Abstract
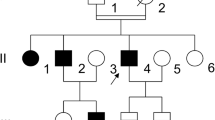
A screening project to identify candidate molecular defects causing von Willebrand disease type IIC (VWD IIC) in a German family was carried out using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of all 52 exons of the von Willebrand factor (VWF) gene, subsequent electrophoresis of single and double stranded DNA and direct sequencing of PCR products with aberrant electrophoretic patterns. Only one candidate mutation, G550R, caused by a G→A transition, was detected in exon 14 of the pro-VWF gene sequence. This mutation was not found on 200 chromosomes of normal individuals. The propositus was homozygous for the mutation and for an extended intragenic haplotype, composed of eight polymorphic markers. Further family members were heterozygous for the mutation and were phenotypically normal or only mildly affected, in accordance with the recessive pattern of inheritance for VWD type IIC. The mutation could influence one of the presumed active centers for the suspected multimerizing enzymatic activity of pro-VWF localized in the D1 and D2 domain, which corresponds to exon 5 and exon 14 of the VWF gene.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armitage H, Rizza CR (1979) Two populations of factor VIII-related antigen in a family with von Willebrand's disease. Br J Haematol 41:279–289
Batlle J, Lopez Fernandez MF, Lasierra J, Fernandez Villamor A, Lopez Berges C, Lopez Borrasca A, Ruggeri ZM, Zimmerman TS (1986) Von Willebrand disease type IIC with different abnormalities of von Willebrand factor in the same sibship. Am J Hematol 21: 177–188
Bird AP (1980) DNA methylation and the frequency of CpG in animal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8: 1499–1504
Bowen DJ, Webb CE, Peake IR, Bloom AL (1991) AatII polymorphism in von Willebrand factor gene at codon 471. Nucleic Acids Res 19:3159
Brown JE, Bosak JO (1986) An ELISA test for the binding of von Willebrand antigen to collagen. Thromb Res 43:303–311
Budowle B, Chakraborty R, Giusti AM, Eisenberg AJ, Allen RC (1991) Analysis of the VNTR locus DIS80 by the PCR followed by high resolution PAGE. Am J Hum Genet 48:137–144
Bulleid NJ, Freedman RB (1988) Defective cotranslational formation of disulphide bonds in protein disulphide-isomerase-deficient microsomes. Nature 335:649–651
Donner M, Holmberg L, Kristoffersson AC, Nilsson IM (1991) An HphI-polymorphism in exon 28 of the von Willebrand factor gene, and its frequency among patients with various forms of von Willebrand's disease. Br J Haematol 78:403–407
Edman JC, Ellis L, Blacher RW, Roth RA, Rutter WJ (1985) Sequence of protein disulphide isomerase and implications of its relationship to thioredoxin. Nature 317:267–270
Fowler WE, Fretto LJ, Hamilton KK, Erickson HP, McKee PA (1985) Substructure of human von Willebrand factor. J Clin Invest 76: 1491–1500
Gaucher C, Diéval J, Mazurier C (1994) Characterization of von Willebrand factor gene defects in two unrelated patients with type IIC von Willebrand disease. Blood 84:1024–1030
Ginsburg D, Sadler JE (1993) Von Willebrand disease: a database of point mutations, insertions, and deletions. For the Consortium on von Willebrand Factor Mutations and Polymorphisms, and the Subcommittee on von Willebrand Factor of the Scientific and Standardization Committee of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Thromb Haemost 69:177–184
Holmberg L, Dent JA, Schneppenheim R, Budde U, Ware J, Ruggeri ZM (1993) Von Willebrand factor mutation enhancing interaction with platelets in patients with normal multimeric structure. J Clin Invest 91:2169–2177
Kunkel GR, Graham JB, Fowlkes DM, Lord ST (1990) RsaI polymorphism in von Willebrand factor (VWF) at codon 789. Nucleic Acids Res 18:4961
Kunkel GR, Graham JB, Fowlkes DM, Lord ST (1991) AccI polymorphism in von Willebrand factor (F8VWF) at codon 516. Nucleic Acids Res 19:1729
Ledford MR, Rabinowitz I, Sadler JE, Kent JW, Civantos F (1993) New variant of von Willebrand disease type II with markedly increased levels of von Willebrand factor antigen and dominant mode of inheritance: von Willebrand disease type IIC Miami. Blood 82: 169–175
Lowe T, Sharefkin J, Yang SQ, Dieffenbach CW (1990) A computer program for selection of oligonucleotide primers for polymerase chain reactions. Nucleic Acids Res 18: 1757–1761
Macfarlane DE, Stibbe J, Kirby EP, Zucker MB, Grant RA, McPherson J (1975) Letter: a method for assaying von Willebrand factor (ristocetin cofactor). Thromb Diath Haemorrh 34: 306–308
Mancuso DJ, Tuley EA, Westfield LA, Worrall NK, Shelton Inloes BB, Sorace JM, Alevy YG, Sadler JE (1989) Structure of the gene for human von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem 264: 19514–19527
Mancuso DJ, Tuley EA, Westfield LA, Lester Mancuso TL, Le Beau MM, Sorace JM, Sadler JE (1991) Human von Willebrand factor gene and pseudogene: structural analysis and differentiation by polymerase chain reaction. Biochemistry 30: 253–269
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Mannucci PM, Lombardi R, Pareti FI, Solinas S, Mazzucconi MG, Mariani G (1983) A variant of von Willebrand's disease characterized by recessive inheritance and missing triplet structure of von Willebrand factor multimers. Blood 62: 1000–1005
Mayadas TN, Wagner DD (1989) In vitro multimerization of von Willebrand factor is triggered by low pH. Importance of the propolypeptide and free sulfhydryls. J Biol Chem 264: 13497–13503
Mayadas TN, Wagner DD (1992) Vicinal cysteines in the prosequence play a role in von Willebrand factor multimer assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:3531–3535
Mazurier C, Parquet Gernez A, Goudemand M (1977) Enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent assay of factor VIII-related antigen. Interest in study of von Willebrand's disease. Pathol Biol (Paris) 25:18–24
Mazurier C, Mannucci PM, Parquet Gernez A, Goudemand M, Meyer D (1986) Investigation of a case of subtype IIC von Willebrand disease: characterization of the variability of this subtype. Am J Hemalol 22:301–311
Mercier B, Gaucher C, Mazurier C (1990) An MspI polymorphism in the von Willebrand factor gene. Nucleic Acids Res 18:7467
Orita M, Iwahana H, Kanazawa H, Hayashi K, Sekiya T (1989) Detection of polymorphisms of human DNA by gel electrophoresis as single-strand conformation polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:2766–2770
Peake IR, Bowen D, Bignell P, Liddell MB, Sadler JE, Standen G, Bloom AL (1990) Family studies and prenatal diagnosis in severe von Willebrand disease by polymerase chain reaction amplification of a variable number tandem repeat region of the von Willebrand factor gene. Blood 76:555–561
Ploos van Amstel HK, Reitsma PH (1990) Tetranucleotide repeat polymorphism in the VWF gene. Nucleic Acids Res 18:4957
Raines G, Aumann H, Sykes S, Street A (1990) Multimeric analysis of von Willebrand factor by molecular sieving electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulphate agarose gel. Thromb Res 60: 201–212
Ruggeri ZM (1987) Classification of von Willebrand disease. In: Verstraete M, Vermylen J, Lijnen R, Arnout J (eds) Thrombosis and haemostasis. Leuven University Press, Leuven pp 419–445
Ruggeri ZM, Zimmerman TS (1981) The complex multimeric composition of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor. Blood 57: 1140–1143
Ruggeri ZM, Nilsson IM, Lombardi R, Holmberg L, Zimmerman TS (1982) Aberrant multimeric structure of von Willebrand factor in a new variant of von Willebrand's disease (type IIC). J Clin Invest 70: 1124–1127
Sadler JE (1994) A revised classification of von Willebrand disease. Thromb Haemost 71:520–525
Saiki RK, Gelfand DH, Stoffel S, Scharf SJ, Higuchi R, Horn GT, Mullis KB, Erlich HA (1988) Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science 239:487–491
Takahashi Y, Kalafatis M, Girma JP, Meyer D (1988) Abnormality of the N-terminal portion of von Willebrand factor in type IIA and IIC von Willebrand disease. Thromb Haemost 60:498–505
Thomas KB, Sutor AH, Zieger B, Jessat U, Budde U, Grohmann A, Choong SC, Tune EP (1994) Von Willebrand factor — collagen binding activity and ristocetin cofactor activity. A comparison of methods able to differentiate von Willebrand disease type I and II. Hämostaseologie 14: 133–139
Verweij CL, Hart M, Pannekoek H (1987) Expression of variant von Willebrand factor (VWF) cDNA in heterologous cells: requirement of the pro-polypeptide in VWF multimer formation. EMBO J 6:2885–2890
Wagner DD (1990) Cell biology of von Willebrand factor. Annu Rev Cell Biol 6:217–246
Wise RJ, Pittman DD, Handin RI, Kaufman RJ, Orkin SH (1988) The propeptide of von Willebrand factor independently mediates the assembly of von Willebrand multimers. Cell 52:229–236
Zimmerman TS, Dent JA, Ruggerie ZM, Nannini LH (1986) Sub-unit composition of plasma von Willebrand factor. Cleavage is present in normal individuals, increased in IIA and IIB von Willebrand disease, but minimal in variants with aberrant structure of individual oligomers (type IIC, IID and IIE). J Clin Invest 77:947–951
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schneppenheim, R., Thomas, K.B., Krey, S. et al. Identification of a candidate missense mutation in a family with von Willebrand disease type IIC. Hum Genet 95, 681–686 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00209487
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00209487