Abstract
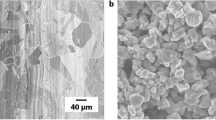
This article was dedicated to explore the combined lubrication of silver, MoS2 and carbon nanotubes (CNTs) based on the changes in applied loads and sliding speeds. The results showed that the formed lubricating films played the major role in undertaking the equivalent stress, as well as effectively reduced friction resistance and material loss. It led to small friction coefficient and less wear rate at 1.2 m/s. At 1.2 m/s-16 N, an integrated lubricating film containing Ag, CNTs and MoS2 was continuously formed, which well provided the excellent lubricating property, resulting in lower friction coefficient (0.19) and less wear rate (1.56 × 10−5 mm3/N m). The formation of Ag and CNTs enriched islands acted as the bearing areas and played the major role in resisting friction resistance. Meanwhile, solid lubricant MoS2 was enriched in the lubricating film and effectively protected lubricating film from being destroyed, resulting in small friction coefficient and less wear rate at 1.2 m/s-16 N.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Zhang, X.L. Shi, and K. Yang, Tribological Behavior of TiAl Matrix Composites with MoO3 Tabular Crystal, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2015, 24, p 4482–4487
Z.S. Xu, Q.X. Zhang, and K. Yang, An Approximate Model for the Migration of Solid Lubricant on Metal Matrix Self-Lubricating Composites, Tribol. Int., 2016, 93, p 104–114
Z. Yan, J.L. Zou, and K. Yang, Investigation of Tribological Behaviors of TiAl-Multilayer Graphene-Microsphere Composites at Different Applied Loads, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2017, 26, p 2305–2312
K. Yang, X.L. Shi, and W.Z. Zhai, Effects of MoS2 and Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes on Tribological Behavior of TiAl Matrix Composite, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2016, 25, p 1094–1102
B. Luan and R. Zhou, Wettability and Friction of Water on a MoS2 Nanosheet, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2016, 108(13), p 1316011–1316015
W. Gulbisnki and T. Suszko, Thin Films of MoO3-Ag2O Binary Oxides-The High Temperature Lubricants, Wear, 2006, 261, p 867–873
N. Zeng, J. Ma, and Y. Zhang, Silver Nanosheet-Coated Copper Nanowire/Epoxy Resin Nanocomposites with Enhanced Electrical Conductivity and Wear Resistance, J. Nanopart. Res., 2017, 19(3), p 91–101
R.H. Estrada-Ruiz, R. Flores-Campos, and G.A. Treviño-Rodríguez, Wear Resistance Analysis of the Aluminum 7075 Alloy and the Nanostructured Aluminum 7075-Silver Nanoparticles Composites, J. Min. Metall. B., 2016, 52, p 11–20
S. Carrera, O. Salas, J.J. Moore, A. Woolverton, and E. Sutter, Performance of CrN/MoS2 (Ti) Coatings for High Wear Low Friction Applications, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2003, 167, p 25–32
J.L. Li, D.S. Xiong, and Y. Wan, Effect of Counterface Material on Friction and Wear Behavior of Ni-Cr-W-Al-Ti-MoS2 Composite, Chin. J. Aeronaut., 2006, 19, p 74–79
K. Yang, X.L. Shi, and A. Zhang, Effect of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes on the Lubricating Properties of TiAl-Ag Composites Based on the Changes in Applied Loads and Testing Temperatures, RSC Adv., 2016, 6, p 74269–74277
K. Yang, X.L. Shi, and J.L. Zou, The Study of the Preparation and Tribological Behavior of TiAl Matrix Composites Containing 1 wt% Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes, RSC Adv., 2016, 6, p 29334–29341
K. Yang, H.R. Ma, X.Y. Liu, and Y.M. Zhang, Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Enhanced the Friction Layer Evolution and Self-Lubricating Property of TiAl-10 wt.% Ag-1 wt.% MWCNTs Sample, RSC Adv., 2017, 7, p 40592–40599
X.H. Chen, G. Zhang, and C.S. Chen, Tribological-Behavior of Eletroless Ni-P-Carbon Nanotube Composite Coating, J. Inorg. Mater., 2003, 18(6), p 1320–1324
C. Li, J. Xia, and H. Dong, Sliding Wear of TiAl Intermetallics Against Steel and Ceramics of Al2O3, Si3N4 and WC/Co, Wear, 2006, 261(5–6), p 693–701
G. Straffelini, M. Pellizzari, and A. Molinari, Influence of Load and Temperature on the Dry Sliding Behaviour of Al-Based Metal-Matrix-Composites Against Friction Material, Wear, 2004, 256(7–8), p 754–763
R. Tyagi, D.S. Xiong, and J.L. Li, Effect of Load and Sliding Speed on Friction and Wear Behavior of Silver/h-BN Containing Ni-Base P/M Composites, Wear, 2011, 270(7–8), p 423–430
B. Breching, R. Flack, H. Cloud, L. Barrett, and H. Minhui, Influence of Speed and Load on the Static Operating Characteristics of a Tilting-Pad Journal Bearing with Ball-and-Socket Pivots, Tribol. Trans., 2005, 48(3), p 283–288
D.L. Duan, S. Li, X.H. Duan, and S.Z. Li, Wear Behavior of Thermally Sprayed Coatings Under Different Loading Conditions, Tribol. Trans., 2005, 48(1), p 45–50
M. Masuko, S. Aoki, and A. Suzuki, Influence of Lubricant Additive and Surface Texture on the Sliding Friction Characteristics of Steel Under Varying Speeds Ranging from Ultralow to Moderate, Tribol. Trans., 2005, 48(3), p 289–298
C.Q. Peng, B.Y. Huang, and Y.H. He, Effects of Alloying on Properties of TiAl-Based Alloys and Mechanisms, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. Chin., 1998, 8, p 11–16
American Society for Testing and Materials, Standard Test Method for Vickers Hardness of Metallic Materials. ASTM E92-82; e2 2003.
American Society for Testing and Materials, Standard Test Methods for Density of Compacted or Sintered Powder Metallurgy (PM) Products Using Archimedes’ Principle. ASTM B962-08; 2008.
American Society for Testing and Materials, Standard Test Method for Wear Testing with a Pin-on-Disk Apparatus. ASTM G99-05; 2010.
S.Y. Zhu, Q.L. Bi, M.Y. Niu, J. Yang, and W.M. Liu, Tribological Behavior of NiAl Matrix Composites with Addition of Oxides at High Temperatures, Wear, 2012, 274–275, p 423–434
J. Cheng, J. Yang, X.H. Zhang, H. Zhong, J.Q. Ma, F. Li, L.C. Fu, Q.L. Bi, J.S. Li, and W.M. Liu, High Temperature Tribological Behavior of a Ti-46Al-2Cr-2Nb Intermetallics, Intermetallics, 2012, 31, p 120–126
W. Lu, C.L. Chen, and L.L. He, Effect of Niobium on Oxidation Behavior of TiAl, J. Mater. Res., 2007, 22(6), p 1486–1490
T.J. Rupert and C.A. Schuh, Sliding Wear of Nanocrystalline Ni-W: Structural Evolution and the Apparent Breakdown of Archard Scaling, Acta Mater., 2010, 58, p 4137–4148
J. Cao, Y.T. Ding, and Z.H. Lu, Effect of Microstructure and Temperature on Oxidation Behavior of Pure Copper, Trans. Mater. Heat Treat., 2011, 32, p 147–150
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51275370); Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities (2017-YB-019); Authors also wish to gratefully thank the Material Research and Testing Center of Wuhan University of Technology for their assistance. Authors were grateful to M.J. Yang, X.L. Nie, S.L. Zhao, Y.M. Li and W.T. Zhu in Material Research and Test Center of WUT for their kind help with EPMA and FESEM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Shen, Q., Shi, X. et al. Effect of Applied Load and Sliding Speed on Tribological Behavior of TiAl-Based Self-Lubricating Composites. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 27, 194–201 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-3106-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-3106-8