlepes SP, Bekiari V, Medici S, Zoroddu MA (2022) Biological effects of human exposure to environmental cadmium. Biomolecules 13(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13010036
Genchi G, Sinicropi MS, Lauria G, Carocci A, Catalano A (2020) The effects of cadmium toxicity. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17113782
Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ (2012) Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. Exp Suppl 101:133–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7643-8340-4_6
Taha MM, Mahdy-Abdallah H, Shahy EM, Ibrahim KS, Elserougy S (2018) Impact of occupational cadmium exposure on bone in sewage workers. Int J Occup Environ Health 24(3–4):101–108. https://doi.org/10.1080/10773525.2018.1518745
Liang Y, Zeng T, Tian J, Yan J, Lan Z, Chen J, Xin X, Lei B, Cai Z (2021) Long-term environmental cadmium exposure induced serum metabolic changes related to renal and liver dysfunctions in a female cohort from Southwest China. Sci Total Environ 798:149379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149379
Nawrot TS, Van Hecke E, Thijs L, Richart T, Kuznetsova T, Jin Y, Vangronsveld J, Roels HA, Staessen JA (2008) Cadmium-related mortality and long-term secular trends in the cadmium body burden of an environmentally exposed population. Environ Health Perspect 116(12):1620–1628. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.11667
Kumar S, Sharma A (2019) Cadmium toxicity: effects on human reproduction and fertility. Rev Environ Health 34(4):327–338. https://doi.org/10.1515/reveh-2019-0016
Jain RB (2020) Cadmium and kidney function: concentrations, variabilities, and associations across various stages of glomerular function. Environ Pollut 256:113361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113361
Wilk A, Romanowski M, Wiszniewska B (2021) Analysis of cadmium, mercury, and lead concentrations in erythrocytes of renal transplant recipients from Northwestern Poland. Biol (Basel) 10(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10010062
Rani A, Kumar A, Lal A, Pant M (2014) Cellular mechanisms of cadmium-induced toxicity: a review. Int J Environ Health Res 24(4):378–399. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2013.835032
Rinaldi M, Micali A, Marini H, Adamo EB, Puzzolo D, Pisani A, Trichilo V, Altavilla D, Squadrito F, Minutoli L (2017) Cadmium, organ toxicity and therapeutic approaches: a review on brain, kidney and testis damage. Curr Med Chem 24(35):3879–3893. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867324666170801101448
Yang H, Shu Y (2015) Cadmium transporters in the kidney and cadmium-induced nephrotoxicity. Int J Mol Sci 16(1):1484–1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16011484
Nordberg M, Nordberg GF (2022) Metallothionein and cadmium toxicology-historical review and commentary. Biomolecules 12(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12030360
Rana MN, Tangpong J, Rahman MM (2018) Toxicodynamics of lead, cadmium, mercury and arsenic- induced kidney toxicity and treatment strategy: a mini review. Toxicol Rep 5:704–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2018.05.012
Friberg L (1984) Cadmium and the kidney. Environ Health Perspect 54:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.84541
Klaassen CD, Liu J, Choudhuri S (1999) Metallothionein: an intracellular protein to protect against cadmium toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 39:267–294. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.39.1.267
Park JH, Lee BM, Kim HS (2021) Potential protective roles of curcumin against cadmium-induced toxicity and oxidative stress. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev 24(3):95–118. https://doi.org/10.1080/10937404.2020.1860842
Hernandez-Cruz EY, Amador-Martinez I, Aranda-Rivera AK, Cruz-Gregorio A, Pedraza Chaverri J (2022) Renal damage induced by cadmium and its possible therapy by mitochondrial transplantation. Chem Biol Interact 361:109961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2022.109961
Han YL, Sheng Z, Liu GD, Long LL, Wang YF, Yang WX, Zhu JQ (2015) Cloning, characterization and cadmium inducibility of metallothionein in the testes of the mudskipper Boleophthalmus pectinirostris. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 119:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.04.055
Hassanein EHM, Mohamed WR, Ahmed OS, Abdel-Daim MM, Sayed AM (2022) The role of inflammation in cadmium nephrotoxicity: NF-kappaB comes into view. Life Sci 308:120971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120971
Zhao Y, Yan T, Xiong C, Chang M, Gao Q, Yao S, Wu W, Yi X, Xu G (2021) Overexpression of lipoic acid synthase gene alleviates diabetic nephropathy of Lepr(db/db) mice. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care 9(1). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjdrc-2021-002260
Mason SA, Trewin AJ, Parker L, Wadley GD (2020) Antioxidant supplements and endurance exercise: current evidence and mechanistic insights. Redox Biol 35:101471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101471
Tsou PS, Balogh B, Pinney AJ, Zakhem G, Lozier A, Amin MA, Stinson WA, Schiopu E, Khanna D, Fox DA, Koch AE (2014) Lipoic acid plays a role in scleroderma: insights obtained from scleroderma dermal fibroblasts. Arthritis Res Ther 16(5):411. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-014-0411-6
Li X, Zou Y, Fu YY, Xing J, Wang KY, Wan PZ, Zhai XY (2021) A-lipoic acid alleviates folic acid-induced renal damage through inhibition of ferroptosis. Front Physiol 12:680544. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2021.680544
Veljkovic AR, Nikolic RS, Kocic GM, Pavlovic DD, Cvetkovic TP, Sokolovic DT, Jevtovic TM, Basic JT, Laketic DM, Marinkovic MR, Stojanovic SR, Djordjevic BS, Krsmanovic MM (2012) Protective effects of glutathione and lipoic acid against cadmium-induced oxidative stress in rat’s kidney. Ren Fail 34(10):1281–1287. https://doi.org/10.3109/0886022X.2012.723661
Lee DC, Choi H, Oh JM, Lee DH, Kim SW, Kim SW, Kim BG, Cho JH, Lee J (2019) Protective effects of alpha-lipoic acid on cultured human nasal fibroblasts exposed to urban particulate matter. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 9(6):638–647. https://doi.org/10.1002/alr.22296
Tudose M, Culita DC, Musuc AM, Somacescu S, Ghica C, Chifiriuc MC, Bleotu C (2017) Lipoic acid functionalized SiO(2)@Ag nanoparticles. Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of biological activity. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 79:499–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.05.083
Mayr JA, Zimmermann FA, Fauth C, Bergheim C, Meierhofer D, Radmayr D, Zschocke J, Koch J, Sperl W (2011) Lipoic acid synthetase deficiency causes neonatal-onset epilepsy, defective mitochondrial energy metabolism, and glycine elevation. Am J Hum Genet 89(6):792–797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.11.011
Zou H, Chen Y, Qu H, Sun J, Wang T, Ma Y, Yuan Y, Bian J, Liu Z (2022) Microplastics exacerbate cadmium-induced kidney injury by enhancing oxidative stress, autophagy, apoptosis, and fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci 23(22). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214411
Fujishiro H, Sumino M, Sumi D, Umemoto H, Tsuneyama K, Matsukawa T, Yokoyama K, Himeno S (2022) Spatial localization of cadmium and metallothionein in the kidneys of mice at the early phase of cadmium accumulation. J Toxicol Sci 47(12):507–517. https://doi.org/10.2131/jts.47.507
Luo T, Liu G, Long M, Yang J, Song R, Wang Y, Yuan Y, Bian J, Liu X, Gu J, Zou H, Liu Z (2017) Treatment of cadmium-induced renal oxidative damage in rats by administration of alpha-lipoic acid. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24(2):1832–1844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7953-x
Lin Q, Li S, Jiang N, Shao X, Zhang M, Jin H, Zhang Z, Shen J, Zhou Y, Zhou W, Gu L, Lu R, Ni Z (2019) PINK1-parkin pathway of mitophagy protects against contrast-induced acute kidney injury via decreasing mitochondrial ROS and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Redox Biol 26:101254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2019.101254
Chen C, Han X, Wang G, Liu D, Bao L, Jiao C, Luan J, Hou Y, Xu Y, Wang H, Zhang Q, Zhou H, Fu J, Pi J (2021) Nrf2 deficiency aggravates the kidney injury induced by subacute cadmium exposure in mice. Arch Toxicol 95(3):883–893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-020-02964-3
RafatiRahimzadeh M, RafatiRahimzadeh M, Kazemi S, Moghadamnia AA (2017) Cadmium toxicity and treatment: an update. Caspian J Intern Med 8(3):135–145. https://doi.org/10.22088/cjim.8.3.135
Gu X, Xu L, Wang Z, Ming X, Dang P, Ouyang W, Lin C, Liu X, He M, Wang B (2021) Assessment of cadmium pollution and subsequent ecological and health risks in Jiaozhou Bay of the Yellow Sea. Sci Total Environ 774:145016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145016
Fang J, Xie S, Chen Z, Wang F, Chen K, Zuo Z, Cui H, Guo H, Ouyang P, Chen Z, Huang C, Liu W, Geng Y (2021) Protective effect of vitamin E on cadmium-induced renal oxidative damage and apoptosis in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 199(12):4675–4687. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02606-4
Sanjeev S, Bidanchi RM, Murthy MK, Gurusubramanian G, Roy VK (2019) Influence of ferulic acid consumption in ameliorating the cadmium-induced liver and renal oxidative damage in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26(20):20631–20653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05420-7
Li Z, Chi H, Zhu W, Yang G, Song J, Mo L, Zhang Y, Deng Y, Xu F, Yang J, He Z, Yang X (2021) Cadmium induces renal inflammation by activating the NLRP3 inflammasome through ROS/MAPK/NF-kappaB pathway in vitro and in vivo. Arch Toxicol 95(11):3497–3513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-021-03157-2
Zhang H, Reynolds M (2019) Cadmium exposure in living organisms: a short review. Sci Total Environ 678:761–767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.395
Ge J, Zhang C, Sun YC, Zhang Q, Lv MW, Guo K, Li JL (2019) Cadmium exposure triggers mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in chicken (Gallus gallus) kidney via mitochondrial UPR inhibition and Nrf2-mediated antioxidant defense activation. Sci Total Environ 689:1160–1171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.405
Ma Y, Su Q, Yue C, Zou H, Zhu J, Zhao H, Song R, Liu Z (2022) The effect of oxidative stress-induced autophagy by cadmium exposure in kidney, liver, and bone damage, and neurotoxicity. Int J Mol Sci 23(21). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113491
Umar Ijaz M, Batool M, Batool A, Al-Ghanimd KA, Zafar S, Ashraf A, Al-Misned F, Ahmed Z, Shahzadi S, Samad A, Atique U, Al-Mulhm N, Mahboob S (2021) Protective effects of vitexin on cadmium-induced renal toxicity in rats. Saudi J Biol Sci 28(10):5860–5864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.06.040
Block G, Jensen CD, Morrow JD, Holland N, Norkus EP, Milne GL, Hudes M, Dalvi TB, Crawford PB, Fung EB, Schumacher L, Harmatz P (2008) The effect of vitamins C and E on biomarkers of oxidative stress depends on baseline level. Free Radic Biol Med 45(4):377–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.04.005
Huang X, Xiong G, Feng Y, Fan W, Yang S, Duan J, Duan Y, Wang K, Ou Y, Rehman T, Geng Y, Chen D, Yin L (2020) Protective effects of metallothionein and vitamin E in the trunk kidney and blood of cadmium poisoned Ctenopharyngodon idellus. Fish Physiol Biochem 46(3):1053–1061. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-020-00771-2
Huang J, Ma XT, Xu DD, Yao BJ, Zhao DQ, Leng XY, Liu J (2021) Xianling Gubao Capsule prevents cadmium-induced kidney injury. Biomed Res Int 2021:3931750. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/3931750
Dastan D, Karimi S, Larki-Harchegani A, Nili-Ahmadabadi A (2019) Protective effects of Allium hirtifolium Boiss extract on cadmium-induced renal failure in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26(18):18886–18892. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04656-7
Karami E, Goodarzi Z, Ghanbari A, Dehdashti A, Bandegi AR, Yosefi S (2022) Dataset on biochemical markers and histological alterations in rat kidney intoxicated with cadmium chloride and treated with antioxidant. Data Brief 43:108394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2022.108394
Handan BA, De Moura CFG, Cardoso CM, Santamarina AB, Pisani LP, Ribeiro DA (2020) Protective effect of grape and apple juices against cadmium intoxication in the kidney of rats. Drug Res (Stuttg) 70(11):503–511. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1221-4733
Wan X, Xing Z, Ouyang J, Liu H, Cheng C, Luo T, Yu S, Meihua L, Huang S (2022) Histomorphological and ultrastructural cadmium-induced kidney injuries and precancerous lesions in rats and screening for biomarkers. Biosci Rep 42(6). https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20212516
Cho MR, Kang HG, Jeong SH, Cho MH (2010) Time-dependent changes of cadmium and metallothionein after short-term exposure to cadmium in rats. Toxicol Res 26(2):131–136. https://doi.org/10.5487/TR.2010.26.2.131
Chen S, Liu G, Long M, Zou H, Cui H (2018) Alpha lipoic acid attenuates cadmium-induced nephrotoxicity via the mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in rat. J Inorg Biochem 184:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2018.04.001
Trinchella F, Esposito MG, Scudiero R (2012) Metallothionein primary structure in amphibians: insights from comparative evolutionary analysis in vertebrates. C R Biol 335(7):480–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crvi.2012.05.003
Atukeren P, Aydin S, Uslu E, Gumustas MK, Cakatay U (2010) Redox homeostasis of albumin in relation to alpha-lipoic acid and dihydrolipoic acid. Oxid Med Cell Longev 3(3):206–213. https://doi.org/10.4161/oxim.3.3.11786
Lobato RO, Nunes SM, Wasielesky W, Fattorini D, Regoli F, Monserrat JM, Ventura-Lima J (2013) The role of lipoic acid in the protection against of metallic pollutant effects in the shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Crustacea, Decapoda). Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 165(4):491–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2013.03.015
Pizzino G, Irrera N, Cucinotta M, Pallio G, Mannino F, Arcoraci V, Squadrito F, Altavilla D, Bitto A (2017) Oxidative stress: harms and benefits for human health. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017:8416763. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8416763
Macias-Barragan J, Huerta-Olvera SG, Hernandez-Canaveral I, Pereira-Suarez AL, Montoya-Buelna M (2017) Cadmium and alpha-lipoic acid activate similar de novo synthesis and recycling pathways for glutathione balance. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 52:38–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2017.03.007
Tsikas D (2017) Assessment of lipid peroxidation by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and relatives in biological samples: analytical and biological challenges. Anal Biochem 524:13–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2016.10.021
Jacobson KB, Turner JE (1980) The interaction of cadmium and certain other metal ions with proteins and nucleic acids. Toxicology 16(1):1–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/0300-483x(80)90107-9
Xu L, Hiller S, Simington S, Nickeleit V, Maeda N, James LR, Yi X (2016) Influence of different levels of lipoic acid synthase gene expression on diabetic nephropathy. PLoS ONE 11(10):e0163208. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0163208
Fan SR, Ren TT, Yun MY, Lan R, Qin XY (2021) Edaravone attenuates cadmium-induced toxicity by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation in ICR mice. Neurotoxicol 86:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2021.06.003
Ren TT, Yang JY, Wang J, Fan SR, Lan R, Qin XY (2021) Gisenoside Rg1 attenuates cadmium-induced neurotoxicity in vitro and in vivo by attenuating oxidative stress and inflammation. Inflamm Res 70(10–12):1151–1164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-021-01513-7
Kamt SF, Liu J, Yan LJ (2023) Renal-protective roles of lipoic acid in kidney disease. Nutrients 15(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071732
Funding
This work was supported by grants 222300420516, 81703183, 222102320325, S202110472029, and YJSCX202281Y. Guangcui Xu has received research support from the Nature Science Foundation of Henan Provincial and the National Natural Science Foundation of China. Zijiang Yang and Qiyu Gao have received research support from the Scientific and Technological Research Project of Henan Provincial. Weibing Li and Jingming Gao have received research support from the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Project for University Students of Henan Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guangcui Xu, Yingzheng Zhao and Zijiang Yang designed this project. Guangcui Xu and Weibing Li wrote the draft. Guangcui Xu, Weibing Li, Yingzheng Zhao, Qiyu Gao and Zhen An completed the experimental work. Weibing Li,Ting Fan and Yongbin Wang performed software work and data curation. Mingjing Gao and Fengquan Zhang did animal house work. Zijiang Yang reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics Approval
All operating protocols for mice were in following the standards set by the Animal Ethics Committee from Xinxiang Medical University (approval number: No. XYLL-2017086).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, G., Li, W., Zhao, Y. et al. Overexpression of Lias Gene Alleviates Cadmium-Induced Kidney Injury in Mice Involving Multiple Effects: Metabolism, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation. Biol Trace Elem Res 202, 2797–2811 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-023-03883-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-023-03883-x