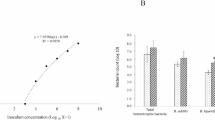
Abstract
Dissolved chemical inducers of settlement behavior of veliger larvae of the oysterCrassostrea gigas are found in supernatants of both pigmented species of bacteria (Alteromonas colwelliana, Vibrio cholerae strain HTX) as well as nonpigmented bacteria (Excherichia coli, Vibrio cholerae strain 596-B). Usually less than 10% of veligers exhibited settlement behavior in response to supernatants from the early bacterial growth phases, whereas 30–90% of larvae responded when exposed to supernatant from late-log and stationary phase cultures. Percentages of larvae exhibiting settlement behavior were inversely correlated with oxygen levels in the culture. Furthermore, the behavioral response decreased with pigment formation, suggesting that quantities of noxious compounds such as quinones may build up in the supernatants of cultures of pigmented bacteria. Tyrosinase, an enzyme that converts L-tyrosine to L-DOPA in the first step of melanogenesis, was detected both in the bacterial pellet and the supernatant during growth of the pigmented species. The enzyme is not required for the production of settlement inducer as the nonpigmented speciesE. coli andV. cholerae (596-B) also released inducer into the supernatant and had no detectable tyrosinase. The data suggest either that there is more than one inducer of settlement behavior found in bacterial supernatants or that the inducer is not L-DOPA or an L-DOPA-mimetic associated with the melanin biochemical pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coon SL, Bonar DB, Weiner RM (1985) Induction of settlement and metamorphosis of the Pacific oysterCrassostrea gigas (Thunberg) by L-DOPA and catecholamines. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 94:211–221
Coon SL, Fitt WK, Bonar DB (in press) Competence and delay of metamorphosis in the Pacific oyster,Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg) Mar Biol
Crisp DJ (1974) Factors influencing the settlement of marine invertebrate larvae. In: Grant PT, Mackie AM (eds) Chemoreception in marine organisms. Academic Press, New York, PP 117–265
Fitt WK, Hofmann DK (1985) Chemical induction of settlement and metamorphosis of the reef-dwelling coelenterateCassiopea andromeda. Proc 5th Int Coral Reef Congr 5:239–244
Fitt WK, Hofmann DK, Wolk M, Rahat M (1987) Requirement of exogenous inducers for metamorphosis of axenic larvae and buds ofCassiopea andromeda (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa). Mar Biol 94:415–422
Fitt WK, Coon SL, Walch M, Weiner RM, Colwell RR, Bonar DB (in press) Settlement behavior and metamorphosis of oyster larvae ofCrassostrea gigas in response to bacterial supernatants. Mar Biol
Hobbie JE, Daley RJ, Jasper S (1977) Use of Nucleopore filters for counting bacteria by fluorescence microscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol 33:1225–1228
Hofmann DK, Bernardy K, Brand U (1984) Asexual reproduction inCassiopea andromeda (Scyphozoa): induction of settlement and metamorphosis in vegetative buds. In: Engels W (ed) Advances in invertebrate reproduction, vol. 3, Elsevier, Amsterdam, p 592
Hofmann DK, Brand U (1987) Induction of metamorphosis in the symbiotic scyphozoanCassiopea andromeda: role of marine bacteria and of biochemicals. Symbiosis 4:99–116
Kirchman D, Graham S, Reish D, Mitchell R (1982a) Bacteria induce settlement and metamorphosis ofJanua (Dexiospira) brasiliensis Grube (Polychaeta: Spirorbidae). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 56:153–163
Kirchman D, Graham S, Reish D, Mitchell R (1982b) Lectins may mediate in the settlement and metamorphosis ofJanua brasiliensis (Grube). Mar Biol Lett 3:131–142
Kjelleberg S, Hermansson M, Marden P (1987) The transient phase between growth and nongrowth of heterotrophic bacteria, with emphasis on the marine environment. Ann Rev Microbiol 41:25–49
Meadows TS, Campbell JI (1972) Habitat selection by aquatic invertebrates. Adv Mar Biol 10:271–382
Müller WEG (1973) Induction of metamorphosis by bacteria and ions in the planulae ofHydraactinia echinata: an approach to the mode of action. Pub Seto Mar Biol Lab 20:195–208
Neumann R (1979) Bacterial induction of settlement and metamorphosis in the planula larvae ofCassiopea andromeda (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa, Rhizostomeae). Mar Ecol Progr Ser 1:21–28
Pomerantz SH, Murthy VV (1974) Purification and properties of tyrosinases fromVibrio tyrosinaticus. Arch Biochem Biophys 160:73–82
Scheltema RS (1974) Biological interactions determining larval settlement of marine invertebrates. Thalassia Jugosl 10:263–296
Walch M, Labare M, Weiner R, Fitt W, Bonar D (1987) Use of specific bacterial biofilms and their products to enhance spat set of the oystersCrassostrea virginica andC. gigas. J Shellfish Res 7:179–180
Weiner RM, Segall AM, Colwell RR (1985) Characterization of a marine bacterium associated withCrassostrea virginica, the Eastern Oyster. App Environ Microbiol 49:83–90
Weiner RM, Coyne, VE, Brayton P, West P, Raiken SF (1988)Alteromonas colwelliana sp. nov., an isolate from oyster habitats. Int J Syst Bacteriol 38:240–244
Wolk M, Rahat M, Fitt WK, Hofmann DK (1985) Cholera toxin and thyrotropine can replace natural inducers required for the metamorphosis of larvae and buds of the scyphozoanCassiopea andromeda. Roux's Arch Dev Biol 194:487–490
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fitt, W.K., Labare, M.P., Fuqua, W.C. et al. Factors influencing bacterial production of inducers of settlement behavior of larvae of the oysterCrassostrea gigas . Microb Ecol 17, 287–298 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02012841
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02012841