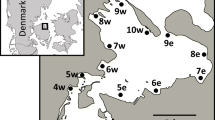
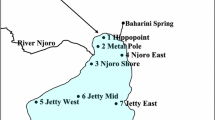
Abstract
Carbon stable isotope ratios were determined in dominant biotic components of pelagic and littoral systems in Alchichica crater-lake. Results showed that carbon signatures were significantly different between both systems. The pelagic environment was more depleted (−26.15 to −15.14 per mille) than the littoral zone (−21.03 to −17.91 per mille). The potential source end-point in the simplified pelagic community was established to be diatomaceous phytoplankton; its predicted value was −21.7 per mille. There is a clear evidence thatNodularia does not sustain the pelagic food chain. In contrast, the highly diverse littoral community was sustained by epiphytes. No allochthonous sources seemed to influence this food web.13C enrichment was observed along the components of both systems with fractionations of 0.8 to 1.4 per mille. The contribution of the seagrassRuppia maritima is probably associated with the detritus pathway. Carbon source partitioning between both systems was not recorded. The δ13C in Alchichica crater-lake was more enriched than in other saline lakes and could be attributed to different salinity and CO2 concentrations among lakes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcocer, J. 1995. Análisis holístico de la comunidad de macroinvertebrados bentónicos litorales de seis lagos-cráter con un gradiente de salinidad. Ph.D. Thesis. School of Sciences, UNAM. 106 pp.
Alcocer, J., Lugo, A., Estrada, S., Ubeda, M. and Escobar, E. 1993a. La macrofauna bentónica de los axalapazcos mexicanos. Actas del VI Congreso Español de Limnología 33: 409–415.
Alcocer, J., Lugo, A., Ubeda, M., Estrada, S. and Escobar, E. 1993b. Littoral chironomids of a Mexican Plateau athalassohaline lake. Verhandlungen International Vereinigung Limnology 25: 444–447.
Alcocer, J., Escobar, E., Lugo, A. and Peralta, L. 1998. Littoval benthos of the saline crater lakes of the basin of Oriental, Mexico. International Journal of Salt Lake Research 7(2): 87–108.
Arredondo, J.L. 1995. Los axalapazcos de la cuenca Oriental, Puebla. In: G. de la Lanza Espino and J.L. García Calderón (Eds). Lagos y presas de México, pp. 65–87. Centro de Ecología y Desarrollo.
Arredondo, J.L., Borrego, L.E., Castillo, R.M. and Valladolid, M.A. 1983. Batimetría y morfometría de los lagos “maars” de la cuenca de Oriental, Puebla, México. Biótica 8: 37–47.
Berman-Frank, J., Zohary, T., Erez, J. and Dubinsky, Z. 1994. CO2 availability, carbonic anhydrase and the annual dinoflagellate bloom in Lake Kinneret. Limnology and Oceanography 39(8): 1822–18334.
Del Giorgio, P.A. and France, R.L. 1996. Ecosystem-specific patterns in the relationship between zooplankton and POM or microplankton δ13C. Limnology and Oceanography 41(2): 359–365.
Devol, A. and Victoria, R. 1992. Carbon cycling in the Amazone River: Implications from the13C composition of particles and solutes. Limnology and Oceanography 37(4): 857–871.
Dumont, H.J., 1994. Ancient lakes have simplified pelagic food webs. Archiev fuer Hydrobiologie und Beiheft der Ergebnisse der Limnologie 44: 223–234.
Estep, M.L.F. 1984. Carbon and hydrogen isotopic composition in algae and bacteria from hydrothermal environments, Yellowstone National Park. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 48: 591–599.
Estep, M.L.F. and Vigg, S. 1985. Stable carbon and nitrogen isotope tracers of trophic dynamics in natural populations and fisheries of the Lahontan lake system, Nevada. Canadian Journal of Fisheries Aquatic Sciences 42(11): 1712–1719.
France, R.L. 1995. Differentiation between littoral and pelagic food webs in lakes using stable carbon isotopes. Limnology and Oceanography 440(7): 1310–1313.
Fry, B. and Sherr, E.B. 1984. δ13C measurements as indicators of carbon flow in marine and freshwater ecosystems. Contributions in Marine Science 27: 13–47.
García, E. 1988. Modificaciones al sistema de clasificación climática de Koeppen (para adaptarlo a las condiciones de la República Mexicana). E. García. México. 217 pp.
Gearing, J.N., Gearing, P.J., Rudinick, D.T., Requejo, A.G. and Hutchins, M.J. 1984. Isotopic variability of organic carbon in a phytoplankton-based, temperate estuary. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 48: 1089–1098.
Goericke, R., Montoya J.P. and Fry, B. 1993. Physiology of isotope fractionation in algae and cyanobacteria. In: K. Lajtha and B. Michener (Eds) Stable Isotopes in Ecology. 45 pp.
Gu, B., Schell, D.M. and Alexander, V. 1994. Stable carbon and nitrogen isotopic analysis of the plankton food web in a subarctic lake. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 51: 1338–1344.
Guy, R.D., Reid, D.M. and Krouse, H.R. 1980. Shifts in carbon isotope ratios of two C3 halophytes under natural and artificial conditions. Oceanologia 44: 241–247.
Haines, E.B. 1976. Stable carbon isotope ratios in the biota, soils and tidal water of Georgia salt marsh. Estuarine and Coastal Marine Science 4: 609–616.
Keough, J.R., Sierzen, M.E. and Hagley, C.A., 1996. Analysis of a Lake Superior coastal food web with stable isotope techniques. Limnology and Oceanography 41(1): 136–146.
Kikuchi, E. and Wada, E. 1996. Carbon and nitrogen stable isotope ratios of deposit-feeding polychaetes in the Nanakita river estuary, Japan. Hydrobiologia 321: 69–75.
Lugo, A., Alcocer, J., Sánchez, M.R. and Escobar, E. 1993. Trophic status of tropical lakes indicated by littoral protozoan assemblages. Verhandlungen International Vereinigung Limnologie 25: 441–443.
Lyons, W.B., R.M. Lent, Burnett, W.C., Chin, P., Landing, W.M., Orem, W.H. and McArthur, J.M. 1996. Jellyfish Lake, Palau: Regeneration of C, N, Si and P in anoxic marine lake sediments. Limnology and Oceanography 41(7): 1394–1403.
Matson, E.A. and Brinson, M.M. 1990. Stable carbon isotopes and the C:N ratio in the estuaries of the Palmico and Neuse rivers, North Carolina. Limnology and Oceanography 35(6): 1290–1300.
Pennak, R.W. 1978. Fresh-Water of the United States. Wiley Interscience Publications. 803 pp.
Rau, G.H. 1980. Carbon-13/carbon-12 variation in subalpine lake aquatic insects: Food source implications. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 37: 742–745.
Santinelli, M.A. 1995. Historia natural de la salamandra de Alchichica, Puebla (Caudata: Ambystomatidae)Ambystoma taylori. Undergraduate thesis. Universidad del Valle de México, Mexico. 125 pp.
Spero, H.J., Andreasen, D.J., and Sorgeloos, P. 1993. Carbon and nitrogen isotopic composition of different strains ofArtemia sp. International Journal of Salt Lake Research 2(2): 133–1339.
Tavera, R. and Komárek, J. 1996. Cyanoprokaryotes in the volcanic lake of Alchichica, Puebla State, Mexico. Algological Studies 83: 511–538.
Toetz, D. 1992. Use of mass spectroscopy to investigate the diet of brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis) in an alpine lake. Journal of Freshwater Ecology 7(3): 251–257.
Vilaclara, G., Chávez, M., Lugo, A., González, H. and Gaytán, M. 1993. Comparative description of crater-lakes basic chemistry in Puebla State, México. Verhandlungen International Vereinigung Limnologie 25: 435–440.
Waichman, A.V. 1996. Autotrophic carbon sources for heterotrophic bacterioplankton in a flood plain lake of central Amazon. Limnology and Oceanography 41(2): 56–64.
Yoshioka, T. Hayashi, H. and Wada, E. 1989. Seasonal variations of carbon and nitrogen isotope ratios of plankton and sinking particles in Lake Kizaki. Japanese Journal of Limnology 50: 313–320.
Zohary, T., Erez, J., Gophen, M., Berman-Frank, I. and Stiller, M. 1994. Seasonality of stable carbon isotopes within the pelagic food web of Lake Kinneret. Limnology and Oceanography 39(5): 94–103.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Briones, E.E., Alcocer, J., Cienfuegos, E. et al. Carbon stable isotopes ratios of pelagic and littoral communities in Alchichica crater-lake, Mexico. International Journal of Salt Lake Research 7, 345–355 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02442143
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02442143