Abstract.
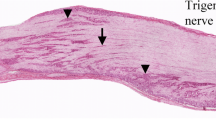
Changes in the expression of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and polyneural protein gene product 9.5 (PGP) in hilar peribronchial innervation was investigated by immunohistochemistry in specific pathogen-free rats chronically infected with Mycoplasma pulmonis. Image analysis of immunostained sections revealed a reduction of approximately 62% in the amount of CGRP- and PGP-immunoreactive innervation of the peribronchial area in the infected animals. The portion of the total bronchial perimeter occupied by bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue was increased six-fold. The decrease in the CGRP-immunoreactive area could be the result either of an enhanced CGRP release or of a loss of nerve fibres. The decrease in the PGP-immunoreactive fibres indicates a degenerative loss of nerves. Increased bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue and decreased bronchial innervation by neurons releasing the immunomodulatory neuropeptide CGRP might both contribute to the pathophysiology and symptoms of mycoplasmosis in the rat.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 29 May 1995 / Accepted: 13 September 1995
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nohr, D., Buob, A., Gärtner, K. et al. Changes in pulmonary calcitonin gene-related peptide and protein gene product 9.5 innervation in rats infected with Mycoplasma pulmonis . Cell Tissue Res 283, 215–219 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004410050532
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004410050532