Summary
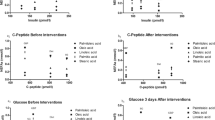
The increments in serum concentrations of unconjugated bilirubin and free fatty acids (FFA) were measured 24 and 48h after reduction of the caloric intake (400 cal/day) in 17 patients with Gilbert’s syndrome (GS) and in 12 healthy control subjects. In males, both normal and with GS, the rise in serum bilirubin was statistically higher (P<0.01) as compared to females. On the contrary, no sex difference was found in FFA concentrations. A linear correlation (p<0.01) between bilirubin and FFA serum levels was present in normal males and in patients with Gilbert’s syndrome of both sexes. Because bilirubin and FFA partly share a common, bilitranslocase-mediated, hepatic uptake mechanism, data reported support the hypothesis that a bilitranslocase function may be one of the metabolic defects in Gilbert’s syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berk P. D., Hove R. B., Bloomer J. R., Berlin N. I.: Studies of bilirubin kinetics in normal adult — J. clin. Invest.48, 2176, 1969.
Cowan R. E., Kaye J., Thompson R. P. H.: Free fatty acids and unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia — Gut16, 399, 1975.
Cowan R. E., Thompson R. P. H., Kaye J., Clark G. M.: The association between fasting hyperbilirubinaemia and serum non-esterified fatty acids in man — Clin. Sci. molec. Med.53, 155, 1977.
Ducombe W. G.: The colorimetric microdetermination of non-esterified fatty acids in plasma — Clin. chim. Acta9, 122, 1974.
Gentile S., Orzes N., Persico M., Marmo R., Bronzino P., Tiribelli C.: Comparison of nicotinic acid- and caloric restriction-induced hyperbilirubinaemia in the diagnosis of Gilbert’s syndrome — J. Hepatol.1, 537, 1985.
Gentile S., Persico M., Baldini G., Lunazzi G. C., Tiribelli C., Sottocasa G. L.: The implication of bilitranslocase function in the impaired rifamycin SV metabolism in Gilbert’s syndrome — Clin. Sci.68, 675, 1985.
Gentile S., Tiribelli C., Baldini G., Lunazzi G. C., Sottocasa G. L.: Sex differences of nicotinate-induced hyperbilirubinemia in Gilbert’s syndrome. Implication of bilitranslocase function — J. Hepatol.1, 417, 1985.
Merimee T. J., Miskin R. I., Pulkkinen A. J.: Sex variation in free fatty acids and ketones during fasting: evidence for a role of glucagon — J. clin. Endocrinol.46, 414, 1978.
Michaelson M., Nosslin B., Sjolin S.: Plasma bilirubin determination in the newborn infant — Pediatrics35, 925, 1965.
Naylor J. M., Kronfeld D. S., Johnson K.: Fasting hyperbilirubinemia and its relationship to free fatty acids and triglycerides in the horse — Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.)165, 86, 1980.
Ockner R. K., Burnett D. A., Lysenko N., Manning J. A.: Sex differences in long-chain fatty acid utilization and fatty acid binding protein concentration in rat liver — J. clin. Invest.64, 172, 1979.
Ockner R. K., Lysenko N., Manning J. A., Monroe S. E., Burnett D. A.: Sex steroid modulation of fatty acid utilization and fatty acid binding protein concentration in rat liver — J. clin. Invest.65, 1013, 1980.
Ockner R. K., Weisiger R. A., Golland J. L.: Hepatic uptake of albumin-bound substances: albumin receptor concept — Amer. J. Physiol.245, 413, 1983.
O’Kell R. T., Elliot J. R.: Development of normal values for use in multitest biochemical screening of sera — Clin. Chem.163, 161, 1970.
Orzes N., Bellentani S., Aldini R., Simoni P., Ferretti I., Lunazzi G. C., Sottocasa G. L., Tiribelli C.: Sex differences in the hepatic uptake of sulfobromophthalein in the rat — Clin. Sci. (In press).
Owens D., Evans J.: Population studies on Gilbert’s syndrome — J. med. Genet.12, 152, 1975.
Owens D., Sherlock S. H.: Diagnosis of Gilbert’s syndrome: role of the reduced caloric intake test — Brit. med. J.iii, 559, 1973.
Renaud G., Foliot A., Infante R.: Inhibitory effect of cholephilic anions on fatty acid uptake by perfused rat liver — Biochem. Pharmacol.27, 897, 1978.
Sottocasa G. L., Tiribelli C., Luciani M., Lunazzi G. C., Gazzin B.: Isolation and some properties of a protein molecule involved in hepatic bilirubin — and other anion — transport. In:Quagliarello E., Palmieri F., Papa S., Klingerberg M. (Eds): Function and molecular aspects of biomembrane transport. Elsevier/North-Holland Biochem. Press, Amsterdam, 1979; p. 451.
Tiribelli C., Luciani M., Lunazzi G. C., Renaud G., Infante R., Sottocasa G. L.: The possible role of bilitranslocase in fatty acid transport. In:Okolicsanji L. (Ed.): Familial hyperbilirubinemia. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester, 1981; p. 43.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orzes, N., Tamaro, G., Parco, S. et al. Serum free fatty acids and bilirubin concentration during fasting in patients with Gilbert’s syndrome and normal controls. La Ricerca Clin. Lab. 17, 61–66 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02909390
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02909390