Abstract
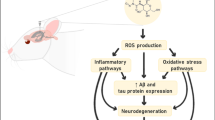
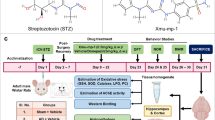
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disease. However, effective drugs for this disease have not yet been developed. The analysis of big data indicated that childhood herpes virus infection may be associated with the incidence of AD, suggesting that anti-herpetic drugs, such as acyclovir, may have preventive and suppressive effects in AD therapy. Moreover, short-term use of dexamethasone (DXMT), a clinical used synthetic corticosteroid, could effectively inhibit AD-related neuroinflammation. In this study, we have found that the combination of acyclovir and DXMT, but not acyclovir or DXMT alone, could protect against AD causing β-amyloid (Aβ) oligomer-induced spatial cognitive impairments. Moreover, acyclovir and DXMT could prevent Aβ oligomer-induced over-activation of microglia and astrocytes, and over-expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, indicating that anti-AD effects of drug combination might be at least partially via neuroinflammation inhibition and immunomodulation. Furthermore, Aβ oligomer-induced decrease of PSD-95 and increase of pTau expression was prevented by the combination of acyclovir and DXMT, suggesting the involvement of synaptic protective effects of the drug combination. Taken together, our studies indicated that the combination of acyclovir and DXMT might be an alternative therapy for the treatment of AD.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Aβ:
-
β-amyloid
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- DXMT:
-
Dexamethasone
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- HFIP:
-
1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-propanol
- ICR:
-
Institute of Cancer Research
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- i.g. :
-
Intragastric
- i.p.:
-
Intraperitoneal
- OD:
-
Optical density
References
Anderson G, Ojala JO (2010) Alzheimer's and seizures: interleukin-18, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and quinolinic acid. International Journal of Tryptophan Research 3. https://doi.org/10.4137/S4603
Chen ZH, Hua Q, Shu ZR, Zhao YY, Kai MA, Wang TT, Yi-Feng XU (2012) Effect of dexamethasone and acyclovir on prognosis and expression of IL-2 in mice with herpes simplex virus encephalitis. Journal of Clinical Pediatrics
Crossin KL, Tai MH, Krushel LA, Mauro VP, Edelman GM (1997) Glucocorticoid receptor pathways are involved in the inhibition of astrocyte proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:2687–2692
Cruz-Topete D, Cidlowski JA (2015) One hormone, two actions: anti- and pro-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids. Neuroimmunomodulation 22:20–32. https://doi.org/10.1159/000362724
Deng Y et al (2014) Astrocyte-derived proinflammatory cytokines induce hypomyelination in the periventricular white matter in the hypoxic neonatal brain. PLoS One 9:e87420
Ding Z, Mathur V, Ho PP, James ML, Lucin KM, Hoehne A, Alabsi H, Gambhir SS, Steinman L, Luo J, Wyss-Coray T (2014) Antiviral drug ganciclovir is a potent inhibitor of microglial proliferation and neuroinflammation. J Exp Med 211:189–198. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20120696
Golub MS, Kalkum M, Hong T, Cantin EM, Ramakrishna C, Chiang A (2017) Effects of acyclovir and IVIG on behavioral outcomes after HSV1 CNS infection. Behavioural Neurology, 2017, (2017-11-19) 2017:1-14
Gu K, Zhao JD, Ren ZG, Ma NY, Lai ST, Wang J, Liu J, Jiang GL (2011) A natural process of cirrhosis resolution and deceleration of liver regeneration after thioacetamide withdrawal in a rat model. Mol Biol Rep 38:1687–1696
Hailer NP, Glomsda B, Blaheta RA (2001) Astrocytic factors down-regulate the expression of major histocompatibility complex-class-II and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 on human monocytes. Neurosci Lett 298:33–36
Harris SA, Harris EA (2018) Molecular mechanisms for herpes simplex virus type 1 pathogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci 10:48. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2018.00048
Huang L et al (2016) Sunitinib, a clinically used anti-cancer drug, is a potent AChE inhibitor and attenuates cognitive impairments in mice. ACS Chem Neurosci 7:1047
Itzhaki RF (2014a) Herpes simplex virus type 1 and Alzheimer’s disease: increasing evidence for a major role of the virus. Front Aging Neurosci 6:202
Itzhaki RF (2014b) Herpes simplex virus type 1 and Alzheimer’s disease: increasing evidence for a major role of the virus. Front Aging Neurosci 6:202
Joshi YB, Chu J, Pratico D (2012) Stress hormone leads to memory deficits and altered tau phosphorylation in a model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 31:167–176. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-2012-120328
Kim HY, Lee DK, Chung BR, Kim HV, Kim Y (2016) Intracerebroventricular injection of amyloid-beta peptides in normal mice to acutely induce Alzheimer-like cognitive deficits. J Vis Exp. https://doi.org/10.3791/53308
Kozai TDY, Jaquins-Gerstl AS, Vazquez AL, Michael AC, Cui XT (2016) Dexamethasone retrodialysis attenuates microglial response to implanted probes in vivo. Biomaterials 87:157–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.02.013
Lawson LJ, Perry VH, Dri P, ., Gordon S, . (1990) Heterogeneity in the distribution and morphology of microglia in the normal adult mouse brain. Neuroscience 39:151–170
Li L, Ma P, Wei J, Qian K, Tao L (2013) LC-ESI-MS method for the determination of dexamethasone acetate in skin of nude mouse. Journal of Chromatography B Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical & Life Sciences 933:44–49
Lin J et al (2017) Fucoxanthin, a marine carotenoid, attenuates β-amyloid oligomer-induced neurotoxicity possibly via regulating the PI3K/Akt and the ERK pathways in SH-SY5Y cells. Oxidative Medicine & Cellular Longevity 2017:6792543
Lu H, Han YJ, Xu JD, Xing WM, Chen J (2014) Proteomic characterization of acyclovir-induced nephrotoxicity in a mouse model. PLoS One 9:e103185. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0103185
Lundberg P, Openshaw H, Wang M, Yang HJ, Cantin E (2007) Effects of CXCR3 signaling on development of fatal encephalitis and corneal and periocular skin disease in HSV-infected mice are mouse-strain dependent. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 48:4162–4170. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.07-0261
Müller AC, Santy D (2008) Acyclovir inhibits rat liver tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase and induces a concomitant rise in brain serotonin and 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid levels. Metab Brain Dis 23:351–360
Rogers JT et al. (2017) Subacute ibuprofen treatment rescues the synaptic and cognitive deficits in advanced-aged mice neurobiology of aging 53:112-121
Seedat A, Winnett G (2012) Acyclovir-induced acute renal failure and the importance of an expanding waist line. BMJ Case Rep. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2012-006264
Shao CY, Mirra SS, Sait HB, Sacktor TC, Sigurdsson EM (2011) Postsynaptic degeneration as revealed by PSD-95 reduction occurs after advanced Abeta and tau pathology in transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 122:285–292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-011-0843-x
Sjostrom PJ, Rancz EA, Roth A, Hausser M (2008) Dendritic excitability and synaptic plasticity. Physiol Rev 88:769–840. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00016.2007
Solito E, Sastre M (2012) Microglia function in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Pharmacol 3:14
Sushmita C et al (2013) Quantitative immunohistochemical analysis reveals association between sodium iodide symporter and estrogen receptor expression in breast cancer. PLoS One 8:e54055
Vyas S, Rodrigues AJ, Silva JM, Tronche F, Almeida OF, Sousa N, Sotiropoulos I (2016) Chronic stress and glucocorticoids: from neuronal plasticity to Neurodegeneration. Neural Plast 2016:6391686. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6391686
Wozniak MA, Frost AL, Preston CM, Itzhaki RF (2011) Antivirals reduce the formation of key Alzheimer's disease molecules in cell cultures acutely infected with herpes simplex virus type 1. PLoS One 6:e25152
Wu X et al (2017) Curcumin attenuates surgery-induced cognitive dysfunction in aged mice. Metab Brain Dis 32:1–10
Yu J, Lin JJ, Yu R, He S, Wang QW, Cui W, Zhang JR (2017) Fucoxanthin prevents H2O2-induced neuronal apoptosis via concurrently activating the PI3-K/Akt cascade and inhibiting the ERK pathway. Food Nutr Res 61:1304678
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81870853), Ningbo Sci and Tech Project for Common Wealth (2017C50042), Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Pathophysiology (201804), Ningbo Municipal Innovation Team of Life Science and Health (2015C110026), LiDakSum Marine Biopharmaceutical Development Fund, and the K. C. Wong Magna Fund in Ningbo University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare there is no financial conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hui, Z., Zhijun, Y., Yushan, Y. et al. The combination of acyclovir and dexamethasone protects against Alzheimer’s disease-related cognitive impairments in mice. Psychopharmacology 237, 1851–1860 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-020-05503-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-020-05503-1