Abstract
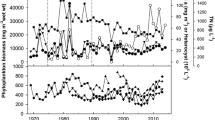
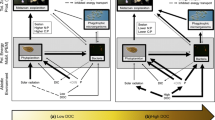
Assessing ammonium (NH4 +) availability in aquatic systems requires accurate concentration and turnover rate data. Water column NH4 + regeneration, potential NH4 + uptake, and nitrogen (N) fixation rates were measured in Missisquoi Bay, Lake Champlain, to help constrain internal N dynamics affecting phytoplankton community structure and cyanobacteria (Cy) blooms. Cyanobacteria dominated phytoplankton biomass during occasional summer bloom periods, but low or undetectable N2 fixation rates and low heterocyte abundances suggested that N fixing cyanobacteria did not rely on atmospheric N2. Light/dark incubations revealed that photosynthetic and dark NH4 + uptake generally were balanced, highlighting the importance of bacterial uptake. Our results suggest that phytoplankton were not controlled by nutrients from the “bottom-up”; rather, water column N dynamics responded to phytoplankton patterns. Basin-scale water column NH4 + regeneration rates were about 700,000 mol N day−1 (9.8 t N day−1), which is almost twice the estimated N load from tributaries, and suggests a primary role for water column N regeneration in supporting primary production. Comparisons of basin-scale NH4 + regeneration and demand imply that primary production is not sustained fully by combined water column regeneration and tributary N inputs; thus, future research should constrain additional sources and sinks affecting N balance in this and other aquatic systems.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikari, B. K., C. A. Madramootoo & A. Sarangi, 2010. Temporal variability of phosphorus flux from Pike River watershed to the Missisquoi Bay of Québec. Current Science 98: 58–64.
Attridge, E. M. & P. Rowell, 1997. Growth, heterocyte differentiation and nitrogenase activity in the cyanobacteria Anabaena variabilis and Anabaena cylindrica in response to molybdenum and vanadium. New Phytologist 135: 517–526.
Bergman, B., J. R. Gallon, A. N. Rai & L. J. Stal, 1997. N2 fixation by non-heterocystous cyanobacteria. FEMS Microbiology Reviews 19: 139–185.
Blackburn, T. H., 1979. Method for measuring rates of NH4 + turnover in anoxic marine sediments, using a 15N-NH4 + dilution technique. Applied & Environmental Microbiology 37: 760–765.
Blomqvist, P., A. Pettersson & P. Hyenstrand, 1994. Ammonium-nitrogen: a key regulatory factor causing dominance of non-nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria in aquatic systems. Archiv fur Hydrobiologie 132: 141–164.
Boesch, D. F., W. R. Boynton, L. B. Crowder, R. J. Diaz, R. W. Howarth, L. D. Mee, S. W. Nixon, N. N. Rabalais, R. Rosenberg, J. G. Sanders, D. Scavia & R. E. Turner, 2009. Nutrient enrichment drives Gulf of Mexico hypoxia. EOS 90(14): 117–119.
Bourbonnais, A., M. F. Lehmann, J. J. Waniek & D. E. Schulz-Bull, 2009. Nitrate isotope anomalies reflect N2 fixation in the Azores front region (subtropical NE Atlantic). Journal of Geophysical Research—Ocean 114: C03003.
Caperon, J., D. Schell, J. Hirota & E. Laws, 1979. Ammonium excretion rates in Kaneohe Bay, Hawaii, measured by a 15N isotope dilution technique. Marine Biology 54: 33–40.
Clark, D. R., K. J. Flynn & N. J. P. Owens, 2002. The large capacity for dark nitrate-assimilation in diatoms may overcome nitrate limitation of growth. New Phytologist 155: 101–108.
Cochlan, W. P., N. M. Price & P. J. Harrison, 1991. Effects of irradiance on nitrogen uptake by phytoplankton: comparison of frontal and stratified communities. Marine Ecology Progress Series 69: 103–116.
Davis, T. W., D. L. Berry, G. L. Boyer & C. J. Gobler, 2009. The effects of temperature and nutrients on the growth and dynamics of toxic and non-toxic strains of Microcystis during cyanobacteria blooms. Harmful Algae 8: 715–725.
Dekas, A. E., R. S. Poretsky & V. J. Orphan, 2009. Deep-sea archaea fix and share nitrogen in methane-consuming microbial consortia. Science 326: 422–426.
Donald, D. B., M. J. Bogard, K. Finlay & P. R. Leavitt, 2011. Comparative effects of urea, ammonium, and nitrate on phytoplankton abundance, community composition, and toxicity in hypereutrophic freshwaters. Limnology & Oceanography 56(6): 2161–2175.
Dunlap, F., T. Mihuc & C. Pershyn, 2008. Missisquoi Bay zooplankton: the crash of 2007. Meeting abstract. Lake Champlain: Our lake, our future (8–9 Jan 2008). Burlington, VT.
Ferber, L. R., S. N. Levine, A. Lini & G. P. Livingston, 2004. Do cyanobacteria dominate in eutrophic lakes because they fix atmospheric nitrogen? Freshwater Biology 49: 690–708.
Finlay, K., A. Patoine, D. B. Donald, M. Bogard & P. R. Leavitt, 2010. Experimental evidence that pollution with urea can degrade water quality in phosphorus-rich lakes of the northern Great Plains. Limnology & Oceanography 55: 1213–1230.
Flores, E. & A. Herrero, 2005. Nitrogen assimilation and nitrogen control in cyanobacteria. Biochemical Society Transactions 33: 164–167.
Gardner, W. S. & G. F. Lee, 1975. The role of amino acids in the nitrogen cycle of Lake Mendota. Limnology & Oceanography 20: 379–388.
Gardner, W. S., H. A. Bootsma, C. Evans & P. A. St John, 1995a. Improved chromatographic analysis of 15N:14N ratios in ammonium or nitrate for isotopic addition experiments. Marine Chemistry 48: 271–282.
Gardner, W. S., J. F. Cavaletto, T. H. Johengen, J. R. Johnson, R. T. Heath & J. B. Cotner, 1995b. Effects of the zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha, on community nitrogen dynamics in Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron. Journal of Great Lakes Research 21: 529–544.
Gardner, W. S., J. F. Cavaletto, H. A. Bootsma, P. J. Lavrentyev & F. Troncone, 1998. Nitrogen cycling rates and light effects in tropical Lake Maracaibo, Venezuela. Limnology & Oceanography 43: 1814–1825.
Gardner, W. S., P. J. Lavrentyev, J. F. Cavaletto, M. J. McCarthy, B. J. Eadie, T. H. Johengen & J. B. Cotner, 2004. Distribution and dynamics of nitrogen and microbial plankton in southern Lake Michigan during spring transition 1999–2000. Journal of Geophysical Research 109: C03007. 16 pp.
Ginn, H. P., L. A. Pearson & B. A. Neilan, 2010. NtcA from Microcystis aeruginosa PCC 7806 is autoregulatory and binds to the microcystin promoter. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 76(13): 4362–4368.
Glibert, P. M., 1993. The interdependence of uptake and release of NH4 + and organic nitrogen. Marine Microbial Food Webs 7: 53–67.
Glibert, P. M., 1998. Interactions of top-down and bottom-up control in planktonic nitrogen cycling. Hydrobiologia 363: 1–12.
Glibert, P. M., D. C. Biggs & J. J. McCarthy, 1982. Utilization of ammonium and nitrate during austral summer in the Scotia Sea. Deep-Sea Research 29: 837–850.
Hyenstrand, P., P. Nyvall, A. Pettersson & P. Blomqvist, 1998. Regulation of non-nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria by inorganic nitrogen sources—experiments from Lake Erken. Archiv fur Hydrobiologie Special Issue 51: 29–40.
James, R. T., W. S. Gardner, M. J. McCarthy & S. A. Carini, 2011. Nitrogen dynamics in Lake Okeechobee: forms, functions, and changes. Hydrobiologia 669: 199–212.
Kana, T. M., C. Darkangelo, M. D. Hunt, J. B. Oldham, G. E. Bennett & J. C. Cornwell, 1994. Membrane inlet mass spectrometer for rapid high-precision determination of N2, O2, and Ar in environmental water samples. Analytical Chemistry 66: 4166–4170.
Kirchman, D. L., 2000. Uptake and regeneration of inorganic nutrients by marine heterotrophic bacteria. In Kirchman, D. L. (ed.), Microbial Ecology of the Oceans. Wiley, Wilmington.
Komárek, J. & K. Anagnostidis, 1989. Modern approach to the classification system of Cyanophytes 4—Nostocales. Algological Studies/Archiv für Hydrobiologie 56(Suppl.): 247–345.
Lavrentyev, P. J., M. J. McCarthy, D. Klarer, F. J. Jochem & W. S. Gardner, 2004. Estuarine microbial food web patterns in a Lake Erie coastal wetland. Microbial Ecology 48: 567–577.
Lean, D. R. S. & R. Knowles, 1987. Nitrogen transformations in Lake Ontario. Canadian Journal of Fisheries & Aquatic Sciences 44: 2133–2143.
Lindell, D. & A. F. Post, 2001. Ecological aspects of ntcA gene expression and its use as an indicator of the nitrogen status of marine Synechococcus spp. Applied & Environmental Microbiology 67: 3340–3349.
Lomas, M. W. & P. M. Glibert, 1999. Interactions between NH4 + and NO3 − uptake and assimilation: comparison of diatoms and dinoflagellates at several growth temperatures. Marine Biology 133: 541–551.
McCarthy, M. J., 2011. Nitrogen availability and transformations in Missisquoi Bay, Lake Champlain: effects on phytoplankton community structure and cyanobacterial blooms. PhD Dissertation, Université du Québec à Montréal: 202 pp.
McCarthy, J. J., W. R. Taylor & J. L. Taft, 1977. Nitrogenous nutrition of the plankton in the Chesapeake Bay. 1. Nutrient availability and phytoplankton preferences. Limnology & Oceanography 22: 996–1011.
McCarthy, M. J., W. S. Gardner, P. J. Lavrentyev, K. M. Moats, F. J. Jochem & D. M. Klarer, 2007a. Effects of hydrological flow regime on sediment–water interface and water column nitrogen dynamics in a Great Lakes coastal wetland (Old Woman Creek, Lake Erie). Journal of Great Lakes Research 33: 219–231.
McCarthy, M. J., P. J. Lavrentyev, L. Yang, L. Zhang, Y. Chen, B. Qin & W. S. Gardner, 2007b. Nitrogen dynamics and microbial food web structure during a summer cyanobacterial bloom in a subtropical, shallow, well-mixed, eutrophic lake (Taihu Lake, China). Hydrobiologia 581: 195–207.
McCarthy, M. J., W. S. Gardner, P. J. Lavrentyev, F. J. Jochem & C. J. Williams, 2009a. Water column nitrogen cycling and microbial plankton in Florida Bay. Contributions in Marine Science 38: 49–62.
McCarthy, M. J., R. T. James, Y. Chen, T. L. East & W. S. Gardner, 2009b. Nutrient ratios and phytoplankton community structure in the large, shallow, eutrophic, subtropical Lakes Okeechobee (Florida, USA) and Taihu (China). Limnology 10: 215–227.
McQueen, D. J. & D. R. S. Lean, 1987. Influence of water temperature and nitrogen–phosphorus ratios on the dominant bluegreen algae in Lake St. George, Ontario. Canadian Journal of Fisheries & Aquatic Sciences 44: 598–604.
McQueen, D. J., E. L. Mills, J. L. Forney, M. R. S. Johannes & J. R. Post, 1992. Trophic level relationships in pelagic food webs: comparisons derived from long-term data sets for Oneida Lake, New York (USA) and Lake St. George, Ontario (Canada). Canadian Journal of Fisheries & Aquatic Sciences 49: 1588–1596.
Mendelsohn, D., C. Swanson & T. Isaji, 1997. Hydrodynamic modeling of Missisquoi Bay in Lake Champlain. Final report submitted to Vermont Geological Survey, Vermont Agency of Natural Resources: 136 pp.
Menden-Deuer, S. & E. J. Lessard, 2000. Carbon to volume relationships for dinoflagellates, diatoms, and other protist plankton. Limnology & Oceanography 45: 569–579.
Mihuc, T. B., G. L. Boyer, M. F. Satchwell, M. Pellam, J. Jones, J. Vasile, A. Bouchard & R. Bonham, 2005. 2002 phytoplankton community composition and cyanobacterial toxins in Lake Champlain, USA. Verhandlungen des Internationalen Verein Limnologie 29: 328–333.
Muro-Pastor, A. M., A. Valladares, E. Flores & A. Herrero, 1999. The hetC gene is a direct target of the NtcA transcriptional regulator in cyanobacterial heterocyte development. Journal of Bacteriology 181: 6664–6669.
Paerl, H. W., 1990. Physiological ecology and regulation of N2 fixation in natural waters. In Marshall, K. C. (ed.), Advances in Microbial Ecology, Vol. 2. Plenum, New York: 304–355.
Paerl, H. W. & J. Huisman, 2008. Blooms like it hot. Science 320: 57–58.
Paerl, H. W. & J. Huisman, 2009. Climate change: a catalyst for global expansion of harmful cyanobacterial blooms. Environmental Microbiology Reports 1: 27–37.
Paerl, H. W., H. Xu, M. J. McCarthy, G. Zhu, B. Qin, Y. Li & W. S. Gardner, 2011. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): the need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water Research 45: 1973–1983.
Poister, D. & D. E. Armstrong, 2004. Seasonal sedimentation trends in a mesotrophic lake: influence of diatoms and implications for phosphorus dynamics. Biogeochemistry 65: 1–13.
Presing, M., S. Herodek, T. Preston & L. Voros, 2001. Nitrogen uptake and the importance of internal nitrogen loading in Lake Balaton. Freshwater Biology 46: 125–139.
Presing, M., T. Preston, A. Takatsy, P. Sprober, A. W. Kovacs, L. Voros, G. Kenesi & I. Kobor, 2008. Phytoplankton nitrogen demand and the significance of internal and external nitrogen sources in a large shallow lake (Lake Balaton, Hungary). Hydrobiologia 599: 87–95.
Smeltzer, E. & M. Simoneau, 2008. Phosphorus loading to Missisquoi Bay from sub-basins in Vermont and Québec, 2002–2005. Report submitted to the Lake Champlain Steering Committee, November 25, 2008. 22 pp.
Syrett, P. J., 1981. Nitrogen metabolism of microalgae. Canadian Bulletin of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 210: 182–210.
Vanderploeg, H. A., J. R. Liebig, W. W. Carmichael, M. A. Agy, T. H. Johengen, G. L. Fahnenstiel & T. F. Nalepa, 2001. Zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) selective filtration promoted toxic Microcystis blooms in Saginaw Bay (Lake Huron) and Lake Erie. Canadian Journal of Fisheries & Aquatic Sciences 58: 1208–1221.
Ward, B. B., D. G. Capone & J. P. Zehr, 2007. What’s new in the nitrogen cycle? Oceanography 20: 101–109.
Wilhelm, S. W., & C. A. Suttle, 1999. Viruses as regulators of nutrient cycles in aquatic environments. In Bell, C. R., M. Brylinsky & P. Johnson-Green (eds), Microbial Biosystems: New Frontiers Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Microbial Ecology. Atlantic Canada Society for Microbial Ecology, Halifax, NS: 6 pp.
Acknowledgments
This project was funded by grants from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada to DFB, Fonds de recherche du Québec—Nature et technologies (FQRNT) to DFB and MFL, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration—Center for Sponsored Coastal Ocean Research (Grant # NA07NOS4780225) to WSG, and FQRNT via a Bourse d’excellence pour étudiants étrangers (scholarship for foreign students) to MJM. We thank Alexandre Guindon for assistance in the field and lab. Irina Moukhina and Serge Paquet performed the phytoplankton counts, and Jennifer Boisvert, Martine Camiré, Guillaume Cloutier, Catalina Gonzalez-Rueda, Pierre Marcoux, Dr. Alexandrine Pannard, Isabelle Roby, Genevieve Thibodeau, and Gabriela von Rückert Heleno assisted at various stages of this project. Catherine Beauchemin and Alice Parkes analyzed nutrient samples (except NH4 +) and assisted with field work logistics. Veronique Ducharme-Riel, Lisa Fauteux, François Guillemette, and Paul del Giorgio assisted with the membrane inlet mass spectrometer. Dr. Silvia E. Newell provided comments on earlier versions of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: David Philip Hamilton
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCarthy, M.J., Gardner, W.S., Lehmann, M.F. et al. Implications of water column ammonium uptake and regeneration for the nitrogen budget in temperate, eutrophic Missisquoi Bay, Lake Champlain (Canada/USA). Hydrobiologia 718, 173–188 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1614-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1614-6