Abstract
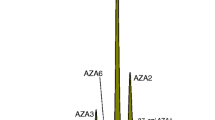
The production and certification of a series of azaspiracid (AZA) calibration solution reference materials is described. Azaspiracids were isolated from contaminated mussels, purified by preparative liquid chromatography and dried under vacuum to the anhydrous form. The purity was assessed by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The final concentration of each AZA in a CD3OH stock solution was determined by quantitative NMR spectroscopy. This solution was then diluted very accurately in degassed, high purity methanol to a concentration of 1.47 ± 0.08 μmol/L for CRM-AZA1, 1.52 ± 0.05 μmol/L for CRM-AZA2, and 1.37 ± 0.13 μmol/L for CRM-AZA3. Aliquots were dispensed into argon-filled glass ampoules, which were immediately flame-sealed. The calibration solutions are suitable for method development, method validation, calibration of liquid chromatography or mass spectrometry instrumentation and quality control of shellfish monitoring programs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
McMahon T, Silke J (1996) Winter toxicity of unknown aetiology in mussels. Harmful Algae News 14
Satake M, Ofuji K, James K, Furey A, Yasumoto T (1998) New toxic event caused by Irish mussels. In: Reguera B BJ, Fernandez ML, Wyatt T (ed) Harmful Algae. Santiago de Compostela; Xunta de Galicia and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO, p 2
Satake M, Ofuji K, Naoki H, James KJ, Furey A, McMahon T, Silke J, Yasumoto T (1998) Azaspiracid, a new marine toxin having unique spiro ring assemblies, isolated from Irish mussels, Mytilus edulis. J Am Chem Soc 120:9967–9968
Ofuji K, Satake M, McMahon T, Silke J, James K, Naoki H, Oshima Y, Yasumoto T (1999) Two analogs of azaspiracid isolated from mussels, Mytilus edulis, involved in human intoxication in Ireland. Nat Toxins 7:4
James KJ, Sierra MD, Lehane M, Magdalena AB, Furey A (2003) Detection of five new hydroxyl analogues of azaspiracids in shellfish using multiple tandem mass spectrometry. Toxicon 41:277–283
Rehmann N, Hess P, Quilliam MA (2008) Discovery of new analogs of the marine biotoxin azaspiracid in blue mussels (Mytilus edulis) by ultra-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 22:549–558
Tillmann U, Elbrachter M, Krock B, John U, Cembella A (2009) Azadinium spinosum gen. et sp nov (Dinophyceae) identified as a primary producer of azaspiracid toxins. Eur J Phycol 44:63–79
Krock B, Tillmann U, John U, Cembella AD (2009) Characterization of azaspiracids in plankton size-fractions and isolation of an azaspiracid-producing dinoflagellate from the North Sea. Harmful Algae 8:254–263
McCarron P, Kilcoyne J, Miles CO, Hess P (2009) Formation of azaspiracids-3,-4,-6, and-9 via decarboxylation of carboxyazaspiracid metabolites from shellfish. J Agric Food Chem 57:160–169
Amzil Z, Sibat M, Royer F, Savar V (2008) First report on azaspiracid and yessotoxin groups detection in French shellfish. Toxicon 52:39–48
Furey A, Moroney C, Magdalena AB, Saez MJF, Lehane M, James KJ (2003) Geographical, temporal, and species variation of the polyether toxins, azaspiracids, in shellfish. Environ Sci Technol 37:3078–3084
Vale P, Bire R, Hess P (2008) Confirmation by LC-MS/MS of azaspiracids in shellfish from the Portuguese north-western coast. Toxicon 51:1449–1456
Taleb H, Vale P, Amahir R, Benhadouch A, Sagou A, Chafik R (2006) First detection of azaspiracids in mussels in North West Africa. J Shellfish Res 25:1067–1070
European Food Safety Authority Marine biotoxins in shellfish - Azaspiracid group, Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Contaminants in the Food chain (2008). EFSA Journal 723:1-52
Ito E, Satake M, Ofuji K, Kurita N, McMahon T, James K, Yasumoto T (2000) Multiple organ damage caused by a new toxin azaspiracid, isolated from mussels produced in Ireland. Toxicon 38:917–930
Twiner MJ, Hess P, Dechraoui MYB, McMahon T, Samons MS, Satake M, Yasumoto T, Ramsdell JS, Doucette GJ (2005) Cytotoxic and cytoskeletal effects of azaspiracid-1 on mammalian cell lines. Toxicon 45:891–900
Twiner MJ, Ryan JC, Morey JS, Smith KJ, Hammad SM, Van Dolah FM, Hess P, McMahon T, Satake M, Yasumoto T, Doucette GJ (2008) Transcriptional profiling and inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis in human T lymphocyte cells by the marine toxin azaspiracid. Genomics 91:289–300
Hess P, Butter T, Petersen A, Silke J, McMahon T (2009) Performance of the EU-harmonised mouse bioassay for lipophilic toxins for the detection of azaspiracids in naturally contaminated mussel (Mytilus edulis) hepatopancreas tissue homogenates characterised by liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Toxicon 53:713–722
Twiner MJ, Rehmann N, Hess P, Doucette GJ (2008) Azaspiracid shellfish poisoning: a review on the chemistry, ecology, and toxicology with an emphasis on human health impacts. Mar Drugs 6:39–72
Regulation (EC) Nº 853/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 laying down specific hygiene rules for on the hygiene of foodstuffs. Official Journal of the European Union L 139/55
DG Sanco (EU Directorate General for Consumer Health and Protection). Report of the meeting of the Working Group on Toxicology of DSP and AZP, 21 to 23rd May 2001, Brussels.
ISO/IEC 17025:2005 General requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories. 2nd edn. International Organizaiton for Standardization (ISO), Geneva, Switzerland
Burton I, Quilliam MA, Walter JA (2005) Quantitative 1H NMR with external standards: use in preparation of calibration solutions for algal toxins and other natural products. Anal Chem 77:3123–3131
Quilliam MA, Wechsler D, Fraser H (2003) Analysis of Natural Toxins by Liquid Chromatography and Chemiluminescent Nitrogen Detection, HABTech 2003. Workshop, Nelson, New Zealand, pp 103–106
Ellison SLR, Burke S, Walker RF, Heydorn K, Mansson M, Pauwels J, Wegscheider W, te Nijenhuis B (2001) Uncertainty for reference materials certified by interlaboratory study: Recommendations of an international study group. Accredit Qual Assur 6:274–277
Linsinger TPJ, van der Veen AMH, Gawlik B, Pauwels J, Lamberty A (2004) Planning and combining of isochronous stability studies of CRMs. Accredit Qual Assur 9:464–472
Linsinger TPJ, Pauwels J, Lamberty A, Schimmel H, van der Veen AMH, Siekmann L (2001) Estimating the uncertainty of stability for matrix CRMs. Fresenius J Anal Chem 370:183–188
McCarron P, Emteborg H, Hess P (2007) Freeze-drying for the stabilisation of shellfish toxins in mussel tissue (Mytilus edulis) reference materials. Anal Bioanal Chem 387:2475–2486
ISO Guide 35 (2006) Reference materials - General and statistical principles for certification. International Organizaiton for Standardization (ISO), Geneva, Switzerland
Ciardullo S, Held A, D'Amato M, Emons H, Caroli S (2005) Homogeneity and stability study of the candidate reference material Adamussium colbecki for trace elements. J Environ Monit 7:1295–1298
Acknowledgments
The first two authors contributed equally to this work. The authors would like to thank all members of the NRC Certified Reference Materials Program for assistance with ampouling the AZA calibration solutions. Funding for materials retrieval and isolation of AZAs was provided by the Irish National Development Plan through the ASTOX project (ST/02/02, 2003–2007), and the ASTOX2 project (Irish National Development Plan 2007–2013, grant number PBA/AF/08/001(01)). This is NRC publication number 51766.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perez, R.A., Rehmann, N., Crain, S. et al. The preparation of certified calibration solutions for azaspiracid-1, -2, and -3, potent marine biotoxins found in shellfish. Anal Bioanal Chem 398, 2243–2252 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-4161-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-4161-2