Abstract
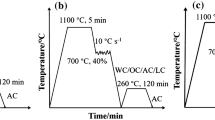
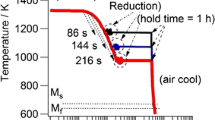
To develop low-cost low carbon bainitic steel, Mo-bearing and Cr-bearing steels were melted in a vacuum induction furnace and were researched by thermal simulation and hot rolling at the laboratory. As the cooling rate increases from 0.2 to 50°C/s, the transformation temperatures of two steels lie between 650 and 400°C, and the final microstructures of them change from quasi-polygonal ferrite and granular bainite to lath bainite. Compared with cooling in air or by interrupted cooling, Mo-bearing and Cr-bearing steel plates cooled by sprayed water boast higher strength and superior toughness, for large-size islands are responsible for the poor mechanical properties. Compared to Mo, Cr is effective to isolate the bainitic reaction in low carbon steel, and the bainitic microstructure can also be obtained in Cr-bearing steel cooled at a wide range of cooling rate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.B. Cota and D.B. Santos, Microstructural characterization of bainitic steel submitted to torsion testing and interrupted accelerated cooling, Mater. Charact., 44(2000), p.291.
C.J. Shang, X.M. Wang, S.W. Yang, et al., Refinement of packet size in low carbon bainitic steel by special thermo-mechanical control process, J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing, 11(2004), p.221.
P.C.M. Rodrigues, E.V. Pereloma, and D.B. Santos, Mechanical properties of an HSLA bainitic steel subjected to controlled rolling with accelerated cooling, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 283(2000), p.136.
B. Hwang, C.G. Lee, and T.H. Lee, Correlation of microstructure and mechanical properties of thermomechanically processed low-carbon steels containing boron and copper, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 41(2010), p.85.
I.A. Yakubtsov, P. Poruks, and J.D. Boyd, Microstructure and mechanical properties of bainitic low carbon high strength plate steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 480(2008), p.109.
S. Shanmugam, N.K. Ramisetti, R.D.K. Misra, et al., Effect of cooling rate on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Nb-microalloyed steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 460-461(2007), p.335.
C.P. Reip, S. Shanmugam, and R.D.K. Misra, High strength microalloyed CMn(V-Nb-Ti) and CMn(V-Nb) pipeline steels processed through CSP thin-slab technology: microstructure, precipitation and mechanical properties, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 424(2006), p.307.
Y.T. Zhao, C.J. Shang, S.W. Yang, et al., Metastable austenite transformation in low carbon microalloying steel, J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing (in Chinese), 29(2007), p.694.
C.L. Zhang, D.Y. Cai, Y.H. Wang, et al., Effects of deformation and Mo, Nb, V, Ti on continuous cooling transformation in Cu-P-Cr-Ni-Mo weathering steels, Mater. Charact., 59(2008), p.1638.
P. Cizek, B.P. Wynne, C.H.J. Davies, et al., Effect of composition and austenite deformation on the transformation characteristics of low-carbon and ultralow-carbon microalloyed steels, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 33(2002), p.1331.
D.Q. Bai, S. Yue, T.M. Maccagno, and J.J. Jonas, Continuous cooling transformation temperatures determined by compression tests in low carbon bainitic grades, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 29(1998), p.989.
W. You, W.H. Xu, Y.X. Liu, et al., Effect of chromium on CCT diagrams of novel air-cooled bainite steels analyzed by neural network, J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 14(2007), p.39.
R.L. Klueh, P.J. Maziasz, and D.J. Alexander, Bainite chromium-tungsten steels with 3pct chromium, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 28(1997), p.335.
Y.J. Park and F.B. Fletcher, Effects of manganese, chromium and molybdenum on the isothermal transformation of austenite in eutectoid steels, J. Heat Treat., 4(1986), p.247.
P.L. Mangonon, Effect of alloying elements on the microstructure and properties of a hot-rolled low-carbon low-alloy bainitic steel, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 7(1976), p.1389.
H.S. Fang, Q. Li, B.Z. Bai, et al., The developing prospect of air-cooled bainitic steels, Mater. Sci Forum, 426–432(2003), p.201.
T. Siwecki, J. Eliasson, R. Lagneborg, et al., Vanadium microalloyed bainitic hot strip steels, ISIJ Int., 50(2010), p.760.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huo, Xd., Li, Yq., Zhao, Yt. et al. Effect of cooling parameters on the microstructure and properties of Mo-bearing and Cr-bearing steels. Int J Miner Metall Mater 18, 551–556 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-011-0476-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-011-0476-z