Abstract
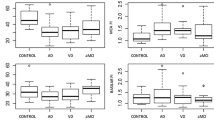
Vascular dementia (VD) and Alzheimer’s dementia (AD) are the most common differential diagnoses in patients with cognitive impairment. Although of different etiology, small vessel disease is postulated to be present in both conditions. We investigated global cerebral blood flow (CBF), global cerebral circulation time (CCT) and global cerebral blood volume (CBV) in VD and AD patients using a multimodal ultrasound (US) approach. 20 VD and 20 AD patients were included and compared with 12 age–matched controls. Duplex US of both internal carotid and vertebral arteries was performed to measure CBF. CCT was defined as the time delay of an echo–contrast bolus arrival between the internal carotid artery and internal jugular vein using extracranial Doppler. CBV was calculated as the product of CBF and CCT. CBF was significantly lower (VD: 570 ± 61; AD: 578 ± 77; controls: 733 ± 54ml/min) and CCT significantly longer (8.8 ± 2.6; 8.2 ± 1.4; 6.4 ± 0.8 s) in both patient groups compared with controls (p < 0.003). No difference in CBF and CCT was found between the two patient groups. CBV was similar in all three groups (82 ± 20; 79 ± 19; 78 ± 9 ml). The equally reduced CBF and prolonged CCT in VD and AD support the hypothesis, that small vessel disease is a relevant factor in both types of dementia. The presented multimodal US approach helps to assess the extent of changes in the global cerebral hemodynamics in patients with dementia but does not allow a differentiation between VD and AD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akkawi MN, Borroni B, Agosti C, Pezzini A, Magoni M, Rozzini L, Prometti P, Romanelli G, Vignolo LA, Padovani A (2003) Volume reduction in cerebral blood flow in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: a sonographic study. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 16:163–169
Biedert S, Forstl H, Hewer W (1995) Multiinfarct dementia vs Alzheimer’s disease: Sonographic criteria. Angiology 46:129–135
Bozzao A, Floris R, Baviera ME, Appruzese A, Simonetti G (2001) Diffusion and perfusion MR imaging in cases of Alzheimer’s disease: Correlation with cortical atrophy and lesion load. Am J Neuroradiol 22:1030–1036
Chui HC, Victoroff JI, Margolin D, Jagust W, Shankle R, Katzmann R (1992) Criteria for the diagnosis of ischemic vascular dementia proposed by the State of California Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnostic and Treatment Centers. Neurology 42:473–480
De Deyn PP, Goeman J, Engelborghs S, Hauben U, D’Hooge R, Baro F, Pickut BA (1999) From neuronal and vascular impairment to dementia. Pharmacopsychiatry 32(Suppl):17–24
De la Torre JC (2002) Alzheimer disease as a vascular disorder: nosological evidence. Stroke 33:1152–1162
De la Torre JC (2002) Vascular basis of Alzheimer’s pathogenesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 977:196–215
Doepp F, Schreiber SJ, Brunecker P, Valdueza JM (2003) Ultrasonographic assessment of global cerebral blood volume in healthy adults. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23:972–977
Doepp F, Schreiber SJ, Spruth E, Kopp U, Valdueza JM (2003) Ultrasonographic measurement of cerebral blood flow, cerebral circulation time and cerebral blood 9 volume in vascular and Alzheimer’s dementia. (Abstract) Cerebrovasc Dis 16(Suppl 2):8
Dörfler P, Puls I, Schließer M, Mäurer M, Becker G (2000) Measurement of cerebral blood volume flow by extracranial sonography. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20:269–271
Foster NL (2003) Validating FDG-PET as a biomarker for frontotemporal dementia. Exp Neurol 184(Suppl 1):S2–S8
Gold G, Giannakopoulos P, Montes-Paixao C, Hermann FR, Mulligan R, Michel JP Bouras C (1997) Sensitivity and Specificity of newly proposed clinical criteria for possible vascular dementia. Neurology 49:690–694
Hachinski VS, Iliff LD, Zilkha E, et al. (1975) Cerebral blood flow in dementia. Arch Neurol 32:632–637
Halliday GM, Double KL, Macdonald V, Kril JJ (2003) Identifying severely atrophic cortical subregions in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24:797–806
Hanyu H, Shimizu T, Tanaka Y, Takasaki M, Koizumi K, Abe K (2003) Regional cerebral blood flow patterns and response to donepezil treatment in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 15:177–182
Harris GJ, Lewis RF, Satlin A, English CD, Scott TM, Yurgelun-Todd DA, Renshaw PF (1996) Dynamic susceptibility contrast MRI of regional cerebral blood volume in Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Psychiatry 153:721–724
Harris GJ, Lewis RF, Satlin A, English CD, Scott TM, Yurgelun-Todd DA, Renshaw PF (1998) Dynamic susceptibility contrast MR imaging of regional cerebral blood volume in Alzheimer’s disease: A promising alternative to nuclear medicine. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1727–1732
Hunter R, Merrick MV, Ferrington C, Notghi A, McLuskie R, Christie JE, Goodwin GM (1989) Cerebral vascular transit time in Alzheimer’s disease and Korsakoff ’s psychosis and its relation to cognitive function. Br J Psychiatry 154:790–796
Kalaria RN (2002) Small vessel disease and Alzheimer’s dementia: pathological considerations. Cerebrovasc Dis 13 (Suppl 2):48–52
Launer LJ (2002) Demonstrating the case that AD is a vascular disease: epidemiologic evidence. Ageing Res Rev 1:61–77
Liebetrau M, Herzog J, Kloss CUA, Hamann GF, Dichgans M (2002) Prolonged cerebral transit time in CADASILA transcranial ultrasound study. Stroke 33:509–512
Maas LC, Harris GJ, Satlin A, English CD, Lewis RF, Renshaw PF (1997) Regional cerebral blood volume measured by dynamic suscceptibility contrast MR imaging in Alzheimer’s disease: principal components analysis. J Magn Reson Imaging 7:215–219
Markus HS, Lythgoe, Ostegaard L, O’Sullivan M, Williams SCR (2000) Reduced cerebral blood flow in white matter in ischaemic leukoaraiosis demonstrated using quantitative exogenous contrast based perfusion MRI. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 69:48–53
Mc Khann G, Drachmann D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health an Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 34:939–944
Meyer JS, Muramatsu K, Mortel KF, Obara K, Shirai T (1995) Prospective CT confirms differences between vascular and Alzheimer’s dementia. Stroke 26:735–742
Nagata K, Kondoh Y, Atchison R, Sato M, Satoh Y, Watahiki Y, Hirata Y, Yokoyama E (2000) Vascular and metabolic reserve in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 21:301–307
Nagata K, Maruya H, Yuya H, Terashi H, Mito Y, Kato H, Sato M, Satoh Y, Watahiki Y, Hirata Y, Yokoyama E, Hatazawa J (2000) Can PET data differentiate Alzheimer’s disease from vascular dementia? Ann N Y Acad Sci 903:252–261
Nagata K, Sato M, Satoh Y, Watahiki Y, Kondoh Y, Sugawara M, Box G, Wright D Leung S, Yuya H, Shimosegawa E (2002) Hemodynamic aspects of Alzheimer’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 977:391–402
Nobili F, Koulibaly M, Vitali P, Migneco O, Mariani G, Ebmeier K, Pupi A, Robert PH Rodriguez G, Darcourt J (2002) Brain Perfusion follow up in Alzheimer’s patients during treatment with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. J Nucl Med 43:983–990
Puls I, Becker G, Mäurer M, Müllges W (1999) Cerebral arteriovenous transit time (CCT): A sonographic assessment of cerebral microcirculation using ultrasound contrast agents. Ultrasound Med Biol 25:503–507
Puls I, Hauck K, Demuth K, Horowski A, Schließer M, Dörfler P, Scheel P, Toyka KV, Reiners K, Schöning M, Becker G (1999) Diagnostic impact of cerebral transit time in the identification of microangiopathy in dementia. A transcranial ultrasound study. Stroke 30:2291–2295
Ries F, Horn R, Hillekamp J, Honisch C, König M, Solymosi L (1993) Differentiation of multi-infarct and Alzheimer Dementia by intracranial hemodynamic parameters. Stroke 24:228–235
Roman GC, Tatemichi TK, Erkinjuntti T, Cummings JL, Masdeu JC, Garcia JH Amaducci L, Orgogozo JM, Brun A, Hofman A, et al. (1993) Vascular Dementia: diagnostic criteria for research studies. Report of the NINDS-AIREN International Workshop. Neurology 43:250–260
Sattel H, Förstl H, Biedert S (1996) Senile Dementia of Alzheimer type and multiinfarct dementia investigated by transcranial Doppler sonography. Dementia 7:41–46
Scheel P, Puls I, Becker G, Schöning M (1999) Volume reduction in cerebral blood flow in patients with vascular dementia. Lancet 354:2137
Schöning M, Walter J, Scheel P (1994) Estimation of cerebral blood flow through color duplex sonography of the carotid and vertebral arteries in healthy adults. Stroke 25:17–22
Schöning M, Scheel P (1996) Color duplex measurement of cerebral blood flow volume: intra- and interobserver reproducibility and habituation to serial measurements in normal subjects. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16:523–531
Schreiber SJ, Franke U, Doepp F, Staccioli E, Valdueza JM (2002) Dopplersonographic measurement of global cerebral circulation time using echo contrast enhanced ultrasound in normal individuals and patients with arteriovenous malformations. Ultrasound Med Biol 28:453–458
Staff RT, Gemmel HG, Shanks MF, Murray AD, Venneri A (2000) Changes in the rCBF images of patients with Alzheimer’s disease receiving Donepezil therapy. Nucl Med Commun 21:37–41
Tohgi H, Yonezawa H, Takahashi S, Sato N, Kato E, Kudo M, Hatano K, Sasaki T (1998) Cerebral blood flow and oxygen metaolism in senile dementia of Alzheimer’s type and vascular dementia with deep white matter changes. Neuroradiology 40:131–137
Tonini G, Shanks MF, Venneri A (2003) Short-time longitudinal evaluation of cerebral blood flow in mild Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol Sci 24:24–30
Verhey FR, Lodder J, Rozendaal N, Jolles J (1996) Comparison of seven sets of criteria used for the diagnosis of vascular dementia. Neuroepidemiology 15:166–172
Wetterling T, Kanitz RD, Borgis KJ (1996) Comparison of different diagnostic criteria for vascular dementia (ADDTC, DSM-IV, ICD-10, NINDSAIREN). Stroke 27:30–36
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Drs. Schreiber and Doepp contributed equally to their work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schreiber, S.J., Doepp, F., Spruth, E. et al. Ultrasonographic measurement of cerebral blood flow, cerebral circulation time and cerebral blood volume in vascular and Alzheimer’s dementia. J Neurol 252, 1171–1177 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0826-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0826-8