Abstract
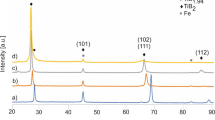
The diamond/BNi-2 alloy composite coatings with different diamond particles were prepared on the surface of a 65Mn steel matrix by using induction brazing. The microstructure and phase composition of the brazed joints were analysed, and the formation mechanism of the diamond/brazing interface was uncovered. The wear resistance of the coating was investigated, and the wear reinforcement mechanism of the coating was elucidated. The results showed that the phases in the brazing coating are mainly Ni4B3, (Ni, Fe) solid solution, Ni3Si2 and CrB phases. The metallurgical reaction between the diamond and the brazing alloy occurred on the surface of the diamond, and the distribution of C elements at the diamond/brazing alloy interface promoted the emergence of a double-layer carbide structure, including the Cr3C2 on the diamond side and Cr7C3 on the surface of Cr3C2. When the diamond particle size is 200 mesh, the wear rate of the composite coating is 0.22 g/h, indicating the coating exhibiting excellent wear resistance. The diamond plays a vital role in blocking the expansion of the plough groove during the wear process, and the failure mechanism of the coating is attributed to the nickel-based alloy wear and diamond shedding.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu J, Yang S, Xia W et al (2016) Microstructure and wear resistance performance of Cu-Ni-Mn alloy based hardfacing coatings reinforced by WC particles. J Alloys Compd 654:63–70
Berger L (2015) Application of hard metals as thermal spray coatings. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater 49:350–364
Gisario A, Puopolo M, Venettacci S et al (2015) Improvement of thermally sprayed WC–Co/NiCr coatings by surface laser processing. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater 52:123–130
Li S, Huang K, Zhang Z (2023) Wear mechanisms and micro-evaluation of WC + TiC particle-reinforced Ni-based composite coatings fabricated by laser cladding. Mater Charact 197:112699
Mahdi MS, Sanjabi S (2022) Vacuum brazed Ni-based coating reinforced with core-shell WC@Cu/Co-P. Surf Coat Technol 448:128920
Staia MH, Suárez M, Chicot D (2013) Cr2C3–NiCr VPS thermal spray coatings as candidate for chromium replacement. Surf Coat Technol 220:225–231
Chattopadhyay AK, Chollet L, Hintermann HE (1991) Induction brazing of diamond with Ni-Cr hardfacing alloy under argon atmosphere. Surf Coat Technol 45(1-3):293–298
Su H, Li Q, Xu J, Fu Y (2012) Study on influence factors of temperature in localized ultra-high frequency induction brazing. Trans China Weld Inst 12:13–17 (In Chinese)
Wang S, Xiao B, Xiao H et al (2022) Interface microstructure and bonding performance of brazed W-coated diamonds using Ni-Cr alloy. Ceram Int 48(7):9864–9872
Ma B, Lou J, Pang Q (2014) Brazed diamond micropowder bur fabricated by supersonic frequency induction heating for precision machining. J Mater Eng Perform 23(4):1505–1510
Zhang L, Long W, Du D et al (2022) The microstructure and wear properties of diamond composite coatings on TC4 made by induction brazing. Diam Relat Mater 125:109032
Mukhopadhyay P, Ghosh A (2018) On bond wear, grit-alloy interfacial chemistry and joint strength of synthetic diamond brazed with Ni-Cr-B-Si-Fe and Ti activated Ag-Cu filler alloys. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater 72:236–243
Ohsasa K, Narita T, Shinmura T (1999) Numerical modeling of the transient liquid phase bonding process of Ni using Ni-B-Cr ternary filler metal. Journal of phase equilibria 20(3):199
Lu J, Zhang W, Zhang L, Ding T, Meng P, Zhao B (2014) Effect on microstructure for adding graphite to Ni-Cr alloy when brazing diamond abrasive in controlled atmosphere. J Mech Eng 50(4):80–84 (In Chinese)
Qin J, Long W, Lu Q, Li S, Huang J (2020) Microstructure and wear properties of diamond/NiCrBSi composite brazing coating. Materials Reports 34(Z2):457–461 (In Chinese)
Chen Y, Xu H, Fu Y et al (2008) Effects of brazing atmospheres on interfacial microstructure between diamond grits and brazing alloy. Trans Nanjing Univ Aeronaut Astronaut 25(4):248–253
Li W, Zhang J, Dong H et al (2013) Thermodynamic and kinetic study on interfacial reaction and diamond graphitization of Cu-Fe-based diamond composite. Chinese Physics B 22(1):018102
Duan DZ, Xiao B, Wang W et al (2015) Interface characteristics and performance of pre-brazed diamond grains with Ni-Cr composite alloy. J Alloys Compd 644:626–631
Huang S, Tsai H, Lin S (2004) Effects of brazing route and brazing alloy on the interfacial structure between diamond and bonding matrix. Mater Chem Phys 84(2-3):251–258
Wang C, Zhou Y, Zhang F et al (2009) Interfacial microstructure and performance of brazed diamond grits with Ni-Cr-P alloy. J Alloys Compd 476(1-2):884–888
Ma W, Xiao H, Wang S et al (2022) Interface characteristics and mechanical properties of vacuum-brazed diamond with Ni-Cr+W composite filler alloy. Vacuum 198:110897
Xu Q, Zhang J, Mao C et al (2022) Cu-induced enhancement of interfacial bonding for brazed diamond grits with NiCr filler alloys. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater 106:105874
Raju S, Kumar N, Jeyaganesh B et al (2007) Characterization of crystallization kinetics of a Ni-(Cr, Fe, Si, B, C, P) based amorphous brazing alloy by non-isothermal differential scanning calorimetry. J Alloys Compd 440(1-2):173–177
Xi Y, Feng L, Xu J (2010) Microstructure of undercooled Ni-B eutectic alloy of non-equilibrium solidification. Foundry Techn 31(4):411 (In Chinese)
Okamoto H (2002) Phase diagrams of dilute binary alloys. ASM International Materials Park, OH
Hodaj F, Dezellus O, Barbier J et al (2007) Diffusion-limited reactive wetting: effect of interfacial reaction behind the advancing triple line. J Mater Sci 42:8071–8082
Yang L, Shen P, Lin Q et al (2011) Effect of Cr on the wetting in Cu/graphite system. Appl Surf Sci 257(14):6276–6281
Ruiz-Vargas J, Siredey-Schwaller N, Gey N et al (2013) Microstructure development during isothermal brazing of Ni/BNi-2 couples. J Mater Process Technol 213(1):20–29
Tian J In situ preparation and abrasive wear resistance research on chromium carbide particles reinforced iron matrix c-omposites. University of Architecture and Technology, Xian: Xi’an (In Chinese)
Chen J, Wang X, Li X et al (2020) Effects of brazing temperature and holding time on wettability of brazing diamond and brazing interface analysis. Weld World 64:1763–1770
Wang X (2016) Research of the preparation methods of high diamond content composite coating. Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics (In Chinese)
Yu Y, Tie X, Zhang G et al (2014) Comparison of brazed and sintered diamond tools for grinding of stone. Mater Res Innov 18(sup2):S2–S869
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. U2004186) to Weimin Long
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Recommended for publication by Commission XVII - Brazing, Soldering and Diffusion Bonding
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, J., You, M., Si, H. et al. Microstructure and properties of diamond/Ni-based alloy composite coatings by induction brazing. Weld World 67, 2621–2634 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-023-01580-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40194-023-01580-w