Summary
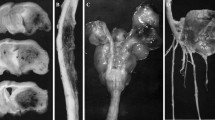
Simultaneous peroral application of ethylurea and sodium nitrite to pregnant Sprague-Dawley rats, on the 9th and 10th days of gestation, causes embryotoxic and/or teratogenic effects. Each substance alone does not afflict the fetuses, whereas the combined addition to the food permits the formation of ethyl nitroso-urea in the digestive tract. The latter readily passes the placenta and develops the teratogenic effect. It is to be considered that teratogenic substances can occur from food constituents in the human organism also.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
N. P. Napalkov undV. A. Alexandrov, Z. Krebsf.71, 32 (1968).
J. Sander undG. Bürkle, Z. Krebsf.73, 54 (1969).
S. Ivankovic undR. Preussmann, Naturwissenschaften57, 460 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alexandrov, V.A., Jänisch, W. Die teratogene Wirkung von Äthylharnstoff und Nitrit bei Ratten. Experientia 27, 538–539 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02147586
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02147586