Abstract
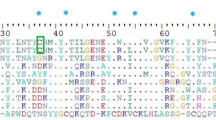
Inhibitor cystine knots (ICKs) are a family of structural peptides with a large number of cysteine residues that form intramolecular disulfide bonds, resulting in a knot. These peptides are involved in a variety of biological functions including predation and defense, and are found in various species, such as spiders, scorpions, sea anemones, and plants. The Loxosceles intermedia venom gland transcriptome identified five groups of ICK peptides that represent more than 50 % of toxin-coding transcripts. Here, we describe the molecular cloning of U2-Sicaritoxin-Lit2 (U2-SCRTX-Lit2), bioinformatic characterization, structure prediction, and molecular dynamic analysis. The sequence of U2-SCRTX-Lit2 obtained from the transcriptome is similar to that of μ-Hexatoxin-Mg2, a peptide that inhibits the insect Nav channel. Bioinformatic analysis of sequences classified as ICK family members also showed a conservation of cysteine residues among ICKs from different spiders, with the three dimensional molecular model of U2-SCRTX-Lit2 similar in structure to the hexatoxin from μ-hexatoxin-Mg2a. Molecular docking experiments showed the interaction of U2-SCRTX-Lit2 to its predictable target—the Spodoptera litura voltage-gated sodium channel (SlNaVSC). After 200 ns of molecular dynamic simulation, the final structure of the complex showed stability in agreement with the experimental data. The above analysis corroborates the existence of a peptide toxin with insecticidal activity from a novel ICK family in L. intermedia venom and demonstrates that this peptide targets Nav channels.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
King GF, Hardy MC (2013) Spider-venom peptides: structure, pharmacology, and potential for control of insect pests. Annu Rev Entomol 58:475–496
Vassilevski AA, Kozlov SA, Grishin EV (2009) Molecular diversity of spider venom. Biochem Biokhimiia 74:1505–1534
Jackson H, Parks TN (1989) Spider toxins: recent applications in neurobiology. Annu Rev Neurosci 12:405–414
Corzo G, Gilles N, Satake H, Villegas E, Dai L, Nakajima T, Haupt J (2003) Distinct primary structures of the major peptide toxins from the venom of the spider Macrothele gigas that bind to sites 3 and 4 in the sodium channel. FEBS Lett 547:43–50
Iyer S, Acharya KR (2011) Tying the knot: The cystine signature and molecular-recognition processes of the vascular endothelial growth factor family of angiogenic cytokines. FEBS J 278:4304–4322
Craik DJ, Daly NL, Waine C (2001) The cystine knot motif in toxins and implications for drug design. Toxicon 39:43–60
Werle M, Loretz B, Entstrasser D, Foger F (2007) Design and evaluation of a chitosan-aprotinin conjugate for the peroral delivery of therapeutic peptides and proteins susceptible to enzymatic degradation. J Drug Target 15:327–333
Werle M, Kolmar H, Albrecht R, Bernkop-Schnurch A (2008) Characterisation of the barrier caused by luminally secreted gastro-intestinal proteolytic enzymes for two novel cystine-knot microproteins. Amino Acids 35:195–200
Gracy JRM, Le-Nguyen D, Gelly J-C, Kaas Q, Heitz A, Chiche L (2007) The knottin or inhibitor cystine knot scaffold in. Nucleic Acids Res 36(2008):D314–D319
Gelly JC, Gracy JRM, Kaas Q, Le†Nguyen D, Heitz A, Chiche L (2004) The KNOTTIN website and database: a new information system dedicated to the knottin scaffold. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D156–D159
Pallaghy PK, Alewood D, Alewood PF, Norton RS (1997) Solution structure of robustoxin, the lethal neurotoxin from the funnel-web spider Atrax robustus. FEBS Lett 419:191–196
Wang CK, Kaas Q, Chiche L, Craik DJ (2008) CyBase: a database of cyclic protein sequences and structures, with applications in protein discovery and engineering. Nucleic Acids Res 36:D206–210
Mulvenna JP, Wang C, Craik DJ (2006) CyBase: a database of cyclic protein sequence and structure. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D192–194
Craik DJ, Swedberg JE, Mylne JS, Cemazar M (2012) Cyclotides as a basis for drug design. Expert Opin Drug Discovery 7:179–194
Chaim OM, Trevisan-Silva D, Chaves-Moreira D, Carolina AM, Valéria Pereira Ferrer W, Hitomi Matsubara F, Mangili OC, da Silveira RB, Luiza Helena G, Waldemiro G, Andrea S-R, Silvio Sanches V (2011) Brown spider (Loxosceles genus) venom toxins: tools for biological purposes. Toxins 3:309–344
de Castro CS, Silvestre FG, Araujo SC, de Gabriel MY, Mangili OC, Cruz I, Chavez-Olortegui C, Kalapothakis E (2004) Identification and molecular cloning of insecticidal toxins from the venom of the brown spider Loxosceles intermedia. Toxicon 44:273–280
King GF, Gentz MC, Escoubas P, Nicholson GM (2008) A rational nomenclature for naming peptide toxins from spiders and other venomous animals. Toxicon 52:264–276
Corzo G, Escoubas P, Stankiewicz M, Pelhate M, Kristensen CP, Nakajima T (2000) Isolation, synthesis and pharmacological characterization of δ-palutoxins IT, novel insecticidal toxins from the spider Paracoelotes luctuosus (Amaurobiidae). Eur J Biochem 267:5783–5795
Matsubara FH, Gremski LH, Meissner GO, Constantino Lopes ES, Gremski W, Senff-Ribeiro A, Chaim OM, Veiga SS (2013) A novel ICK peptide from the Loxosceles intermedia (brown spider) venom gland: Cloning, heterologous expression and immunological cross-reactivity approaches. Toxicon 71:147–158
Gremski LH, da Silveira RB, Chaim OM, Probst CM, Ferrer VP, Nowatzki J, Weinschutz HC, Madeira HM, Gremski W, Nader HB, Senff-Ribeiro A, Veiga SS (2010) A novel expression profile of the Loxosceles intermedia spider venomous gland revealed by transcriptome analysis. Mol Biosyst 6:2403–2416
Reinwarth M, Nasu D, Kolmar H, Avrutina O (2012) Chemical synthesis, backbone cyclization and oxidative folding of cystine-knot peptides: promising scaffolds for applications in drug design. Molecules 17:12533–12552
Feitosa L, Gremski W, Veiga SS, Elias MC, Graner E, Mangili OC, Brentani RR (1998) Detection and characterization of metalloproteinases with gelatinolytic, fibronectinolytic and fibrinogenolytic activities in brown spider (Loxosceles intermedia) venom. Toxicon 36:1039–1051
Artimo P, Jonnalagedda M, Arnold K, Baratin D, Csardi G, de Castro E, Duvaud S, Flegel V, Fortier A, Gasteiger E, Grosdidier A, Hernandez C, Ioannidis V, Kuznetsov D, Liechti R, Moretti S, Mostaguir K, Redaschi N, Rossier G, Xenarios I, Stockinger H (2012) ExPASy: SIB bioinformatics resource portal. Nucleic Acids Res 40:W597–603
Petersen TN, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H (2011) SignalP 4.0: discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat Methods 8:785–786
Wilkins MR, Gasteiger E, Bairoch A, Sanchez JC, Williams KL, Appel RD, Hochstrasser DF (1999) Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol Biol 112:531–552
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
N. Eswar, B Webb, MA Marti-Renom, MS. Madhusudhan, D. Eramian, MY. Shen, U Pieper, A Sali (2007) Comparative protein structure modeling using MODELLER. Curr Protoc Protein Sci Chapt 2:Unit 2.9. doi:10.1002/0471140864.ps0209s50
Shaya D, Findeisen F, Abderemane-Ali F, Arrigoni C, Wong S, Nurva SR, Loussouarn G, Minor DL Jr (2014) Structure of a prokaryotic sodium channel pore reveals essential gating elements and an outer ion binding site common to eukaryotic channels. J Mol Biol 426:467–483
Soding J, Biegert A, Lupas AN (2005) The HHpred interactive server for protein homology detection and structure prediction. Nucleic Acids Res 33:W244–248
Laskowski RA, Rullmannn JA, MacArthur MW, Kaptein R, Thornton JM (1996) AQUA and PROCHECK-NMR: programs for checking the quality of protein structures solved by NMR. J Biomol NMR 8:477–486
Van Der Spoel D, Lindahl E, Hess B, Groenhof G, Mark AE, Berendsen HJ (2005) GROMACS: fast, flexible, and free. J Comput Chem 26:1701–1718
Jo S, Lim JB, Klauda JB, Im W (2009) CHARMM-GUI Membrane Builder for mixed bilayers and its application to yeast membranes. Biophys J 97:50–58
Jo S, Kim T, Im W (2007) Automated builder and database of protein/membrane complexes for molecular dynamics simulations. PLoS ONE 2, e880
Jo S, Kim T, Iyer VG, Im W (2008) CHARMM-GUI: a web-based graphical user interface for CHARMM. J Comput Chem 29:1859–1865
Jorgensen WL, Chandrasekhar J, Madura JD, Impey RW, Klein ML (1983) Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J Chem Phys 79:926–935
Brooks BR, Brooks CL 3rd, Mackerell AD Jr, Nilsson L, Petrella RJ, Roux B, Won Y, Archontis G, Bartels C, Boresch S, Caflisch A, Caves L, Cui Q, Dinner AR, Feig M, Fischer S, Gao J, Hodoscek M, Im W, Kuczera K, Lazaridis T, Ma J, Ovchinnikov V, Paci E, Pastor RW, Post CB, Pu JZ, Schaefer M, Tidor B, Venable RM, Woodcock HL, Wu X, Yang W, York DM, Karplus M (2009) CHARMM: the biomolecular simulation program. J Comput Chem 30:1545–1614
Buck M, Bouguet-Bonnet S, Pastor RW, MacKerell AD Jr (2006) Importance of the CMAP correction to the CHARMM22 protein force field: dynamics of hen lysozyme. Biophys J 90:L36–38
Floquet N, Durand P, Maigret B, Badet B, Badet-Denisot MA, Perahia D (2009) Collective motions in glucosamine-6-phosphate synthase: influence of ligand binding and role in ammonia channelling and opening of the fructose-6-phosphate binding site. J Mol Biol 385:653–664
Louet M, Perahia D, Martinez J, Floquet N (2011) A concerted mechanism for opening the GDP binding pocket and release of the nucleotide in hetero-trimeric G-proteins. J Mol Biol 411:298–312
Philot EA, Perahia D, Braz AS, Costa MG, Scott LP (2013) Binding sites and hydrophobic pockets in Human Thioredoxin 1 determined by normal mode analysis. J Struct Biol 184:293–300
Batista PR, Pandey G, Pascutti PG, Bisch PM, Perahia D, Robert CH (2011) Free energy profiles along consensus normal modes provide insight into HIV-1 protease flap opening. J Chem Theory Comput 7:2348–2352
Louet M, Karakas E, Perret A, Perahia D, Martinez J, Floquet N (2013) Conformational restriction of G-proteins Coupled Receptors (GPCRs) upon complexation to G-proteins: a putative activation mode of GPCRs? FEBS Lett 587:2656–2661
Ritchie DW, Venkatraman V (2010) Ultra-fast FFT protein docking on graphics processors. Bioinformatics 26:2398–2405
Ritchie DW (2008) Recent progress and future directions in protein-protein docking. Curr Protein Pept Sci 9:1–15
Durrant JD, McCammon JA (2011) BINANA: a novel algorithm for ligand-binding characterization. J Mol Graphics Model 29:888–893
Nicholson GM (2007) Insect-selective spider toxins targeting voltage-gated sodium channels. Toxicon 49:490–512
Nicholson GM, Little MJ, Birinyi-Strachan LC (2004) Structure and function of d-atracotoxins: lethal neurotoxins targeting the voltage-gated sodium channel. Toxicon 43:587–599
Nicholson GM, Blanche T, Mansfield K, Tran Y (2002) Differential blockade of neuronal voltage-gated Na(+) and K(+) channels by antidepressant drugs. Eur J Pharmacol 452:35–48
Liang S (2004) An overview of peptide toxins from the venom of the Chinese bird spider Selenocosmia huwena Wang [=Ornithoctonus huwena (Wang)]. Toxicon 43:575–585
Liang SP, Pan X (1995) A lectin-like peptide isolated from the venom of the Chinese bird spider Selenocosmia huwena. Toxicon 33:875–882
King GF, Tedford HW, Maggio F (2002) Structure and function of insecticidal neurotoxins from Australian funnel-web spiders. Toxin Rev 21:361–389
Li D, Xiao Y, Xu X, Xiong X, Lu S, Liu Z, Zhu Q, Wang M, Gu X, Liang S (2004) Structure--activity relationships of hainantoxin-IV and structure determination of active and inactive sodium channel blockers. J Biol Chem 279:37734–37740
Yamaji N, Little MJ, Nishio H, Billen B, Villegas E, Nishiuchi Y, Tytgat J, Nicholson GM, Corzo G (2009) Synthesis, solution structure, and phylum selectivity of a spider delta-toxin that slows inactivation of specific voltage-gated sodium channel subtypes. J Biol Chem 284:24568–24582
O.M. Chaim (2005) Estudo da atividade citotóxica da proteína dermonecrótica do veneno de aranha-marrom (Loxosceles intermedia) com enfase no efeito nefrotóxico
Appel MH, da Silveira RB, Chaim OM, Paludo KS, Silva DT, Chaves DM, da Silva PH, Mangili OC, Senff-Ribeiro A, Gremski W, Nader HB, Veiga SS (2008) Identification, cloning and functional characterization of a novel dermonecrotic toxin (phospholipase D) from brown spider (Loxosceles intermedia) venom. Biochim Biophys Acta 1780:167–178
Moore SR, Cochran JR, Wittrup KD, Gregory LV (2012) Engineering knottins as novel binding agents. . Methods Enzymol 503:223–251
Richardson M, Pimenta AMC, Bemquerer MP, Santoro MM, Beirao PSL, Lima ME, Figueiredo SG, Bloch C Jr, Vasconcelos EAR, Campos FAP, Gomes PC, Cordeiro MN (2006) Comparison of the partial proteomes of the venoms of Brazilian spiders of the genus Phoneutria. Comp Biochem Physiol C: Toxicol Pharmacol 142:173–187
Liu Z, Yu Z, Liu N, Zhao C, Hu J, Dai Q (2010) cDNA cloning of conotoxins with framework XII from several Conus species. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 42:656–661
Liu Z,Li H, Liu N, Wu C, Jiang J, Yue J, Jing Y, Dai Q (2012) Diversity and evolution of conotoxins in Conus virgo, Conus eburneus, Conus imperialis and Conus marmoreus from the South China Sea. Toxicon 60:982–989
Kalapothakis E, Penaforte CL, Leao RM, Cruz JS, Prado VF, Cordeiro MN, Diniz CR, Romano-Silva MA, Prado MA, Gomez MV, Beirao PS (1998) Cloning, cDNA sequence analysis and patch clamp studies of a toxin from the venom of the armed spider (Phoneutria nigriventer). Toxicon 36:1971–1980
Kozlov SA, Grishin EV (2007) The universal algorithm of maturation for secretory and excretory protein precursors. Toxicon 49:721–726
Sollod BL, Wilson D, Zhaxybayeva O, Gogarten JP, Drinkwater R, King GF (2005) Were arachnids the first to use combinatorial peptide libraries? Peptides 26:131–139
Escoubas P, Sollod B, King GF (2006) Venom landscapes: mining the complexity of spider venoms via a combined cDNA and mass spectrometric approach. Toxicon 47:650–663
Branton WD, Kolton L, Jan YN, Jan LY (1987) Neurotoxins from Plectreurys spider venom are potent presynaptic blockers in Drosophila. J Neurosci : Off J Soc Neurosci 7:4195–4200
Sermadiras I, Revell J, Linley JE, Sandercock A, Ravn P (2013) Recombinant expression and in vitro characterisation of active Huwentoxin-IV. PLoS ONE 8: e83202
Windley MJ, Herzig V, Dziemborowicz SAA, Hardy MC, King GF, Nicholson GM (2012) Spider-venom peptides as bioinsecticides. Toxins 4:191–227
Wang X-h, Connor M, Smith R, Maciejewski MW, Howden MEH, Nicholson GM, Christie MJ, King GF (2000) Discovery and characterization of a family of insecticidal neurotoxins with a rare vicinal disulfide bridge. Nat Struct Mol Biol 7:505–513
Wen S, Wilson DT, Kuruppu S, Korsinczky ML, Hedrick J, Pang L, Szeto T, Hodgson WC, Alewood PF, Nicholson GM (2005) Discovery of an MIT-like atracotoxin family: spider venom peptides that share sequence homology but not pharmacological properties with AVIT family proteins. Peptides 26:2412–2426
Liang PH, Ko TP, Wang AH (2002) Structure, mechanism and function of prenyltransferases. Eur J Biochem 269:3339–3354
Villegas E, Adachi-Akahane S, Bosmans F, Tytgat J, Nakajima T, Corzo G (2008) Biochemical characterization of cysteine-rich peptides from Oxyopes sp. venom that block calcium ion channels. Toxicon 52:228–236
Wang P, Liao Z, Guo L, Li W, Chen M, Pi Y, Gong Y, Sun X, Tang K (2004) Cloning and functional analysis of a cDNA encoding Ginkgo biloba farnesyl diphosphate synthase. Mol Cells 18:150–156
McNulty JC, Jackson PJ, Thompson DA, Chai B, Gantz I, Barsh GS, Dawson PE, Millhauser GL (2005) Structures of the agouti signaling protein. J Mol Biol 346:1059–1070
Undheim EAB, Grimm LL, Low C-F, Morgenstern D, Herzig V, Zobel-Thropp P, Pineda SS, Habib R, Dziemborowicz S, Fry BG, Nicholson GM, Binford GJ, Mobli M, King GF (2015) Weaponization of a hormone: convergent recruitment of hyperglycemic hormone into the venom of arthropod predators. Structure 23:1283–1292
Rinkevich FD, Du Y, Dong K (2013) Diversity and convergence of sodium channel mutations involved in resistance to pyrethroids. Pestic Biochem Physiol 106:93–100
Tedford HW, Steinbaugh BA, Bao L, Tait BD, Tempczyk-Russell A, Smith W, Benzon GL, Finkenbinder CA, Kennedy RM (2013) In silico screening for compounds that match the pharmacophore of omega-hexatoxin-Hv1a leads to discovery and optimization of a novel class of insecticides. Pestic Biochem Physiol 106:124–140
Xu D, Tsai CJ, Nussinov R (1997) Hydrogen bonds and salt bridges across protein-protein interfaces. Protein Eng 10:999–1012
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by grants from CNPq, CAPES, Fundação Araucária-Paraná, UFABC, FAPESP. And Secretaria de Tecnologia e Ensino Superior do Paraná, SETI-PR, Brasil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Highlights
• The importance of cysteine residue conservation among knottin peptide.
• Bioinformatic characterization of an ICK peptide from L. intermedia venom.
• Toxin and channel structure predictions and dynamic interactions.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meissner, G.O., de Resende Lara, P.T., Scott, L.P.B. et al. Molecular cloning and in silico characterization of knottin peptide, U2-SCRTX-Lit2, from brown spider (Loxosceles intermedia) venom glands. J Mol Model 22, 196 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-016-3067-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-016-3067-0