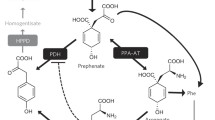
Abstract
A recombinant plasmid, pArab8, harbouring the cDNA encoding the mature form of the tetrapyrrole synthesis enzyme porphobilinogen deaminase (EC 4.3.1.8; also known as hydroxymethylbilane synthase) from Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. has been constructed, and used to transform Escherichia coli. The porphobilinogen deaminase protein from Arabidopsis was overexpressed in this strain, and purified to homogeneity (3000-fold) with a yield of 20%. Antibodies were raised against the purified plant enzyme, and used in Western blot analysis, immunoprecipitation of enzyme activity and immuno-gold electron microscopy. The results indicate that the enzyme is confined to plastids in both leaves and roots. The implications of this finding for plant tetrapyrrole synthesis are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DEAE:
-
diethylaminoethyl
- FPLC:
-
fast protein liquid chromatography
- PBG:
-
porphobilinogen
References
Amann E, Brosius J (1985) ATG vectors for regulated high-level expression of cloned genes in Escherichia coli. Gene 40: 183–190
Appleby CA (1984) Leghemoglobin and Rhizobium respiration. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 35: 443–478
Battersby AR, McDonald E, Wurzinger HKW, James KJ (1975) Stereochemistry of biosynthesis of the vinyl group of protoporphyrin IX: a short synthesis of porphobilinogen. J Chem Soc Chem Commun 493–495
Battersby AR, Fookes CJR, Gustafson-Potter K, Matcham GWJ, McDonald E (1979) Proof by synthesis that unrearranged hydroxymethylbilane is the product from deaminase and the substrate for cosynthetase in the biosynthesis of uroporphyrinogen III. J Chem Soc Chem Commun 1155–1158
Elder GH (1976) Acquired disorders of haem synthesis. Essays Med Biochem 2: 75–114
Hart GJ, Miller AD, Leeper FJ, Battersby AR (1987) Biosynthesis of the natural porphyrins: proof that hydroxymethylbilane synthase (porphobilinogen deaminase) uses a novel binding group in its catalytic action. J Chem Soc Chem Comm 1762–1765
Jacobs JM, Jacobs NJ (1993) Porphyrin accumulation and export by isolated barley (Hordeum vulgare) plastids effect of diphenylether herbicides. Plant Physiol 101: 1181–1187
Jones RM, Jordan PM (1994) Purification and properties of porphobilinogen deaminase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochem J 299: 895–902
Jordan PM (1991) The biosynthesis of 5-aminolaevulinic acid and its transformation into uroporphyrinogen III. In: Jordan PM (ed) Biosynthesis of tetrapyrroles. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1–59
Jordan PM, Seehra JS (1986) Purification of porphobilinogen synthase from bovine liver. Methods Enzymol 123: 427–434
Jordan PM, Warren MJ (1987) Evidence for a dipyrromethane cofactor at the catalytic site of E. coli porphobilinogen deaminase. FEBS Lett 225: 87–92
Jordan PM, Woodcock SC (1991) Mutagenesis of arginine residues in the catalytic cleft of Escherichia coli porphobilinogen deaminase that affects dipyrromethane cofactor assembly and tetrapyrrole chain initiation and elongation. Biochem J 280: 445–449
Jordan PM, Burton G, Nordlov H, Schneider M, Pryde LM, Scott AI (1979) Preuroporphyrinogen, a substrate for uroporphyrinogen III cosynthase. J Chem Soc Chem Commun: 204–205
Jordan PM, Warren MJ, Williams HJ, Stolowich NJ, Roessner CA, Grant SK, Scott AI (1988) Identification of a cysteine residue as the binding-site for the dipyrromethane cofactor at the active site of Escherichia coli porphobilinogen deaminase. FEBS Lett 235: 189–193
Lamppa GK, Abad MS (1987) Processing of a wheat light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein-precursor by a soluble enzyme from higher plant chloroplasts. J Cell Biol 105: 2641–2648
Lim SH, Witty M, Wallace-Cook ADM, Ilag LI, Smith AG (1994) Porphobilinogen deaminase is encoded by a single gene in Arabidopsis thaliana and is targeted to the chloroplasts. Plant Mol Biol 26: 863–872
Louie GV, Brownlie PD, Lambert R, Cooper JB, Blundell TL, Wood SP, Warren MJ, Woodcock SC, Jordan PM (1992) Structure of porphobilinogen deaminase reveals a flexible multidomain polymerase with a single catalytic site. Nature 359: 33–39
Madsen O, Sandal L, Sandal NN, Marcker KA (1993) A soybean coproporphyrinogen oxidase gene is highly expressed in root nodules. Plant Mol Biol 23: 35–43
Miller A, Hart GJ, Packman LC, Battersby AR (1988) Evidence that the pyrromethane cofactor of hydroxymethylbilane synthase (porphobilinogen deaminase) is bound to the protein through the sulfur atom of cysteine-242. Biochem J 254: 915–918
Pluscec J, Bogorad L (1970) A dipyrrylmethane intermediate in the enzymic synthesis of uroporphyrinogen. Biochemistry 9: 4736–4743
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual (2nd edn). Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Sharif AL, Smith AG, Abell C (1989) Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone for a chlorophyll synthesis enzyme from Euglena gracilis. Eur J Biochem 184: 353–359
Smith AG (1988) Subcellular localization of two porphyrin-synthesis enzymes in Pisum sativum (pea) and Arum (cuckoo-pint) species. Biochem J 249: 423–428
Smith AG, Marsh O, Elder GH (1993) Investigation of the subcellular location of the tetrapyrrole biosynthesis enzyme coproporphyrinogen oxidase in higher plants. Biochem J 292: 503–508
Thomas SD, Jordan PM (1986) Nucleotide sequence of the hemC locus encoding porphobilinogen deaminase of Escherichia coli K12. Nucleic Acids Res 14: 6215–6226
Werck-Reichhart D, Jones OTG, Durst F (1988) Haem synthesis during cytochrome P-450 induction in higher plants. Biochem J 249: 473–480
Williams DC, Morgan GS, McDonald E, Battersby AR (1981) Purification of porphobilinogen deaminase from Euglena gracilis and studies of its kinetics. Biochem J 193: 301–310
Witty M, Wallace-Cook ADM, Albrecht H, Spano AJ, Michel H, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Timko MP, Smith AG (1993) Structure and expression of chloroplast-localized porphobilinogen deaminase from pea (Pisum sativum L.) isolated by redundant polymerase chain reaction. Plant Physiol 103: 139–147
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by Science and Engineering Research Council (SERC) and Agricultural and Food Research Council (AFRC) grants to P.M.J. and an AFRC grant to A.G.S. The protein sequencing was carried out by Mr Lawrence Hunt of the SERC MRI Protein Sequencing Unit (Director Dr M.G. Gore) at Southampton University. We acknowledge the Wellcome Foundation for financial support of the Protein and Nucleic Acid Chemistry Facility at the University of Cambridge, where the oligonucleotide primers were synthesised.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Witty, M., Jones, R.M., Robb, M.S. et al. Subcellular location of the tetrapyrrole synthesis enzyme porphobilinogen deaminase in higher plants: an immunological investigation. Planta 199, 557–564 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00195187
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00195187