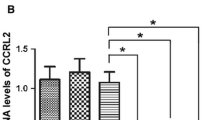
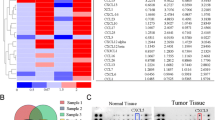
Abstract
Although metastasis accounts for >90% of cancer-related deaths, no therapeutic that targets this process has yet been approved. Because the chemokine receptor CXCR4 is one of the targets closely linked with tumor metastasis, inhibitors of this receptor have the potential to abrogate metastasis. In the current report, we demonstrate that celastrol can downregulate the CXCR4 expression on breast cancer MCF-7 cells stably transfected with HER2, an oncogene known to induce the chemokine receptor. Downregulation of CXCR4 by the triterpenoid was not cell type-specific as downregulation occurred in colon cancer, squamous cell carcinoma, and pancreatic cancer cells. Decrease in CXCR4 expression was not due to proteolysis as neither proteasome inhibitors nor lysosomal stabilization had any effect. Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction analysis revealed that downregulation of CXCR4 messenger RNA (mRNA) by celastrol occurred at the translational level. Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis revealed regulation at the transcriptional level as well. Abrogation of the chemokine receptor by celastrol or by gene-silencing was accompanied by suppression of invasiveness of colon cancer cells induced by CXCL12, the ligand for CXCR4. This effect was not cell type-specific as celastrol also abolished invasiveness of pancreatic tumor cells, and this effect again correlated with the disappearance of both the CXCR4 mRNA and CXCR4 protein. Other triterpenes, such as withaferin A and gedunin, which are known to inhibit Hsp90, did not downregulate CXCR4 expression, indicating that the effects were specific to celastrol. Overall, these results show that celastrol has potential in suppressing invasion and metastasis of cancer cells by down-modulation of CXCR4 expression.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wong DJ, Liu H, Ridky TW, Cassarino D, Segal E, Chang HY (2008) Module map of stem cell genes guides creation of epithelial cancer stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2:333–344
Orosz P, Echtenacher B, Falk W, Ruschoff J, Weber D, Mannel DN (1993) Enhancement of experimental metastasis by tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med 177:1391–1398
Leivonen SK, Kahari VM (2007) Transforming growth factor-beta signaling in cancer invasion and metastasis. Int J Cancer 121:2119–2124
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2000) Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 407:249–257
Muller A, Homey B, Soto H, Ge N, Catron D, Buchanan ME, McClanahan T, Murphy E, Yuan W, Wagner SN, Barrera JL, Mohar A, Verastegui E, Zlotnik A (2001) Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis. Nature 410:50–56
Xu L, Duda DG, di Tomaso E, Ancukiewicz M, Chung DC, Lauwers GY, Samuel R, Shellito P, Czito BG, Lin PC, Poleski M, Bentley R, Clark JW, Willett CG, Jain RK (2009) Direct evidence that bevacizumab, an anti-VEGF antibody, up-regulates SDF1alpha, CXCR4, CXCL6, and neuropilin 1 in tumors from patients with rectal cancer. Cancer Res 69:7905–7910
Paez-Ribes M, Allen E, Hudock J, Takeda T, Okuyama H, Vinals F, Inoue M, Bergers G, Hanahan D, Casanovas O (2009) Antiangiogenic therapy elicits malignant progression of tumors to increased local invasion and distant metastasis. Cancer Cell 15:220–231
Porcile C, Bajetto A, Barbero S, Pirani P, Schettini G (2004) CXCR4 activation induces epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation in an ovarian cancer cell line. Ann NY Acad Sci 1030:162–169
Zeelenberg IS, Ruuls-Van Stalle L, Roos E (2003) The chemokine receptor CXCR4 is required for outgrowth of colon carcinoma micrometastases. Cancer Res 63:3833–3839
Marchesi F, Monti P, Leone BE, Zerbi A, Vecchi A, Piemonti L, Mantovani A, Allavena P (2004) Increased survival, proliferation, and migration in metastatic human pancreatic tumor cells expressing functional CXCR4. Cancer Res 64:8420–8427
Taichman RS, Cooper C, Keller ET, Pienta KJ, Taichman NS, McCauley LK (2002) Use of the stromal cell-derived factor-1/CXCR4 pathway in prostate cancer metastasis to bone. Cancer Res 62:1832–1837
Li YM, Pan Y, Wei Y, Cheng X, Zhou BP, Tan M, Zhou X, Xia W, Hortobagyi GN, Yu D, Hung MC (2004) Upregulation of CXCR4 is essential for HER2-mediated tumor metastasis. Cancer Cell 6:459–469
Holm NT, Byrnes K, Li BD, Turnage RH, Abreo F, Mathis JM, Chu QD (2007) Elevated levels of chemokine receptor CXCR4 in HER-2 negative breast cancer specimens predict recurrence. J Surg Res 141:53–59
Calixto JB, Campos MM, Otuki MF, Santos AR (2004) Anti-inflammatory compounds of plant origin. Part II. Modulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines and adhesion molecules. Planta Med 70:93–103
Yang H, Chen D, Cui QC, Yuan X, Dou QP (2006) Celastrol, a triterpene extracted from the Chinese “Thunder of God Vine,” is a potent proteasome inhibitor and suppresses human prostate cancer growth in nude mice. Cancer Res 66:4758–4765
Hieronymus H, Lamb J, Ross KN, Peng XP, Clement C, Rodina A, Nieto M, Du J, Stegmaier K, Raj SM, Maloney KN, Clardy J, Hahn WC, Chiosis G, Golub TR (2006) Gene expression signature-based chemical genomic prediction identifies a novel class of HSP90 pathway modulators. Cancer Cell 10:321–330
Hassane DC, Guzman ML, Corbett C, Li X, Abboud R, Young F, Liesveld JL, Carroll M, Jordan CT (2008) Discovery of agents that eradicate leukemia stem cells using an in silico screen of public gene expression data. Blood 111:5654–5662
He W, Huang FC, Gavai A, Chan WK, Amato G, Yu KT, Zilberstein A (1998) Novel cytokine release inhibitors. Part III: truncated analogs of tripterine. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 8:3659–3664
Westerheide SD, Bosman JD, Mbadugha BN, Kawahara TL, Matsumoto G, Kim S, Gu W, Devlin JP, Silverman RB, Morimoto RI (2004) Celastrols as inducers of the heat shock response and cytoprotection. J Biol Chem 279:56053–56060
Zhang T, Li Y, Yu Y, Zou P, Jiang Y, Sun D (2009) Characterization of celastrol to inhibit hsp90 and cdc37 interaction. J Biol Chem 284:35381–35389
Sreeramulu S, Gande SL, Gobel M, Schwalbe H (2009) Molecular mechanism of inhibition of the human protein complex Hsp90-Cdc37, a kinome chaperone-cochaperone, by triterpene celastrol. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 48:5853–5855
Chadli A, Felts SJ, Wang Q, Sullivan WP, Botuyan MV, Fauq A, Ramirez-Alvarado M, Mer G (2010) Celastrol inhibits Hsp90 chaperoning of steroid receptors by inducing fibrillization of the co-chaperone p23. J Biol Chem 285:4224–4231
Mu TW, Ong DS, Wang YJ, Balch WE, Yates JR 3rd, Segatori L, Kelly JW (2008) Chemical and biological approaches synergize to ameliorate protein-folding diseases. Cell 134:769–781
Marchese A, Raiborg C, Santini F, Keen JH, Stenmark H, Benovic JL (2003) The E3 ubiquitin ligase AIP4 mediates ubiquitination and sorting of the G protein-coupled receptor CXCR4. Dev Cell 5:709–722
Peters AH, Kubicek S, Mechtler K, O'Sullivan RJ, Derijck AA, Perez-Burgos L, Kohlmaier A, Opravil S, Tachibana M, Shinkai Y, Martens JH, Jenuwein T (2003) Partitioning and plasticity of repressive histone methylation states in mammalian chromatin. Mol Cell 12:1577–1589
Maroni P, Bendinelli P, Matteucci E, Desiderio MA (2007) HGF induces CXCR4 and CXCL12-mediated tumor invasion through Ets1 and NF-kappaB. Carcinogenesis 28:267–279
Bhandari D, Trejo J, Benovic JL, Marchese A (2007) Arrestin-2 interacts with the ubiquitin-protein isopeptide ligase atrophin-interacting protein 4 and mediates endosomal sorting of the chemokine receptor CXCR4. J Biol Chem 282:36971–36979
Sethi G, Ahn KS, Pandey MK, Aggarwal BB (2007) Celastrol, a novel triterpene, potentiates TNF-induced apoptosis and suppresses invasion of tumor cells by inhibiting NF-kappaB-regulated gene products and TAK1-mediated NF-kappaB activation. Blood 109:2727–2735
Idris AI, Libouban H, Nyangoga H, Landao-Bassonga E, Chappard D, Ralston SH (2009) Pharmacologic inhibitors of IkappaB kinase suppress growth and migration of mammary carcinosarcoma cells in vitro and prevent osteolytic bone metastasis in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther 8:2339–2347
Lee JH, Koo TH, Yoon H, Jung HS, Jin HZ, Lee K, Hong YS, Lee JJ (2006) Inhibition of NF-kappa B activation through targeting I kappa B kinase by celastrol, a quinone methide triterpenoid. Biochem Pharmacol 72:1311–1321
Biswas DK, Iglehart JD (2006) Linkage between EGFR family receptors and nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) signaling in breast cancer. J Cell Physiol 209:645–652
Matsusue R, Kubo H, Hisamori S, Okoshi K, Takagi H, Hida K, Nakano K, Itami A, Kawada K, Nagayama S, Sakai Y (2009) Hepatic stellate cells promote liver metastasis of colon cancer cells by the action of SDF-1/CXCR4 axis. Ann Surg Oncol 16:2645–2653
Kulbe H, Hagemann T, Szlosarek PW, Balkwill FR, Wilson JL (2005) The inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor-alpha regulates chemokine receptor expression on ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res 65:10355–10362
Bachelder RE, Wendt MA, Mercurio AM (2002) Vascular endothelial growth factor promotes breast carcinoma invasion in an autocrine manner by regulating the chemokine receptor CXCR4. Cancer Res 62:7203–7206
Kukreja P, Abdel-Mageed AB, Mondal D, Liu K, Agrawal KC (2005) Up-regulation of CXCR4 expression in PC-3 cells by stromal-derived factor-1alpha (CXCL12) increases endothelial adhesion and transendothelial migration: role of MEK/ERK signaling pathway-dependent NF-kappaB activation. Cancer Res 65:9891–9898
Marchese A, Benovic JL (2001) Agonist-promoted ubiquitination of the G protein-coupled receptor CXCR4 mediates lysosomal sorting. J Biol Chem 276:45509–45512
Helbig G, Christopherson KW 2nd, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Kumar S, Kishimoto H, Miller KD, Broxmeyer HE, Nakshatri H (2003) NF-kappaB promotes breast cancer cell migration and metastasis by inducing the expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR4. J Biol Chem 278:21631–21638
Cabioglu N, Sahin A, Doucet M, Yavuz E, Igci A, OY E, Aktas E, Bilgic S, Kiran B, Deniz G, Price JE (2005) Chemokine receptor CXCR4 expression in breast cancer as a potential predictive marker of isolated tumor cells in bone marrow. Clin Exp Metastasis 22:39–46
Salminen A, Lehtonen M, Paimela T, Kaarniranta K (2010) Celastrol: molecular targets of Thunder God Vine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 394:439–442
Nagase M, Oto J, Sugiyama S, Yube K, Takaishi Y, Sakato N (2003) Apoptosis induction in HL-60 cells and inhibition of topoisomerase II by triterpene celastrol. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 67:1883–1887
Zhang DH, Marconi A, Xu LM, Yang CX, Sun GW, Feng XL, Ling CQ, Qin WZ, Uzan G, d'Alessio P (2006) Tripterine inhibits the expression of adhesion molecules in activated endothelial cells. J Leukoc Biol 80:309–319
Pang X, Yi Z, Zhang J, Lu B, Sung B, Qu W, Aggarwal BB, Liu M (2010) Celastrol suppresses angiogenesis-mediated tumor growth through inhibition of AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. Cancer Res 70:1951–1959
Acknowledgement
Dr. Aggarwal is the Ransom Horne, Jr., Professor of Cancer Research. This work was supported by a program project grant from National Institutes of Health (NIH CA-124787-01A2) and a grant from Clayton Foundation for Research, USA. We would like to thank Dr. J. L. Benovic, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA and Dr. M.C. Hung, Department of Molecular and Cellular Oncology, MD Anderson Cancer Center for HA-CXCR4 plasmid constructs and also Mr. Walter Pagel for his careful reading of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00109-012-0987-8.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, V.R., Sung, B., Prasad, S. et al. Celastrol suppresses invasion of colon and pancreatic cancer cells through the downregulation of expression of CXCR4 chemokine receptor. J Mol Med 88, 1243–1253 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-010-0669-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-010-0669-3