Abstract
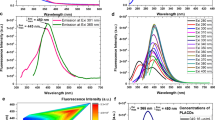
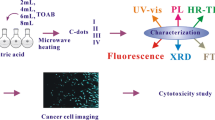
In this work, banana peel (BP) was utilized as a green carbon precursor to synthesize carbon dots (CDs) through the single-step hydrothermal-carbonization method. The structural and optical properties of the resulting BP-CDs were investigated by various techniques. The transmission electron microscopy measurement of BP-CDs displayed uniform morphology with a quasi-spherical shape of 5 nm in size. The optical studies of BP-CDs revealed that BP-CDs emit excitation-dependent fluorescence emission behaviors (redshift) without any capping or passivation agent. The maximum emission was observed at an excitation wavelength of 340 nm, showing an acceptable quantum yield of 19%. The abundant functional groups such as nitrogen- (amine and amide) and oxygen-containing (carbonyl and hydroxyl) groups on the surface of the BP-CDs were confirmed from X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and Attenuated total reflection-Fourier transform infrared studies. These functional groups in BP-CDs are responsible for the negative zeta potential. Since the BP-CDs showed excellent long-term stability (120 days) and photostability (120 min). The biocompatibility of BP-CDs was examined by cytotoxicity studies on cancer cells and utilized as a multi-colored nano-probe for imaging human cancer cells. The aforesaid properties demonstrate that the BP-CDs can be applied to imaging human cells without further modifications.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Liu, L. Zhou, Y. Li, R. Deng, and H. Zhang (2017). Highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots with excellent thermal and photo stability applied as invisible ink for loading important information and anti-counterfeiting. Nanoscale 9 (2), 491–496. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6NR07123F.
S. Perumal, R. Atchudan, T. N. J. I. Edison, and Y. R. Lee (2021). Sustainable synthesis of multifunctional carbon dots using biomass and their applications: A mini-review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9 (4), 105802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105802.
J. Ju and W. Chen (2014). Synthesis of highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for sensitive, label-free detection of Fe (III) in aqueous media. Biosens. Bioelectron. 58, 219–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.02.061.
M. Ghirardello, J. Ramos-Soriano, and M. C. Galan (2021). Carbon dots as an emergent class of antimicrobial agents. Nanomaterials 11 (8), 1877.
H. Lee, Y.-C. Su, H.-H. Tang, Y.-S. Lee, J.-Y. Lee, C.-C. Hu, and T.-C. Chiu (2021). One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of carbon dots as fluorescent probes for the determination of mercuric and hypochlorite ions. Nanomaterials 11 (7), 1831.
X. Sun and Y. Lei (2017). Fluorescent carbon dots and their sensing applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 89, 163–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2017.02.001.
Y. Niu, J. Li, J. Gao, X. Ouyang, L. Cai, and Q. Xu (2021). Two-dimensional quantum dots for biological applications. Nano Res. 14 (11), 3820–3839. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3757-5.
A. Sharma and J. Das (2019). Small molecules derived carbon dots: synthesis and applications in sensing, catalysis, imaging, and biomedicine. J. Nanobiotechnol. 17 (1), 92. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-019-0525-8.
T. Pal, S. Mohiyuddin, and G. Packirisamy (2018). Facile and green synthesis of multicolor fluorescence carbon dots from curcumin: in vitro and in vivo bioimaging and other applications. ACS Omega 3 (1), 831–843. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.7b01323.
R. Atchudan, T. N. J. I. Edison, K. R. Aseer, S. Perumal, N. Karthik, and Y. R. Lee (2018). Highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots derived from Phyllanthus acidus utilized as a fluorescent probe for label-free selective detection of Fe3+ ions, live cell imaging and fluorescent ink. Biosens. Bioelectron. 99, 303–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.07.076.
R. Atchudan, T. N. J. I. Edison, S. Perumal, R. Vinodh, A. K. Sundramoorthy, R. S. Babu, and Y. R. Lee (2021). Leftover kiwi fruit peel-derived carbon dots as a highly selective fluorescent sensor for detection of ferric ion. Chemosensors 9 (7), 166.
D. J. Kim, J. M. Yoo, Y. Suh, D. Kim, I. Kang, J. Moon, M. Park, J. Kim, K.-S. Kang, and B. H. Hong (2021). Graphene quantum dots from carbonized coffee bean wastes for biomedical applications. Nanomaterials 11 (6), 1423.
M. Jorns and D. Pappas (2021). A review of fluorescent carbon dots, their synthesis, physical and chemical characteristics, and applications. Nanomaterials 11 (6), 1448.
R. Atchudan, P. Gangadaran, T. N. J. I. Edison, S. Perumal, A. K. Sundramoorthy, R. Vinodh, R. L. Rajendran, B.-C. Ahn, and Y. R. Lee (2022). Betel leaf derived multicolor emitting carbon dots as a fluorescent probe for imaging mouse normal fibroblast and human thyroid cancer cells. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 136, 115010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2021.115010.
Q. Xu, Y. Niu, J. Li, Z. Yang, J. Gao, L. Ding, H. Ni, P. Zhu, Y. Liu, Y. Tang, Z.-P. Lv, B. Peng, T. S. Hu, H. Zhou, and C. Xu (2022). Recent progress of quantum dots for energy storage applications. Carbon Neutrality 1 (1), 13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43979-022-00002-y.
R. Atchudan, S. Chandra Kishore, P. Gangadaran, T. N. Jebakumar Immanuel Edison, S. Perumal, R. L. Rajendran, M. Alagan, S. Al-Rashed, B.-C. Ahn, and Y. R. Lee (2022). Tunable fluorescent carbon dots from biowaste as fluorescence ink and imaging human normal and cancer cells. Environ. Res. 204, 112365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112365.
J. Liu, R. Li, and B. Yang (2020). Carbon dots: a new type of carbon-based nanomaterial with wide applications. ACS Central Sci. 6 (12), 2179–2195. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscentsci.0c01306.
D. Pan, J. Zhang, Z. Li, and M. Wu (2010). Hydrothermal route for cutting graphene sheets into blue-luminescent graphene quantum dots. Adv. Mater. (Deerfield Beach, Fla) 22 (6), 734–738. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200902825.
J. Peng, W. Gao, B. K. Gupta, Z. Liu, R. Romero-Aburto, L. Ge, L. Song, L. B. Alemany, X. Zhan, G. Gao, S. A. Vithayathil, B. A. Kaipparettu, A. A. Marti, T. Hayashi, J.-J. Zhu, and P. M. Ajayan (2012). Graphene quantum dots derived from carbon fibers. Nano Lett. 12 (2), 844–849. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl2038979.
P. Krishnaiah, R. Atchudan, S. Perumal, E.-S. Salama, Y. R. Lee, and B.-H. Jeon (2022). Utilization of waste biomass of Poa pratensis for green synthesis of n-doped carbon dots and its application in detection of Mn2+ and Fe3+. Chemosphere 286, 131764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131764.
X. Wang, Y. Feng, P. Dong, and J. Huang (2019). A mini review on carbon quantum dots: preparation, properties, and electrocatalytic application. Front Chem. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2019.00671.
P. Wu, W. Li, Q. Wu, Y. Liu, and S. Liu (2017). Hydrothermal synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots from microcrystalline cellulose for the detection of Fe3+ ions in an acidic environment. RSC Adv. 7 (70), 44144–44153. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA08400E.
W. Meng, X. Bai, B. Wang, Z. Liu, S. Lu, and B. Yang (2019). Biomass-derived carbon dots and their applications. Energy Environ. Mater. 2 (3), 172–192. https://doi.org/10.1002/eem2.12038.
R. Atchudan, T. N. Jebakumar Immanuel Edison, M. Shanmugam, S. Perumal, T. Somanathan, and Y. R. Lee (2021). Sustainable synthesis of carbon quantum dots from banana peel waste using hydrothermal process for in vivo bioimaging. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 126, 114417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2020.114417.
W. Chen, C. Hu, Y. Yang, J. Cui, and Y. Liu (2016). Rapid synthesis of carbon dots by hydrothermal treatment of lignin. Materials (Basel) 9 (3), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9030184.
P. Gangadaran and B. C. Ahn (2017). Molecular imaging: a useful tool for the development of natural killer cell-based immunotherapies. Front. Immunol. 8, 1090. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01090.
R. L. Rajendran, M. P. Jogalekar, P. Gangadaran, and B. C. Ahn (2020). Noninvasive in vivo cell tracking using molecular imaging: a useful tool for developing mesenchymal stem cell-based cancer treatment. World J. Stem Cells 12 (12), 1492–1510. https://doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v12.i12.1492.
H. W. Lee, P. Gangadaran, S. Kalimuthu, and B.-C. Ahn (2016). Advances in molecular imaging strategies for in vivo tracking of immune cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 1946585. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1946585.
E. Fanizza, N. Depalo, S. Fedorenko, R. M. Iacobazzi, A. Mukhametshina, R. Zairov, A. Salatino, F. Vischio, A. Panniello, V. Laquintana, M. L. Curri, A. Mustafina, N. Denora, and M. Striccoli (2019). Green fluorescent terbium (III) complex doped silica nanoparticles for TSPO targeting. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20 (13), 3139.
R. R. Zairov, A. P. Dovzhenko, A. S. Sapunova, A. D. Voloshina, D. A. Tatarinov, I. R. Nizameev, A. T. Gubaidullin, K. A. Petrov, F. Enrichi, A. Vomiero, and A. R. Mustafina (2019). Dual red-NIR luminescent EuYb heterolanthanide nanoparticles as promising basis for cellular imaging and sensing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 105, 110057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.110057.
W. Waldeck, G. Mueller, M. Wiessler, M. Brom, K. Tóth, and K. Braun (2009). Autofluorescent proteins as photosensitizer in eukaryontes. Int. J. Med. Sci. 6 (6), 365–373. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.6.365.
A. E. Jablonski, J.-C. Hsiang, P. Bagchi, N. Hull, C. I. Richards, C. J. Fahrni, and R. M. Dickson (2012). Signal discrimination between fluorescent proteins in live cells by long-wavelength optical modulation. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 3 (23), 3585–3591. https://doi.org/10.1021/jz3016414.
R. N. Day and M. W. Davidson (2009). The fluorescent protein palette: tools for cellular imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 38 (10), 2887–2921. https://doi.org/10.1039/b901966a.
E. C. Jensen (2012). Use of fluorescent probes: their effect on cell biology and limitations. Anat. Record 295 (12), 2031–2036. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.22602.
M. S. Amer, P. Arunachalam, A. M. Al-Mayouf, S. Prasad, M. N. Alshalwi, and M. A. Ghanem (2019). Mesoporous tungsten trioxide photoanodes modified with nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots for enhanced oxygen evolution photo-reaction. Nanomaterials 9 (10), 1502.
T. N. Jebakumar Immanuel Edison, R. Atchudan, N. Karthik, D. Xiong, and Y. R. Lee (2020). Facile hydrothermal synthesis of nitrogen rich blue fluorescent carbon dots for cell bio-imaging of Candida albicans. Process Biochem. 88, 113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2019.10.003.
K. Linehan and H. Doyle (2014). Efficient one-pot synthesis of highly monodisperse carbon quantum dots. RSC Adv. 4 (1), 18–21. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3RA45083J.
R. Atchudan, T. N. J. I. Edison, S. Perumal, R. Vinodh, and Y. R. Lee (2019). Betel-derived nitrogen-doped multicolor carbon dots for environmental and biological applications. J. Mol. Liquids 296, 111817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.111817.
Y. Hu, J. Yang, J. Tian, L. Jia, and J.-S. Yu (2014). Waste frying oil as a precursor for one-step synthesis of sulfur-doped carbon dots with pH-sensitive photoluminescence. Carbon 77, 775–782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2014.05.081.
F. Yan, Z. Bai, F. Zu, Y. Zhang, X. Sun, T. Ma, and L. Chen (2019). Yellow-emissive carbon dots with a large Stokes shift are viable fluorescent probes for detection and cellular imaging of silver ions and glutathione. Microchimica Acta 186 (2), 113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3221-8.
P. Thirukumaran, R. Balasubramanian, R. Atchudan, A. Shakila Parveen, Y. R. Lee, and S.-C. Kim (2020). Metal-free nitrogen-rich glassy carbon as an electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Mater. Res. Bull. 124, 110734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2019.110734.
T. N. J. I. Edison, R. Atchudan, M. G. Sethuraman, J.-J. Shim, and Y. R. Lee (2016). Microwave assisted green synthesis of fluorescent N-doped carbon dots: Cytotoxicity and bio-imaging applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 161, 154–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.05.017.
W.-K. Jo, S. Kumar, M. A. Isaacs, A. F. Lee, and S. Karthikeyan (2017). Cobalt promoted TiO2/GO for the photocatalytic degradation of oxytetracycline and Congo Red. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 201, 159–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.08.022.
H. Liu, Y. Zhang, and C. Huang (2019). Development of nitrogen and sulfur-doped carbon dots for cellular imaging. J. Pharm. Anal. 9 (2), 127–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2018.10.001.
P. Thirukumaran, R. Atchudan, A. Shakila Parveen, M. Santhamoorthy, V. Ramkumar, and S.-C. Kim (2021). N-doped mesoporous carbon prepared from a polybenzoxazine precursor for high performance supercapacitors. Polymers 13 (13), 2048.
R. Atchudan, T. N. J. I. Edison, S. Perumal, N. Clament Sagaya Selvam, and Y. R. Lee (2019). Green synthesized multiple fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots as an efficient label-free optical nanoprobe for in vivo live-cell imaging. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 372, 99–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.12.011.
P. Xie, Q. Xin, S.-T. Yang, T. He, Y. Huang, G. Zeng, M. Ran, and X. Tang (2017). Skeleton labeled (13)C-carbon nanoparticles for the imaging and quantification in tumor drainage lymph nodes. Int J Nanomed. 12, 4891–4899. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S134493.
R. Atchudan, T. N. J. I. Edison, D. Chakradhar, S. Perumal, J.-J. Shim, and Y. R. Lee (2017). Facile green synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon dots using Chionanthus retusus fruit extract and investigation of their suitability for metal ion sensing and biological applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 246, 497–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.02.119.
Y. Hu, X. Geng, L. Zhang, Z. Huang, J. Ge, and Z. Li (2017). Nitrogen-doped carbon dots mediated fluorescent on-off assay for rapid and highly sensitive pyrophosphate and alkaline phosphatase detection. Sci. Rep. 7 (1), 5849. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-06356-z.
Y. Li, X. Zhong, A. E. Rider, S. A. Furman, and K. Ostrikov (2014). Fast, energy-efficient synthesis of luminescent carbon quantum dots. Green Chem. 16 (5), 2566–2570. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3GC42562B.
L. Zhao, Y. Wang, X. Zhao, Y. Deng, and Y. Xia (2019). Facile synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots with chitosan for fluorescent detection of Fe3+. Polymers 11 (11), 1731.
K. M. George, T. C. Ruthenburg, J. Smith, L. Yu, Q. Zhang, C. Anastasio, and A. M. Dillner (2015). FT-IR quantification of the carbonyl functional group in aqueous-phase secondary organic aerosol from phenols. Atmos. Environ. 100, 230–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.11.011.
R. Atchudan, T. N. J. I. Edison, M. G. Sethuraman, and Y. R. Lee (2016). Efficient synthesis of highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots for cell imaging using unripe fruit extract of Prunus mume. Appl. Surf. Sci. 384, 432–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.05.054.
R. Zhang and W. Chen (2014). Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots: Facile synthesis and application as a “turn-off” fluorescent probe for detection of Hg2+ ions. Biosens. Bioelectron. 55, 83–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.11.074.
H. Wang, P. Sun, S. Cong, J. Wu, L. Gao, Y. Wang, X. Dai, Q. Yi, and G. Zou (2016). Nitrogen-doped carbon dots for “green” quantum dot solar cells. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 11 (1), 27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1231-1.
R. Kannan, U. Bipinlal, S. Kurungot, and V. K. Pillai (2011). Enhanced electrocatalytic performance of functionalized carbon nanotube electrodes for oxygen reduction in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13 (21), 10312–10317. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CP02853C.
R. Atchudan, N. Muthuchamy, T. N. J. I. Edison, S. Perumal, R. Vinodh, K. H. Park, and Y. R. Lee (2019). An ultrasensitive photoelectrochemical biosensor for glucose based on bio-derived nitrogen-doped carbon sheets wrapped titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 126, 160–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.10.049.
S. Zhao, M. Lan, X. Zhu, H. Xue, T.-W. Ng, X. Meng, C.-S. Lee, P. Wang, and W. Zhang (2015). Green synthesis of bifunctional fluorescent carbon dots from garlic for cellular imaging and free radical scavenging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7 (31), 17054–17060. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b03228.
S. Karthikeyan and G. Sekaran (2014). In situ generation of a hydroxyl radical by nanoporous activated carbon derived from rice husk for environmental applications: kinetic and thermodynamic constants. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16 (9), 3924–3933. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CP54185A.
X. Li, Z. Zhao, and C. Pan (2016). Electrochemical exfoliation of carbon dots with the narrowest full width at half maximum in their fluorescence spectra in the ultraviolet region using only water as electrolyte. Chem. Commun. 52 (60), 9406–9409. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC03080G.
V. Raveendran, A. R. Suresh Babu, and N. K. Renuka (2019). Mint leaf derived carbon dots for dual analyte detection of Fe(iii) and ascorbic acid. RSC Adv. 9 (21), 12070–12077. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA02120E.
R. Atchudan, T. N. J. I. Edison, and Y. R. Lee (2016). Nitrogen-doped carbon dots originating from unripe peach for fluorescent bioimaging and electrocatalytic oxygen reduction reaction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 482, 8–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.07.058.
S. Lu, R. Cong, S. Zhu, X. Zhao, J. Liu, J. S. Tse, S. Meng, and B. Yang (2016). pH-Dependent synthesis of novel structure-controllable polymer-carbon NanoDots with high acidophilic luminescence and super carbon dots assembly for white light-emitting diodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8 (6), 4062–4068. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b11579.
M. Righetto, A. Privitera, I. Fortunati, D. Mosconi, M. Zerbetto, M. L. Curri, M. Corricelli, A. Moretto, S. Agnoli, L. Franco, R. Bozio, and C. Ferrante (2017). Spectroscopic insights into carbon dot systems. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 8 (10), 2236–2242. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.7b00794.
S. Yu, X. Zhang, L. Li, J. Xu, Y. Song, X. Liu, S. Wu, and J. Zhang (2019). High photostability and luminescent efficiency of quantum dots: ultrathin epitaxial Al self-passivation layer with a homogeneous ligand. Mater. Res. Express 6 (8), 08500857. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab28b6.
M. Yahaya Pudza, Z. Zainal Abidin, S. Abdul Rashid, F. Md Yasin, A. S. M. Noor, and M. A. Issa (2020). Eco-friendly sustainable fluorescent carbon dots for the adsorption of heavy metal ions in aqueous environment. Nanomaterials 10 (2), 315.
S. Y. Park, C. Y. Lee, H.-R. An, H. Kim, Y.-C. Lee, E. C. Park, H.-S. Chun, H. Y. Yang, S.-H. Choi, H. S. Kim, K. S. Kang, H. G. Park, J.-P. Kim, Y. Choi, J. Lee, and H. U. Lee (2017). Advanced carbon dots via plasma-induced surface functionalization for fluorescent and bio-medical applications. Nanoscale 9 (26), 9210–9217. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NR03026F.
H. Wang, J. Di, Y. Sun, J. Fu, Z. Wei, H. Matsui, C. A. del Alonso, and S. Zhou (2015). Biocompatible PEG-Chitosan@Carbon Dots Hybrid Nanogels for Two-Photon Fluorescence Imaging, Near-Infrared Light/pH Dual-Responsive Drug Carrier, and Synergistic Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 25 (34), 5537–5547. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201501524.
A. B. Bourlinos, R. Zbořil, J. Petr, A. Bakandritsos, M. Krysmann, and E. P. Giannelis (2012). Luminescent Surface Quaternized Carbon Dots. Chem. Mater. 24 (1), 6–8. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm2026637.
B. Zhi, Y. Cui, S. Wang, B. P. Frank, D. N. Williams, R. P. Brown, E. S. Melby, R. J. Hamers, Z. Rosenzweig, D. H. Fairbrother, G. Orr, and C. L. Haynes (2018). Malic Acid Carbon Dots: From Super-resolution Live-Cell Imaging to Highly Efficient Separation. ACS Nano 12 (6), 5741–5752. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b01619.
V. N. Mehta, S. Jha, R. K. Singhal, and S. K. Kailasa (2014). Preparation of multicolor emitting carbon dots for HeLa cell imaging. New J. Chem. 38 (12), 6152–6160. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NJ00840E.
Y. Song, S. Zhu, and B. Yang (2014). Bioimaging based on fluorescent carbon dots. RSC Adv. 4 (52), 27184–27200. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3RA47994C.
Y. Zhang, X. Zhang, Y. Shi, C. Sun, N. Zhou, and H. Wen (2020). The Synthesis and Functional Study of Multicolor Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots for Live Cell Nuclear Imaging. Molecules 25 (2), 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25020306.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant funded by the Korean government MSIT (Grant No. 2021R1A2B5B02002436)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Atchudan, R., Gangadaran, P., Perumal, S. et al. Green Synthesis of Multicolor Emissive Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots for Bioimaging of Human Cancer Cells. J Clust Sci 34, 1583–1594 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-022-02337-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-022-02337-z