Abstract
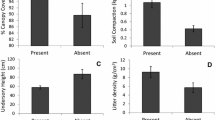
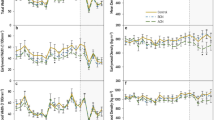
By using two thinning intensity regimes on a dense 16-year-old black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.) stand, two silvopastures were created: a medium density silvopasture (MDS) with 60% mean crown cover and a low density silvopasture (LDS) with 30% mean crown cover. An unthinned section of the stand with 90% mean crown cover was used as control (high density silvopasture: HDS). We measured the diameter at breast height (DBH) and tree height of black locust trees, in all three silvopastures, in 2011 (year of thinning), 2012 and 2013. In addition, we determined the forage production (in 2012 and 2013) and nutritive value (in 2013) of herbaceous vegetation and black locust shoots in the understory. The mean DBH for HDS, MDS and LDS increased from 7.6, 9.5 and 10.9 cm in 2011 to 8.6, 10.7 and 12.1 cm in 2013, respectively. The mean tree height also increased in the same period from 7.9, 9.1 and 9.8 m to 8.9, 10.1 and 10.6 m, for HDS, MDS and LDS, respectively. The mean herbage production was similar (P > 0.05) among silvopastures, although there was a tendency to be higher in the MDS and LDS (1866 and 1957 kg DM/ha, respectively) compared to HDS (1682 kg DM/ha). Additionally, browse from black locust shoots increased forage in MDS and LDS by 751 and 1201 kg DM/ha, respectively. Black locust browse had a higher overall nutritive value than herbage across silvopastures and months. In terms of crude protein, the content in black locust browse was on average twice as high, across sites and years, as that of herbage (239.4 vs. 104.1 g/kg DM; P < 0.05). While neutral detergent fiber and acid detergent fiber content of black locust browse were consistently lower (P < 0.05) than that of herbage, acid detergent lignin content of browse material was higher (P < 0.05) than that of herbage and averaged 94.7 and 75.4 g/kg DM, respectively. Overall, our results show that thinning resulted in higher values for both DBH and height of trees and increased forage in the understory by supplementing herbage with browse of high nutritive value.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addlestone BJ, Mueller JP, Luginbuhl J-M (1998) The establishment and early growth of three leguminous tree species for use in silvopastoral systems of the southeastern USA. Agrofor Syst 44:253–265
Ainalis AB, Tsiouvaras CN (1998) Forage production of woody fodder species and herbaceous vegetation in a silvopastoral system in northern Greece. Agrofor Syst 42:1–11
Arianoutsou M, Bazos I, Delipetrou P, Kokkoris Y (2010) The alien flora of Greece: taxonomy, life traits and habitat preferences. Biol Invasions 12:3525–3549
Baertsche SR, Yokoyama MT, Hanover JW (1986) Short rotation, hardwood tree biomass as potential ruminant feed-chemical composition, nylon bag ruminal degradation and ensilement of selected species. J Anim Sci 63:2028–2043
Boring LR, Monk CD, Swank WT (1981) Early regeneration of a clear-cut Southern Appalachian forest. Ecology 62:1244–1253
Cutter BE, Lowell KE, Dwyer JP (1991) Thinning effects on diameter growth in black and scarlet oak as shown by tree ring analyses. For Ecol Manag 43:1–13
Ford MM, Zamora DS, Current D, Magner J, Wyatt G, Walter WD, Vaughan S (2019) Impact of managed woodland grazing on forage quantity, quality and livestock performance: the potential for silvopasture in Central Minnesota, USA. Agrofor Syst 93:67–79
Garrett HE, Jones JE, Kurtz WB, Slusher JP (1991) Black walnut (Juglans nigra L.) agroforestry: its design and potential as a land-use alternative. For Chron 67:213–218
Garrett HE, Kerley MS, Ladyman KP, Walter WD, Godsey LD, Van Sambeek JW, Brauer DK (2004) Hardwood silvopasture management in North America. Agrofor Syst 61:21–33
Hatfield RD, Ralph J, Grabber J (1999) Cell wall structural foundations: molecular basis for improving forage digestibilities. Crop Sci 39:27–37
Holechek JL (1984) Comparative contribution of grasses, forbs, and shrubs to the nutrition of range ungulates. Rangelands 6:245–248
Holechek JL, Pieper RD, Herbel CH (2004) Range management: principles and practices, 5th edn. Pearson Education Inc, Upper Saddle River
Huntley JC (1990) Robinia pseudoacacia L, black locust. In: Burns RM, Honkala BH (eds) Silvics of North America, vol 2, Hardwoods. USDA Forest Service Agriculture Handbook 654. US Gov Print Office, Washington, DC, pp 755–761
Jose S, Dollinger J (2019) Silvopasture: a sustainable livestock production system. Agrofor Syst 93:1–9
Jose S, Walter D, Mohan Kumar B (2019) Ecological considerations in sustainable silvopasture design and management. Agrofor Syst 93:317–331
Jung HG, Mertens DR, Payne AJ (1997) Correlation of acid detergent lignin and klason lignin with digestibility of forage dry matter and neutral detergent fiber. J Dairy Sci 80:1622–1628
Juodvalkis A, Kairiukstis L, Vasiliauskas R (2005) Effects of thinning on growth of six tree species in north-temperate forests of Lithuania. Eur J For Res 124:187–192
Kim M, Lee W-K, Kim Y-S, Lim C-H, Song C, Park T, Son Y, Son Y-M (2016) Impact of thinning intensity on the diameter and height growth of Larix kaempferi stands in central Korea. For Sci Technol 12:77–87
Macdonald E, Gardiner B, Mason W (2010) The effects of transformation of even-aged stands to continuous cover forestry on conifer log quality and wood properties in the UK. Forestry (Lond) 83:1–16
Mäkinen H, Isomäki A (2004a) Thinning intensity and growth of Norway spruce stands in Finland. Forestry (Lond) 77:349–364
Mäkinen H, Isomäki A (2004b) Thinning intensity and long-term changes in increment and stem form of Norway spruce trees. For Ecol Manag 2–3:295–309
Ministerial decision/117394/2932 (2014) Guidelines for grazing management plans. In: Official Journal of the Hellenic Government No 3557
Moore KJ, Jung H-JG (2001) Lignin and fiber digestion. J Range Manag 54:420–430
Morikawa Y, Hattori S, Kiyono Y (1986) Transpiration of a 31-year-old Chamaecyparis obtusa Endl. stand before and after thinning. Tree Physiol 2:105–114
Nicolescu VN, Rédei K, Mason WL, Vor T, Pöetzelsberger E, Bastien JC, Brus R, Benčať T, Dodan M, Cvjetkovic B, Andrašev S, La Porta N, Lavnyy V, Mandžukovski D, Petkova K, Roženbergar D, Wąsik R, Mohren GMJ, Monteverdi MC, Musch B, Klisz M, Perić S, Keça L, Bartlett D, Hernea C, Pástor M (2020) Ecology, growth and management of black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.), a non-native species integrated into European forests. J For Res 31:1081–1101
Nishizono T (2010) Effects of thinning level and site productivity on age-related changes in stand volume growth can be explained by a single rescaled growth curve. For Ecol Manag 259:2276–2291
NRC (1975) Nutrient requirements of sheep. No 5. National Academy of Sciences, Washington
NRC (1981) Nutrient requirements of goats: angora, dairy, and meat goats in temperate and tropical countries. No 15. National Academy Press, Washington
Orefice J, Smith RG, Carroll J, Asbjornsen H, Howard T (2019) Forage productivity and profitability in newly-established open pasture, silvopasture, and thinned forest production systems. Agrofor Syst 93:51–65
Panagopoulos T, Hatzistathis A (1995) Early growth of Pinus nigra and Robina pseudoacacia stands: contributions to soil genesis and landscape improvement on lignite spoils in Ptolemaida. Landsc Urban Plan 32:19–29
Pang K, Van Sambeek JW, Lin C-H, Jose S, Garrett HE (2019a) Responses of legumes and grasses to non-, moderate, and dense shade in Missouri, USA. I. Forage yield and its species-level plasticity. Agrofor Syst 93:11–24
Pang K, Van Sambeek JW, Navarrete-Tindall NE, Lin C-H, Jose S, Garrett HE (2019b) Responses of legumes and grasses to non-, moderate, and dense shade in Missouri, USA. II. Forage quality and its species-level plasticity. Agrofor Syst 93:25–38
Papachristou TG (1999) Assessing the value of black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.) browse for animal feeding. In: Papanastasis V, Frame J, Nastis A (eds) Grasslands and woody plants in Europe. International symposium, Thessaloniki, May 27–29, 1999. European Grassland Federation, vol 4. Grassland Science in Europe, pp 99–103
Papachristou TG (2016) Greece’s grazing / forage resources for livestock production. In: Kyriazopoulos A, Lopez-Francos A, Porqueddu C, Sklavou P (eds) Ecosystem services and socio-economic benefits of Mediterranean grasslands. Zaragoza, CIHEAM, Options Méditerranéennes (Series A: Mediterranean seminars), vol 114, pp 29–42
Papachristou TG, Nastis AS (1993) Nutritive value of diet selected by goats grazing on kermes oak shrublands with different shrub and herbage cover in Northern Greece. Small Rumin Res 12:35–44
Papachristou TG, Papanastasis VP (1994) Forage value of Mediterranean deciduous woody fodder species and its implication to management of silvo-pastoral systems for goats. Agrofor Syst 27:269–282
Papachristou TG, Platis PD, Papanastasis VP (1996) Forage production and small ruminant grazing responses in Mediterranean shrublands as influenced by the reduction of shrub cover. Agrofor Syst 35:225–238
Papachristou TG, Platis PD, Papanastasis VP, Tsiouvaras CN (1999) Use of deciduous woody species as a diet supplement for goats grazing Mediterranean shrublands during the dry season. Anim Feed Sci Technol 80:267–279
Papachristou TG, Platis PD (2011) Intake by goats browsing kermes oak alone or choices of different browse combinations: implications for Mediterranean grazing systems. Rangel J 33:221–227
Papachristou T, Platis P, Spanos I, Mantzanas K, Samara T, Chavales E, Papachristou I, Bataka A, Vogiatzis D (2014) Final report of the research project: monitoring of growth and ecological characteristics of woody plants planted for environmental reclamation and forest stand establishment using for forest and livestock production (in Greek)
Papanastasis VP (1982) Production of natural grasslands in relation to air temperature and precipitation in Northern Greece (in Greek with English abstract). Dissertation, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki
Papanastasis VP, Platis PD, Dini-Papanastasi O (1997) Productivity of deciduous woody and fodder species in relation to air temperature and precipitation in a Mediterranean environment. Agrofor Syst 37:187–198
Papanastasis VP, Platis PD, Dini-Papanastasi O (1998) Effects of age and frequency of cutting on productivity of Mediterranean deciduous fodder tree and shrub plantations. For Ecol Manag 110:283–292
Papanastasis VP, Tsiouvaras KN, Dini-Papanastasi O, Vaitsis T, Stringi L, Cereti CF, Dupraz C, Armand D, Meuret M, Olea L (1999) Selection and utilization of cultivated fodder trees and shrubs in the Mediterranean Region. Cahiers Options Mediterraneennes, SERIE B: Etudes et Recherches, No 23
Pfister JA, Malechek JC, Balph DF (1988) Foraging behaviour of goats and sheep in the Caatinga of Brazil. J Appl Ecol 25:379–388
Piotto D, Montagnini F, Ugalde L, Kanninen M (2003) Growth and effects of thinning of mixed and pure plantations with native trees in humid tropical Costa Rica. For Ecol Manag 177:427–439
Platis PD, Papanastasis VP, Papachristou TG, Tsiontsis AI, Kandrelis SS (2003) Seasonal changes characteristics in the forage quality and quantity of the pseudoalpine and low grasslands (in Greek with English summary). In: Platis P, Papachristou T (eds) Rangeland management and development of mountainous areas. Proceedings of the 3rd Panhellenic Congress, Karpenissi, September 4–6, 2002. Hellenic rangeland and pasture society and Directorate general for the development and protection of forests and naturally environment, No 10, pp 161–172
Platis P, Papachristou T, Spanos I, Meliadis I, Kazantzidis S, Chalivopoulos G, Giakzidis G, Mantzanas K (2011) Landscaping design for vegetation reclamation of the lignite mines in Ptolemaida, Kozani, Greece. Forest Research Institute, Thessaloniki (in Greek)
Pyšek P, Lambdon PW, Arianoutsou M, Kühn I, Pino J, Winter M (2009) Alien vascular plants of Europe. In: Nentwig W (ed) Handbook of alien species in Europe, DAISIE. Invading nature: Springer series in invasion ecology, vol 3. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 43–61
R Core Team (2020) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/
Ramírez RG, Loyo A, Mora R, Sanchez EM, Chaire A (1991) Forage intake and nutrition of range goats in a shrubland in northeastern Mexico. J Anim Sci 69:879–885
Rédei K, Melby H (2000) Effect of thinning on the diameter increment in black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.) stands. Silva Gaildavensis 65:115–127
Rédei K, Bakti B, Kiss T, Takács M, Keserű Z (2018) Yield and crown structure characteristics in a black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.) stand: a case study—short communication. J For Sci 64:96–100
Roberts SD, Harrington CA (2008) Individual tree growth response to variable-density thinning in coastal Pacific Northwest forests. For Ecol Manag 255:2771–2781
Ryan MG, Binkley D, Fownes JH (1997) Age-related decline in forest productivity: pattern and process. In: Begon M, Fitter AH (eds) Advances in ecological research. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 213–262
Sanon HO, Kaboré-Zoungrana C, Ledin I (2007) Behaviour of goats, sheep and cattle and their selection of browse species on natural pasture in a Sahelian area. Small Rumin Res 67:64–74
Short HL, Blair RM, Segelquist CA (1974) Fiber composition and forage digestibility by small ruminants. J Wildl Manag 38:197–202
Snyder LJU (2003). Evaluation of Robinia pseudoacacia L. as browse for meat goat production in the Southestern USA. Dissertation, University of North Carolina, USA
Son Y, Lee YY, Jun YC, Kim Z-S (2004) Light availability and understory vegetation four years after thinning in a Larix leptolepis plantation of central Korea. J For Res 9:133–139
Steel RGD, Dickey DA, Torrie JH (1997) Principles and procedures of statistics: a biometrical approach, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill Book Co Inc, New York
Unruh LJ, Luginbuhl JM, Mueller, JP (2001) Intake and digestibility of black locust foliage fed to growing goat wethers. In: Gomide JA, Mattos WRS (eds) Grassland ecosystems: an outlook into the 21st century. XIX International Grassland Congress, 10–21 February 2001. San Paulo, Brazil, pp 413–414
Van Soest PJ (1994) Nutritional ecology of the ruminant. Cornell University Press, Ithaca
Vilà M, Basnou C, Gollasch S, Josefsson M, Pergl J, Scalerra R (2009) One hundred of the most invasive alien species in Europe. In: DAISIE (ed) DAISIE handbook of alien species in Europe invading nature: Springer series in invasion ecology, vol 3. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 265–268
Wienk CL, Sieg CH, McPherson GR (2004) Evaluating the role of cutting treatments, fire and soil seed banks in an experimental framework in ponderosa pine forests of the Black Hills, South Dakota. For Ecol Manag 192:375–393
Wilson AD (1969) A review of browse in the nutrition of grazing animals. J Range Manag 22:23–28
Wilson JR, Hatfield RD (1997) Structural and chemical changes of cell wall types during stem development: consequences for fibre degradation by rumen microflora. Aust J Agric Res 48:165–180
Zeide B (2001) Thinning and growth: a full turnaround. J For 99:20–25
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr Nikolaos Nanos for providing constructive comments on the analysis of the tree growth data, and Dimitrios Vogiatzis for his field assistance during the experiments.
Funding
This research was supported by grants from the Public Power Cooperation SA, Hellas (Contract No 435/2010). The Forest Research Institute, Hellenic Agricultural Organization, receives support from the Greek Ministry of Rural Development and Food.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TGP was involved in funding acquisition, conceptualization, methodology, analysis and interpretation of the data, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. PDP was involved in forage production experiment, methodology, analysis and interpretation of the data, critical revision of the article. IP was involved in nutritive value of forages experiment, methodology, forage sample preparation, laboratory analyses and interpretation of the data, critical revision of the article. TS was involved in tree growth and forage production experiments, field measurements, analysis and interpretation of the data, critical revision of the article. IS was involved in tree growth experiment, field measurements, analysis and interpretation of the data, critical revision of the article. EC was involved in tree growth and forage production experiments, field measurements. AB was involved in laboratory analyses. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Papachristou, T.G., Platis, P.D., Papachristou, I. et al. How the structure and form of vegetation in a black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.) silvopastoral system influences tree growth, forage mass and its nutrient content. Agroforest Syst 94, 2317–2330 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-020-00552-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-020-00552-z