Abstract
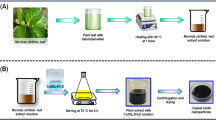
Synthetic synthesis of nanoparticles is harmful to human and environment due to pollution. The use of harmful chemicals in synthetic method has avoided in the biosynthesis. To overcome the hurdles in synthesis of nanoparticles, the biogenic synthesis of CuO nanoparticles has been done with Plectranthus amboinicus leaf extracts. The biosynthesis provides the enhanced efficiency compared to synthetic methods. It establishes the environmentally friendly and pollution-free approach. The powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern exhibited a crystalline nature with the crystallite size in 20–35 nm. The Fourier-Transform InfraRed (FTIR) spectrum explicated the Cu and O metal oxide bonds. The UV–visible analysis emphasized the stability of CuO nanoparticles with the inference of the Surface Plasmon Resonance band at 398 nm. The photoluminescence study displayed the bluish–green emission nature peak at 491 nm. The particle size analyzer manifested the synthesized CuO nanoparticles majority in 5–40 nm. The field-emission scanning electron micrographs (FESEM) and high-resolution transmission electron micrographs (HRTEM) exposed the spherical, circular-shaped nanoparticles with size in 5–30 nm range. The energy dispersive X-ray diffraction (EDAX) spectrum and mapping proved the CuO nanoparticles formation. The antimicrobial activity reported the potent nature of formed CuO nanoparticles on bacteria and fungi. The antioxidant activity identified the effective free-radical scavenging activity nature at 95% in 80 μg/mL and IC50 value at 40.10 μg/mL concentration. The anti-inflammatory activity assessed the efficient nature of CuO nanoparticles in protein denaturation of Egg albumin at 92% in 500 μg/mL and IC50 value at 243.08 μg/mL concentration. The anti-diabetic activity established the effective inhibition on α-Amylase at 94% in 500 μg/mL and IC50 value at 317.19 μg/mL concentration. The anti-larvicidal activity manifested the potent inhibition on Anopheles subpictus mosquito larvae within 24 h in 100 ppm concentration and which exhibited low LC50 value.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar MS, Panwar J, Yun YS (2013) Biogenic synthesis of metallic nanoparticles by plant extracts. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 1(6):591–602
Ali K, Ahmed B, Ansari SM, Saquib Q, Al-Khedhairy AA, Dwivedi S, Musarrat J (2019) Comparative in situ ROS mediated killing of bacteria with bulk analogue, Eucalyptus leaf extract (ELE)-capped and bare surface copper oxide nanoparticles. Mater Sci Eng C 100:747–758
Antonoglou O, Lafazanis K, Mourdikoudis S, Vourlias G, Lialiaris T, Pantazaki A, Dendrinou-Samara C (2019) Biological relevance of CuFeO2 nanoparticles: antibacterial and anti-inflammatory activity, genotoxicity, DNA and protein interactions. Mater Sci Eng C 99:264–274
Arasu MV, Arokiyaraj S, Viayaraghavan P, Kumar TSJ, Duraipandiyan V, Al-Dhabi NA, Kaviyarasu K (2019) One step green synthesis of larvicidal, and azo dye degrading antibacterial nanoparticles by response surface methodology. J Photochem Photobiol B 190:154–162
Arumugam G, Swamy MK, Sinniah UR (2016) Plectranthus amboinicus (Lour.) Spreng: botanical, phytochemical, pharmacological and nutritional significance. Molecule 21(4):369
Arvanag FM, Bayrami A, Habibi-Yangjeh A, Pouran SR (2019) A comprehensive study on antidiabetic and antibacterial activities of ZnO nanoparticles biosynthesized using Silybum marianum L seed extract. Mater Sci Eng C 97:397–405
Awoyinka OA, Balogun IO, Ogunnow AA (2007) Phytochemical screening and in vitro bioactivity of Cnidoscolus aconitifolius (Euphorbiaceae). J Med Plant Res 1:63–95
Chandra S, Chatterjee P, Dey P, Bhattacharya S (2012) Evaluation of in vitro anti-inflammatory activity of coffee against the denaturation of protein. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2(1):S178–S180
Chandra H, Patel D, Kumari P, Jangwan JS, Yadav S (2019) Phyto-mediated synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles of Berberis aristata: characterization, antioxidant activity and antibacterial activity with special reference to urinary tract pathogens. Mater Sci Eng C 102:212–220
Dadi R, Azouani R, Traore M, Mielcarek C, Kanaev A (2019) Antibacterial activity of ZnO and CuO nanoparticles against gram positive and gram negative strains. Mater Sci Eng C 104:109968
Danaei M, Dehghankhold M, Ataei S, Hasanzadeh Davarani F, Javanmard R, Dokhani A, Mozafari MR (2018) Impact of particle size and polydispersity index on the clinical applications of lipidic nanocarrier systems. Pharmaceutics 10(2):57
Dobrucka R, Dlugaszewska J (2016) Biosynthesis and antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticles using Trifolium pratense flower extract. Saudi J Biol Sci 23(4):517–523
Fu L, Fu Z (2015) Plectranthus amboinicus leaf extract–assisted biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their photocatalytic activity. Ceram Int 41(2):2492–2496
Ghidan AY, Al-Antary TM, Awwad AM (2016) Biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Ailanthus altissima Leaf extract and antibacterial activity. Environ Nano Mana 6:95–98
Gunalan S, Sivaraj R, Venckatesh R (2012) A. barbadensis Miller mediated green synthesis of mono-disperse copper oxide nanoparticles: optical properties. Spectrochim Acta A 97:1140–1144
Han F, Lv S, Li Z, Jin L, Fan B, Zhang J, Zhang R, Zhang X, Han L, Li J (2020) Triple-synergistic 2D material-based dual-delivery antibiotic platform. NPG Asia Mater 12(15):1–11
Ishwarya R, Vaseeharan B, Kalyani S, Banumathi B, Govindarajan M, Alharbi NS, Benelli G (2018) Facile green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ulva lactuca seaweed extract and evaluation of their photocatalytic, antibiofilm and insecticidal activity. J Photochem Photobiol B 178:249–258
Jin L, Li J, Liu L, Wang Z, Zhang X (2018) Facile synthesis of carbon dots with superior sensing ability. Appl Nanosci 8(5):1189–1196
Kamaraj C, Bagavan A, Rahuman AA, Zahir AA, Elango G, Pandiyan G (2009) Larvicidal potential of medicinal plant extracts against Anopheles subpictus Grassi and Culex tritaeniorhynchus Giles (Diptera: Culicidae). Parasitol Res 104(5):1163
Lebedev A, Anariba F, Tan JC, Li X, Wu P (2018) A review of physiochemical and photocatalytic properties of metal oxides against Escherichia coli. J Photochem Photobiol A 360:306–315
Li Y, Zhang W, Niu J, Chen Y (2012) Mechanism of photogenerated reactive oxygen species and correlation with the antibacterial properties of engineered metal-oxide nanoparticles. ACS Nano 6(6):5164–5173
Mali SC, Raj S, Trivedi R (2019) Green synthesis of copper and copper oxide nanoparticles using extract of seedless dates. Biochem Biophys Rep 20:100699
Meghana S, Kabra P, Chakraborty S, Padmavathy N (2015) Understanding the pathway of antibacterial activity of copper oxide nanoparticles. RSC Adv 5(16):12293–12299
Mythili R, Selvankumar T, Srinivasan P, Sengottaiyan A, Sabastinraj J, Ameen F, Kim H (2018) Biogenic synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of gold nanoparticles synthesised from vegetable waste. J Mol Liq 262:318–321
Nabila MI, Kannabiran K (2018) Biosynthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO NPs) from actinomycetes. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 15:56–62
Nagajyothi PC, Muthuraman P, Sreekanth TVM, Kim DH, Shim J (2017) Green synthesis: in-vitro anticancer activity of copper oxide nanoparticles against human cervical carcinoma cells. Arab J Chem 10(2):215–225
Nagar N, Devra V (2018) Green synthesis and characterization of copper nanoparticles using Azadirachta indica leaves. Mater Chem Phys 213:44–51
Patil MP, Palma J, Simeon NC, Jin X, Liu X, Ngabire D, Kim GD (2017) Sasa borealis leaf extract-mediated green synthesis of silver–silver chloride nanoparticles and their antibacterial and anticancer activities. New J Chem 41(3):1363–1371
Prakash S, Elavarasan N, Venkatesan A, Subashini K, Sowndharya M, Sujatha V (2018) Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles and its effective applications in Biginelli reaction, BTB photodegradation and antibacterial activity. Adv Powder Technol 29(12):3315–3326
Rajeshkumar S, Kumar SV, Ramaiah A, Agarwal H, Lakshmi T, Roopan SM (2018) Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Mangifera indica leaves and evaluation of their antioxidant and cytotoxic properties in lung cancer (A549) cells. Enzyme Microb Tech 117:91–95
Ravishankar TN, de Oliveira VM, Teixeira SR (2020) The effect of surfactant on sol–gel synthesis of CuO/TiO2 nanocomposites for the photocatalytic activities under UV-visible and visible light illuminations. New J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NJ05246A
Rehana D, Mahendiran D, Kumar RS, Rahiman AK (2017) Evaluation of antioxidant and anticancer activity of copper oxide nanoparticles synthesized using medicinally important plant extracts. Biomed Pharmacol 89:1067–1077
Ren G, Hu D, Cheng EW, Vargas-Reus MA, Reip P, Allaker RP (2009) Characterisation of copper oxide nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications. Int J Antimicrob Agents 33(6):587–590
Reyes-Torres MA, Mendoza-Mendoza E, Miranda-Hernández AM, Pérez-Díaz MA, López-Carrizales M, Peralta-Rodríguez RD, Martinez-Gutierrez F (2019) Synthesis of CuO and ZnO nanoparticles by a novel green route: antimicrobial activity, cytotoxic effects and their synergism with ampicillin. Ceram Int 45(18):24461–24468
Rezaie AB, Montazer M, Rad MM (2017) Photo and biocatalytic activities along with UV protection properties on polyester fabric through green in-situ synthesis of cauliflower-like CuO nanoparticles. J Photochem Photobiol B 176:100–111
Sankar R, Manikandan P, Malarvizhi V, Fathima T, Shivashangari KS, Ravikumar V (2014) Green synthesis of colloidal copper oxide nanoparticles using Carica papaya and its application in photocatalytic dye degradation. Spectrochim Acta A 121:746–750
Sharma JK, Akhtar MS, Ameen S, Srivastava P, Singh G (2015) Green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles with leaf extract of Calotropis gigantea and its dye-sensitized solar cells applications. J Alloys Compd 632:321–325
Sharma P, Pant S, Dave V, Tak K, Sadhu V, Reddy KR (2019) Green synthesis and characterization of copper nanoparticles by Tinospora cardifolia to produce nature-friendly copper nano-coated fabric and their antimicrobial evaluation. J Microbiol Methods 160:107–116
Sharmila G, Thirumarimurugan M, Muthukumaran C (2018) Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Tecoma castanifolia leaf extract: characterization and evaluation of its antioxidant, bactericidal and anticancer activities. Microchem J 145:578–587
Sharmila G, Thirumarimurugan M, Sivakumar VM (2016) Optical, catalytic and antibacterial properties of phytofabricated CuO nanoparticles using Tecoma castanifolia leaf extract. Optik 127(19):7822–7828
Shimada K, Fujikawa K, Yahara K, Nakamura T (1992) Antioxidative properties of xanthum on the autoxidation of soybean oil in cyclodextrin emulsion. J Agr Food Chem 40:945–948
Singh J, Kumar V, Kim KH, Rawat M (2019) Biogenic synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using plant extract and its prodigious potential for photocatalytic degradation of dyes. Environ Res 177:108569
Sone BT, Diallo A, Fuku XG, Gurib-Fakim A, Maaza M (2020) Biosynthesized CuO nano-platelets: physical properties and enhanced thermal conductivity nanofluidics. Arab J Chem 13(1):160–170
Sreeju N, Rufus A, Philip D (2017) Studies on catalytic degradation of organic pollutants and anti-bacterial property using biosynthesized CuO nanostructures. J Mol Liq 242:690–700
Varughese G, Rini V, Suraj SP, Usha KT (2014) Characterization of CuO nanoparticles. Adv Mater Sci 14(4):49–60
Velsankar K, Sudhahar S, Maheshwaran G, Krishna Kumar M (2019) Effect of biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles via Cucurbita seed extract on Culex tritaeniorhynchus mosquito larvae with its biological applications. J Photochem Photobiol B 200:111650
Velsankar K, Sudhahar S, Parvathy G, Kaliammal R (2020) Effect of cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity of biosynthesis of ZnO hexagonal shaped nanoparticles by Echinochloa frumentacea grains extract as a reducing agent. Mater Chem Phys 239:121976
Vidovix TB, Quesada HB, Januario EFD, Bergamasco R, Vieira AMS (2019) Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Punica granatum leaf extract applied to the removal of methylene blue. Matter Lett 257:126685
Yazhiniprabha M, Vaseeharan B, Sonawane A, Behera A (2019) In vitro and in vivo toxicity assessment of phytofabricated ZnO nanoparticles showing bacteriostatic effect and larvicidal efficacy against Culex quinquefasciatus. J Photochem Photobiol B 192:158–169
Yousefi A, Yousefi R, Panahi F, Sarikhani S, Zolghadr AR, Bahaoddini A, Khalafi-Nezhad A (2015) Novel curcumin-based pyrano [2, 3-d] pyrimidine anti-oxidant inhibitors for α-amylase and α-glucosidase: Implications for their pleiotropic effects against diabetes complications. Int J Biol Macromol 78:46–55
Zhang Z, Cui J, Wang B, Wang Z, Kang R, Guo D (2017a) A novel approach of mechanical chemical grinding. J Alloys Compd 726:514–524
Zhang Z, Cui J, Zhang J, Liu D, Yu Z, Guo D (2019) Environment friendly chemical mechanical polishing of copper. Appl Surf Sci 467:5–11
Zhang Z, Du Y, Wang B, Wang Z, Kang R, Guo D (2017b) Nanoscale wear layers on silicon wafers induced by mechanical chemical grinding. Tribol Lett 65(4):132
Zhang Z, Guo D, Wang B, Kang R, Zhang B (2015a) A novel approach of high speed scratching on silicon wafers at nanoscale depths of cut. Sci Rep 5:16395
Zhang Z, Huang S, Wang S, Wang B, Bai Q, Zhang B, Kang R, Guo D (2017c) A novel approach of high-performance grinding using developed diamond wheels. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 91(9–12):3315–3326
Zhang Z, Huo Y, Guo D (2013) A model for nanogrinding based on direct evidence of ground chips of silicon wafers. Sci China Technol Sci 56(9):2099–2108
Zhang Z, Huo F, Zhang X, Guo D (2012a) Fabrication and size prediction of crystalline nanoparticles of silicon induced by nanogrinding with ultrafine diamond grits. Scr Mater 67(7–8):657–660
Zhang Z, Liao L, Wang X, Xie W, Guo D (2020) Development of a novel chemical mechanical polishing slurry and its polishing mechanisms on a nickel alloy. Appl Surf Sci 506:144670
Zhang Z, Shi Z, Du Y, Yu Z, Guo L, Guo D (2018) A novel approach of chemical mechanical polishing for a titanium alloy using an environment-friendly slurry. Appl Surf Sci 427:409–415
Zhang Z, Song Y, Xu C, Guo D (2012b) A novel model for undeformed nanometer chips of soft-brittle HgCdTe films induced by ultrafine diamond grits. Scr Mater 67(2):197–200
Zhang Z, Wang B, Kang R, Zhang B, Guo D (2015b) Changes in surface layer of silicon wafers from diamond scratching. CIRP Ann-Manuf Techn 64(1):349–352
Zhang Z, Wang B, Zhou P, Guo D, Kang R, Zhang B (2016a) A novel approach of chemical mechanical polishing using environment-friendly slurry for mercury cadmium telluride semiconductors. Sci Rep 6:22466
Zhang Z, Wang B, Zhou P, Kang R, Zhang B, Guo D (2016b) A novel approach of chemical mechanical polishing for cadmium zinc telluride wafers. Sci Rep 6:26891
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge the scheme MHRD-RUSA PHASE-2.0 (Grant sanctioned vide Letter No. F.24–51/2014-U, Policy (TNMulti-Gen), Dept. of Edn. Govt. of India, Dt.09.10.2018) New Delhi and DST-PURSE-II New Delhi for a grant. Also, the authors express their thanks to UGC-SAP, DST-FIST and Alagappa University, Karaikudi-03, Tamil Nadu, India for their encouragement and providing excellent facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Velsankar, K., Vinothini, V., Sudhahar, S. et al. Green Synthesis of CuO nanoparticles via Plectranthus amboinicus leaves extract with its characterization on structural, morphological, and biological properties. Appl Nanosci 10, 3953–3971 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01504-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01504-w