Abstract
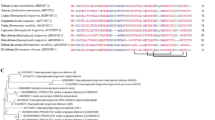
Defensins are a major family of antimicrobial peptides found throughout the phylogenetic tree. From the spider species: Cupiennius salei, Phoneutria reidyi, Polybetes pythagoricus, Tegenaria atrica, and Meta menardi, defensins belonging to the ‘ancestral’ class of invertebrate defensins were cloned and sequenced. The deduced amino acid sequences contain the characteristic six cysteines of this class of defensins and reveal precursors of 60 or 61 amino acid residues. The mature peptides consist of 37 amino acid residues, showing up to 70% identities with tick and scorpion defensins. In C. salei, defensin mRNA was found to be constitutively expressed in hemocytes, ovaries, subesophageal nerve mass, hepatopancreas, and muscle tissue. This is the first report presenting and comparing antimicrobial peptides belonging to the family of defensins from spiders.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiravanichpaisal P, Lee BL, Söderhäll K (2006) Cell-mediated immunity in arthropods: hematopoiesis, coagulation, melanization and opsonization. Immunobiology 211:213–236
Hoffmann JA, Kafatos FC, Janeway CA, Ezekowitz RA (1999) Phylogenetic perspectives in innate immunity. Science 284:1313–1318
Bulet P, Stöcklin R, Menin L (2004) Anti-microbial peptides: from invertebrates to vertebrates. Immunol Rev 198:169–184
Hwang PM, Zhou N, Shan X, Arrowsmith CH, Vogel HJ (1998) Three-dimensional solution structure of lactoferricin B, an antimicrobial peptide derived from bovine lactoferrin. Biochemistry 37:4288–4298
Patel SU, Osborn R, Rees S, Thornton JM (1998) Structural studies of Impatiens balsamina antimicrobial protein (Ib-AMP1). Biochemistry 37:983–990
Froy O, Gurevitz M (2003) Arthropod and mollusk defensins-evolution by exon-shuffling. Trends Genet 19:684–687
Rodríguez de la Vega RC, Possani LD (2005) On the evolution of invertebrate defensins. Trends Genet 21:330–332
Wong JA, Xia L, Ng TB (2007) A review of defensins of diverse origins. Curr Prot Pept Sci 5:446–459
Cornet B, Bonmatin JM, Hetru C, Hoffmann JA, Ptak M, Vovelle F (1995) Refined three-dimensional solution structure of insect defensin A. Structure 3:435–448
Hanzawa H, Shimada I, Kuzuhara T, Komano H, Kohda D, Inagaki F, Natori S, Arata Y (1990) 1H nuclear magnetic resonance study of the solution conformation of an antibacterial protein, sapecin. FEBS Lett 269:413–420
Yang YS, Mitta G, Chavanieu A, Calas B, Sanchez JF, Roch P, Aumelas A (2000) Solution structure and activity of the synthetic four-disulfide bond Mediterranean mussel defensin (MGD-1). Biochemistry 39:14436–14447
Mygind PH, Fischer RL, Schnorr KM, Hansen MT, Sonksen CP, Ludvigsen S, Raventos D, Buskov S, Christensen B, De Maria L, Taboureau O, Yaver D, Elvig-Jorgensen SG, Sorensen MV, Christensen BE, Kjaerulff S, Frimodt-Moller N, Lehrer RI, Zasloff M, Kristensen HH (2005) Plectasin is a peptide antibiotic with therapeutic potential from a saprophytic fungus. Nature 437:975–980
Mandard N, Bulet P, Caille A, Daffre S, Vovelle F (2002) The solution structure of gomesin, an antimicrobial cysteine-rich peptide from the spider. Eur J Biochem 269:1190–1198
Silva PI Jr, Daffre S, Bulet P (2000) Isolation and characterization of gomesin, an 18-residue cysteine-rich defense peptide from the spider Acanthoscurria gomesiana hemocytes with sequence similarities to horseshoe crab antimicrobial peptides of the tachyplesin family. J Biol Chem 275:33464–33470
Lorenzini DM, da Silva PI, Fogaça AC Jr, Bulet P, Daffre S (2003) Acanthoscurrin: a novel glycine-rich antimicrobial peptide constitutively expressed in the hemocytes of the spider Acanthoscurria gomesiana. Dev Comp Immunol 27:781–791
Bachère E, Gueguen Y, Gonzalez M, de Lorgeril J, Garnier J, Romestand B (2004) Insights into the anti-microbial defense of marine invertebrates: the penaeid shrimps and the oyster Crassostrea gigas. Immunol Rev 198:149–168
Mitta G, Vandenbulcke F, Noel T, Romestand B, Beauvillain JC, Salzet M, Roch P (2000) Differential distribution and defence involvement of antimicrobial peptides in mussel. J Cell Sci 113:2759–2769
Shigenaga T, Muta T, Toh Y, Tokunaga F, Iwanaga S (1990) Antimicrobial tachyplesin peptide precursor. cDNA cloning and cellular localization in the horseshoe crab (Tachypleus tridentatus). J Biol Chem 265:21350–21354
Gillespie JP, Kanost MR, Trenczek T (1997) Biological mediators of insect immunity. Annu Rev Entomol 42:611–643
Hoffmann JA, Reichhart JM (2002) Drosophila innate immunity: an evolutionary perspective. Nat Immunol 3:121–126
Söderhäll K, Smith VJ (1983) Separation of the haemocyte populations of Carcinus maenas and other marine decapods, and prophenoloxidase distribution. Dev Comp Immunol 7:229–239
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, von Heijne G, Brunak S (2004) Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J Mol Biol 340:783–795
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Jones DT, Taylor WR, Thornton JM (1992) The rapid generation of mutation data matrices from protein sequences. Comput Appl Biosci 8:275–282
Felsenstein J (1989) PHYLIP, phylogeny inference package (Version 3.2). Cladistics 5:164–166
Fukuzawa AH, Vellutini BC, Lorenzini DM, Silva PI Jr, Mortara RA, da Silva JM, Daffre S (2008) The role of hemocytes in the immunity of the spider Acanthoscurria gomesiana. Dev Comp Immunol 32:716–725
Lorenzini DM, Fukuzawa AH, da Silva PI, Machado-Santelli G Jr, Bijovsky AT, Daffre S (2003) Molecular cloning, expression analysis and cellular localization of gomesin, an anti-microbial peptide from hemocytes of the spider Acanthoscurria gomesiana. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 33:1011–1016
Kuhn-Nentwig L, Müller J, Schaller J, Walz A, Dathe M, Nentwig W (2002) Cupiennin 1, a new family of highly basic antimicrobial peptides in the venom of the spider Cupiennius salei (Ctenidae). J Biol Chem 277:11208–11216
Kuhn-Nentwig L, Trachsel C, Nentwig W (2009) Spider venom and hemolymph-derived cytolytic and antimicrobial peptides. In: Howl J, Jones S (eds) Bioactive Peptides. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 447–464
Hynes WL, Ceraul SM, Todd SM, Seguin KC, Sonenshine DE (2005) A defensin-like gene expressed in the black-legged tick, Ixodes scapularis. Med Vet Entomol 19:339–344
Nakajima Y, van Naters-Yasui A, Taylor D, Yamakawa M (2002) Antibacterial peptide defensin is involved in midgut immunity of the soft tick, Ornithodoros moubata. Insect Mol Biol 11:611–618
Fogaça AC, Lorenzini DM, Kaku LM, Esteves E, Bulet P, Daffre S (2004) Cysteine-rich antimicrobial peptides of the cattle tick Boophilus microplus: isolation, structural characterization and tissue expression profile. Dev Comp Immunol 28:191–200
Todd SM, Sonenshine DE, Hynes WL (2007) Tissue and life-stage distribution of a defensin gene in the Lone Star tick, Amblyomma americanum. Med Vet Entomol 21:141–147
Ceraul SM, Dreher-Lesnick SM, Gillespie JJ, Rahman MS, Azad AF (2007) New tick defensin isoform and antimicrobial gene expression in response to Rickettsia montanensis challenge. Infect Immun 75:1973–1983
Zhou J, Liao M, Ueda M, Gong H, Xuan X, Fujisaki K (2007) Sequence characterization and expression patterns of two defensin-like antimicrobial peptides from the tick Haemaphysalis longicornis. Peptides 28:1304–1310
Saito Y, Konnai S, Yamada S, Imamura S, Nishikado H, Ito T, Onuma M, Ohashi K (2009) Identification and characterization of antimicrobial peptide, defensin, in the taiga tick, Ixodes persulcatus. Insect Mol Biol 18:531–539
Mitta G, Vandenbulcke F, Hubert F, Roch P (1999) Mussel defensins are synthesised and processed in granulocytes then released into the plasma after bacterial challenge. J Cell Sci 112:4233–4242
Gonzalez M, Gueguen Y, Desserre G, de Lorgeril J, Romestand B, Bachère E (2007) Molecular characterization of two isoforms of defensin from hemocytes of the oyster Crassostrea gigas. Dev Comp Immunol 31:332–339
Gueguen Y, Herpin A, Aumelas A, Garnier J, Fievet J, Escoubas JM, Bulet P, Gonzalez M, Lelong C, Favrel P, Bachère E (2006) Characterization of a defensin from the oyster Crassostrea gigas. Recombinant production, folding, solution structure, antimicrobial activities, and gene expression. J Biol Chem 281:313–323
Mitta G, Hubert F, Dyrynda EA, Boudry P, Roch P (2000) Mytilin B and MGD2, two antimicrobial peptides of marine mussels: gene structure and expression analysis. Dev Comp Immunol 24:381–393
Rodríguez de la Vega RC, García BI, D’Ambrosio C, Diego-García E, Scaloni A, Possani LD (2004) Antimicrobial peptide induction in the haemolymph of the Mexican scorpion Centruroides limpidus limpidus in response to septic injury. Cell Mol Life Sci 61:1507–1519
Huber KC, Haider TS, Müller MW, Huber BA, Schweyen RJ, Barth FG (1993) DNA-sequence data indicates the polyphyly of the family Ctenidae (Araneae). J Arachnol 21:194–201
Lorenzini DM, da Silva PI, Soares MB Jr, Arruda P, Setubal J, Daffre S (2006) Discovery of immune-related genes expressed in hemocytes of the tarantula spider Acanthoscurria gomesiana. Dev Comp Immunol 30:545–556
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. C. Kropf for kindly providing M. menardi, Prof. Dr. J. Schaller for MS measurements, Dr. D. Destoumieux-Garzón and Dr. H. Murray for critical comments on the manuscript, and the Swiss National Science Foundation for funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
18_2010_354_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Fig. S1 Partial C. salei defensin gene structure. PCR products of hemocyte cDNA and genomic DNA with defensin-specific primers. The 50-bp molecular weight marker is marked with MW; band sizes are in bp. (TIFF 4753 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baumann, T., Kuhn-Nentwig, L., Largiadèr, C.R. et al. Expression of defensins in non-infected araneomorph spiders. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 67, 2643–2651 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0354-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0354-2