Abstract
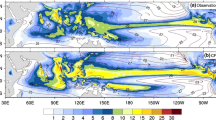
The aim of the study is to evaluate the performance of regional climate model (RegCM) version 4.4 over south Asian CORDEX domain to simulate seasonal mean and monsoon intraseasonal oscillations (MISOs) during Indian summer monsoon. Three combinations of Grell (G) and Emanuel (E) cumulus schemes namely, RegCM-EG, RegCM-EE and RegCM-GE have been used. The model is initialized at 1st January, 2000 for a 13-year continuous simulation at a spatial resolution of 50 km. The models reasonably simulate the seasonal mean low level wind pattern though they differ in simulating mean precipitation pattern. All models produce dry bias in precipitation over Indian land region except in RegCM-EG where relatively low value of dry bias is observed. On seasonal scale, the performance of RegCM-EG is more close to observation though it fails at intraseasonal time scales. In wave number-frequency spectrum, the observed peak in zonal wind (850 hPa) at 40–50 day scale is captured by all models with a slight change in amplitude, however, the 40–50 day peak in precipitation is completely absent in RegCM-EG. The space–time characteristics of MISOs are well captured by RegCM-EE over RegCM-GE, however it fails to show the eastward propagation of the convection across the Maritime Continent. Except RegCM-EE all other models completely underestimates the moisture advection from Equatorial Indian Ocean onto Indian land region during life-cycle of MISOs. The characteristics of MISOs are studied for strong (SM) and weak (WM) monsoon years and the differences in model performances are analyzed. The wavelet spectrum of rainfall over central India denotes that, the SM years are dominated by high frequency oscillations (period <20 days) whereas little higher periods (>30 days) along with dominated low periods (<20 days) observed during WM years. During SM, RegCM-EE is dominated with high frequency oscillations (period <20 days) whereas in WM, RegCM-EE is dominated with periods >20 days. Except RegCM-EE, all other models fail to capture the observed spectral features for SM and WM years.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abhik S, Halder M, Mukhopadhyay P, Jiang X, Goswami BN (2013) A possible new mechanism for northward propagation of boreal summer intraseasonal oscillations based on TRMM and MERRA reanalysis. Clim Dyn 40:1611–1624. doi:10.1007/s00382-012-1425-x
Abhik S, Mukhopadhyay P, Goswami B (2014) Evaluation of mean and intraseasonal variability of Indian summer monsoon simulation in ECHAM5: identification of possible source of bias. Clim Dyn 43:389–406
Ajayamohan RS, Rao SA, Luo JJ, Yamagata T (2009) Influence of Indian Ocean dipole on boreal summer intraseasonal oscillations in a coupled general circulation model. J Geophys Res 114:D06119. doi:10.1029/2008JD011096
Annamalai H, Slingo JM (2001) Active/break cycles: diagnosis of the intraseasonal variability of the Asian summer monsoon. Clim Dyn 18:85–102
Anthes RA, Kuo YH, Hsie EY, Low-Nam S, Bettge TW (1989) Estimation of skill and uncertainty in regional numerical models. Q J R Meteorol Soc 115:763–806
Bhaskaran B, Jones RG, Murphy JM, Noguer M (1996) Simulations of the Indian summer monsoon using a nested regional climate model: domain size experiments. Clim Dyn 12:573–587
Byun YH, Hong SY (2004) Impact of boundary layer processes on simulated tropical precipitation. J Clim 17:4032–4044
Dash SK, Shekhar MS, Singh GP (2006) Simulation of Indian summer monsoon circulation and precipitation using RegCM3. Theor Appl Climatol 86:161–172
Dee DP et al (2011) The ERA-Interim reanalysis: configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Quart J R Meteorol Soc. 137:553–597. doi:10.1002/qj.828
Demott CA, Stan C, Randall DA, Klinter JL III, Khairoutdinov M (2011) The Asian monsoon in the superparameterized CCSM and its relationship to tropical wave activity. J Clim 24:5134–5156. doi:10.1175/2011JCLI4202.1
Duchon CE (1979) Lanczos filtering in one and two dimensions. J Appl Meteorol 18:1016–1022
Emanuel K (1991) A scheme for representing cumulus convection in large scale models. J Atmos Sci 48:2313–2335
Fu X, Wang B (2004) Different solutions of intraseasonal oscillation exist in atmosphere–ocean coupled model and atmosphere-only model. J Clim 17:1263–1271
Fu X, Wang B, Li T, McCreary JP (2003) Coupling between northward propagating intraseasonal oscillations and sea surface temperature in the Indian Ocean. J Atmos Sci 60:1733–1753
Fu X, Wang B, Waliser DE, Tao L (2007) Impact of atmosphere-ocean coupling on the predictability of monsoon intraseasonal oscillations. J Atmos Sci 64:157–174
Giorgi F (2006) Regional climate modeling: status and perspectives. J Phys IV 139:101–118. doi:10.1051/jp4:2006139008
Giorgi F, Marinucci MR, Bates GT (1993a) Development of a second generation regional climate model (REGCM2). Part I: boundary layer and radiative transfer processes. Mon Weather Rev 121:2794–2813
Giorgi F, Marinucci MR, Bates GT, DeCanio G (1993b) Development of a second generation regional climate model (REGCM2). Part II: convective processes and assimilation of lateral boundary conditions. Mon Weather Rev 121:2814–2832
Giorgi F et al (2012) RegCM4: model description and preliminary tests over multiple CORDEX domains. Clim Res 52:7–29
Goswami BN, Xavier PK (2003) Potential predictability and extended range prediction of Indian summer monsoon breaks. Geophys Res Lett 30(18):1966. doi:10.1029/2003GL017.810.2003
Goswami BN, Ajaya Mohan RS (2001) Intraseasonal oscillations and interannual variability of the Indian summer monsoon. J Clim 14:1180–1198
Goswami BN, Shukla J (1984) Quasi-periodic oscillations in a symmetric general circulation model. J Atmos Sci 41:20–37
Goswami BN, Wu G, Yasunari T (2006) The annual cycle, intraseasonal oscillations, and roadblock to seasonal predictability of the Asian summer monsoon. J Clim 19:5078–5098
Goswami BB, Mukhopadhyay P, Khairoutdinov M, Goswami BN (2013) Simulation of Indian summer monsoon intraseasonal oscillations in a superparameterized coupled climate model: need to improve the embedded cloud resolving model. Clim Dyn 41:1497–1507. doi:10.1007/s00382-012-1563-1
Grell GA (1993) Prognostic evaluation of assumptions used by cumulus parameterizations. Mon Weather Rev 121:764–787
Grenier H, Bretherton CS (2001) A moist PBL parameterization for large-scale models and its application to subtropical cloud-topped marine boundary layers. Mon Weather Rev 129:357–377
Hayashi Y (1982) Space-time spectral analysis and its applications to atmospheric waves. J Meteor Soc Jpn 60:156–171
Huffman GJ, Adler RF, Morrissey M, Bolvin DT, Curtis S, Joyce R, McGavock B, Susskind J (2001) Global precipitation at one degree daily resolution from multi-satellite observations. J Hydrometeorol 2:36–50
Jiang X, Li T, Wang B (2004) Structures and mechanisms of the northward propagating boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation. J Clim 17:1022–1039
Joseph S, Sahai AK, Chattopadhyay R, Goswami BN (2011) Can El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) events modulate intraseasonal oscillations of Indian summer monsoon? J Geophys Res 116:D20123. doi:10.1029/2010JD015510
Kiehl JT, Hack JJ, Bonan GB, Boville BA, Breigleb BP, Williamson D, Rasch P (1996) Description of the NCAR community climate model (CCM3). NCAR Tech. Note NCAR/TN-420+STR, 152 pp
Kripalani RH, Kulkarani A, Sabade SS, Revadekar JV, Patwardhan SK, Kulkarani JR (2004) Intraseasonal oscillation during monsoon 2002 and 2003. Curr Sci 87:325–331
Kripalani RH, Oh JH, Kulkarni A, Sabade SS, Chaudhari HS (2007) South Asian summer monsoon precipitation variability: coupled climate model simulations and projections under IPCC AR4. Theor Appl Climatol 90(3–4):133–159. doi:10.1007/s00704-006-0282-0
Krishna Kumar K, Hoerling M, Rajagopalan B (2005) Advancing dynamical prediction of Indian monsoon precipitation. Geophys Res Lett 32(8):L08704. doi:10.1029/2004GL021979
Krishnamurti TN, Subrahmanyam D (1982) The 30–50 day mode at 850 mb during MONEX. J Atmos Sci 39:2088–2095
Lawrence DM, Webster PJ (2002) The boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation: relationship between northward and eastward movement of convection. J Atmos Sci 59:1593–1606
Leung LR, Ghan SJ, Zhao ZC, Luo Y, Wang WC, Wei HL (1999) Inter comparison of regional climate simulations of the 1991 summer monsoon in eastern Asia. J Geophys Res 104:6425–6454
Lin R, Zhou T, Qian Y (2014) Evaluation of global monsoon precipitation changes based on five reanalysis datasets. J Clim 27(3):1271–1289
Maharana P, Dimri AP (2015) Study of intraseasonal variability of Indian summer monsoon using a regional climate model. Clim Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-015-2631-0
Oleson KW, NiuGy Yang ZL, Lawrence DM et al (2008) Improvements to the Community Land Model and their impact on the hydrologic cycle. J Geophys Res 113:G01021. doi:10.1029/2007JD000563
Pal JS, Small EE, Eltahir EAB (2000) Simulation of regional scale water and energy budgets: representation of sub-grid cloud and precipitation processes within RegCM4. J Geophys Res 105:29579–29594
Pal JS, Giorgi F, Bi X, Elguindi N, Solmon F, Gao X, Francisco R, Zakey A, Winter J, Ashfaq M, Syed F, Bell J, Diffenbaugh N, Karmacharya J, Konare A, Martinez-Castro D, Porfirio da Rocha R, Sloan L, Steiner A (2007) Regional climate modeling for the developing world: the ICTP RegCM3 and RegCNET. Bull Am Meteor Soc 88:1395–1409
Philippe LP et al (2011) Can regional climate models represent the Indian monsoon? J Hydrometeorol 12(5):849–868
Pillai PA, Chowdary JS (2015) Indian summer monsoon intra-seasonal oscillation associated with the developing and decaying phase of El Niño. Int J Climatol. doi:10.1002/joc.4464
Rajeevan M, Gadgil S, Bhate J (2010) Active and break spells of the Indian summer monsoon. J Earth Syst Sci 119(3):229–247
Rajeevan M, Rohini P, Niranjan Kumar K, Srinivasan J, Unnikrishnan CK (2013) A study of vertical cloud structure of the Indian summer monsoon using CloudSat data. Clim Dyn 40:637–650
Rajendran K, Kitoh A, Arakawa O (2004) Monsoon low-frequency intraseasonal oscillation and ocean-atmosphere coupling over the Indian Ocean. Geophys Res Lett. doi:10.1029/2003GL019031
Raju A, Parekh Anant, Chowdary JS, Gnanaseelan C (2015a) Assessment of the Indian summer monsoon in the WRF regional climate model. Clim Dyn 44:3077–3100. doi:10.1007/s00382-014-2295-1
Raju PVS, Bhatla R, Almazrouiand M, Assiri M (2015b) Performance of convection schemes on the simulation of summer monsoon features over the South Asia CORDEX domain using RegCM-4.3. Int J Climatol. doi:10.1002/joc.4317
Ratnam JV, Krishna Kumar K (2005) Sensitivity of the simulated monsoons of 1987 and 1988 to convective parameterization schemes in MM5. J Clim 18:2724–2743
Rupa Kumar K, Sahai AK, Krishna Kumar K, Patwardhan SK, Mishra PK, Revadekar JV, Kamala K, Pant GB (2006) High-resolution climate change scenarios for India. Curr Sci 90:334–345
Sharmila S, Joseph S, Chatopadhay R, Sahai AK, Goswami BN (2014) Asymmetry in space time characteristics of Indian summer monsoon intraseasonal oscillations during extreme years: role of seasonal mean state. Int J Climatol 35:1948–1963
Sikka DR, Gadgil S (1980) On the maximum cloud zone and the ITCZ over India longitude during the Southwest monsoon. Mon Weather Rev 108:1840–1853
Singh GP, Oh JH (2007) Impact of Indian Ocean sea surface temperature anomaly on Indian summer monsoon precipitation using a regional climate model. Int J Climatol 27:1455–1465. doi:10.1002/joc.1485
Slingo JM, Annamalai H (2000) 1997: the El Nino of the century and the response of the Indian Summer Monsoon. Mon Weather Rev 128:1778–1797
Suhas E, Neena JM, Goswami BN (2012) An Indian monsoon intraseasonal oscillations (MISO) index for real time monitoring and forecast verification. Clim Dyn 40:2605–2616. doi:10.1007/s00382-012-1462-5
Taylor KE (2001) Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. J Geophys Res 106:7183–7192. doi:10.1029/2000JD900719
Teng H, Wang B (2003) Interannual variations of the boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation in the Asian-Pacific region. J Clim 16:3572–3584
Umakanth U, Kesarkar AP, Rao TN, Rao S (2014) An objective criterion for the identification of breaks in Indian summer monsoon precipitation. Atmos Sci Lett 16(3):193–198. doi:10.1002/asl2.536
Vernekar AD, Ji Y (1999) Simulation of the onset and intraseasonal variability of two contrasting summer monsoons. J Clim 12:1707–1725
Waliser DE et al (2003) AGCM simulations of intraseasonal variability associated with the Asian summer monsoon. Clim Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-003-0337-1
Wang B, Webster PJ, Teng H (2005) Antecedents and self-induction of the active-break Indian summer monsoon. Geophys Res Lett 32:L04704
Wang B, Webster P, Kikuchi K, Yasunari Qi Y (2006) Boreal summer quasi-monthly oscillation in the global tropics. Clim Dyn 27:661–675
Webster PJ, Magana VO, Palmer TN, Shukla J, Tomas RT, Yanai M, Yasunari T (1998) Monsoons: Processes, predictability and the prospects of prediction. J Geophys Res 103:14451–14510
Wu X, Liang X, Zhang GJ (2003) Seasonal migration of ITCZ precipitation across the equator: why Can’t GCMs simulate it. Geophys Res Lett. doi:10.1029/2003GL017198
Yasunari T (1979) Cloudiness fluctuation associated with the northern hemisphere summer monsoon. J Meteor Soc Jpn 57:227–242
Yasunari T (1980) A Quasi stationary appearance of 30–40 day period in the cloudiness fluctuation during summer monsoon over India. J Meteor Soc Jpn 58:225–229
Zhang GJ, Mu M (2005) Simulation of the Madden-Julian oscillation in the NCAR CCM3 using a revised Zhang-McFarlane convection parameterization scheme. J Clim 18:4046–4064
Zhu W, Li T, Fu X, Luo JJ (2010) Influence of the Maritime Continent on the boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation. J Meteor Soc Jpn 88:395–407. doi:10.2151/jmsj.2010-308
Acknowledgments
We thank two anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments that helped to improve the manuscript. The authors are thankful to Director, National Atmospheric Research Laboratory (NARL) for providing necessary facilities to carry out this work. We thankfully acknowledge ICTP for providing the regional climate model RegCM4.4. We wish to thank GPCP, ERA-Interim and OISST data products. We are grateful to Prof. S. K. Das and his team for conducting a workshop on Regional climate modeling at IIT Delhi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Umakanth, U., Kesarkar, A.P., Raju, A. et al. Representation of monsoon intraseasonal oscillations in regional climate model: sensitivity to convective physics. Clim Dyn 47, 895–917 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2878-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2878-5