Abstract
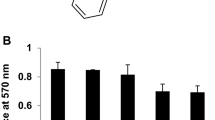
Purmorphamine is a purine analog and it affects osteogenesis, in part, through the modulation of Sonic Hedgehog signaling pathway. However, the underlying mechanism has remained elusive. Previously, we identified two purmorphamine derivatives that modulate the expression of osteogenic markers includingRunx2, Dlx2 andHes1. However, the extents of osteogenesis varied depending on the assay employed, and this necessitates the identification of reliable markers. Here, we report that the expression of osteocalcin was most sensitive to the treatment of purmorphamine derivatives among genes we analyzed by RT-PCR. Purmorphamine derivatives differentially modulated the expression of early and late osteogenic markers; alkaline phosphatase and osteocalcin gene respectively. In addition, the expression of osteocalcin is also modulated differentially by purmorphamine derivatives over time. Although JNK activity is reported to be necessary for osteocalcin expression, its requirement varied among purmorphamine derivatives. Also the overall cytotoxic response to purmorphamine derivatives appeared slightly different.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aikin RA, Ayers KL andTherond PP (2008) The role of kinases in the Hedgehog signalling pathway. EMBO Rep. 9: 330–336.
Akiyama H, Chaboissier MC, Martin JF, Schedl A andde CB (2002) The transcription factor Sox9 has essential roles in successive steps of the chondrocyte differentiation pathway and is required for expression of Sox5 and Sox6. Genes Dev. 16: 2813–2828.
Beloti MM, Bellesini LS andRosa AL (2005) Purmorphamine enhances osteogenic activity of human osteoblasts derived from bone marrow mesenchymal cells. Cell Biol. Int. 29: 537–541.
Briscoe J (2006) Agonizing hedgehog. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2: 10–11.
Cancedda R, Castagnola P, Cancedda FD, Dozin B andQuarto R (2000) Developmental control of chondrogenesis and osteogenesis. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 44: 707–714.
Chari NS andMcDonnell TJ (2007) The sonic hedgehog signaling network in development and neoplasia. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 14: 344–352.
Cohen MM Jr (2006) The new bone biology: pathologic, molecular, and clinical correlates. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 140: 2646–2706.
Eames BF, de la FL andHelms JA (2003) Molecular ontogeny of the skeleton. Birth Defects Res. C. Embryo. Today 69: 93–101.
Guicheux J, Lemonnier J, Ghayor C, Suzuki A, Palmer G andCaverzasio J (2003) Activation of p38 mitogenactivated protein kinase and c-Jun-NH2- terminal kinase by BMP-2 and their implication in the stimulation of osteoblastic cell differentiation. J. Bone Miner. Res. 18: 2060–2068.
Hall BK andMiyake T (1992) The membranous skeleton: the role of cell condensations in vertebrate skeletogenesis. Anat. Embryol. (Berl) 186: 107–124.
Jenkins D (2009) Hedgehog signalling: emerging evidence for non-canonical pathways. Cell Signal. 21: 1023–1034.
Karsenty G andWagner EF (2002) Reaching a genetic and molecular understanding of skeletal development. Dev. Cell 2: 389–406.
Kronenberg HM (2003) Developmental regulation of the growth plate. Nature 423: 332–336.
Lee AJ, Hodges S andEastell R (2000) Measurement of osteocalcin. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 37 (Pt 4): 432–446.
Lee SJ, Lee HK, Cho SY, Choi JK, Shin HK, Kwak EJ, Cho MR, Kim HR, Kim SR, Kim YM, Park KJ andChoi JK (2008) Identification of osteogenic purmorphamine derivatives. Mol. Cells 26: 380–386.
Mukai T, Otsuka F, Otani H, Yamashita M, Takasugi K, Inagaki K, Yamamura M andMakino H (2007) TNFalpha inhibits BMP-induced osteoblast differentiation through activating SAPK/JNK signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 356: 1004–1010.
Shum L andNuckolls G (2002) The life cycle of chondrocytes in the developing skeleton. Arthritis Res. 4: 94–106.
Sinha S andChen JK (2006) Purmorphamine activates the Hedgehog pathway by targeting Smoothened. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2: 29–30.
Wu X, Ding S, Ding Q, Gray NS andSchultz PG (2002) A small molecule with osteogenesis-inducing activity in multipotent mesenchymal progenitor cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124: 14520–14521.
Wu X, Walker J, Zhang J, Ding S andSchultz PG (2004) Purmorphamine induces osteogenesis by activation of the hedgehog signaling pathway. Chem. Biol. 11: 1229–1238.
Yu S, Franceschi RT, Luo M, Zhang X, Jiang D, Lai Y, Jiang Y, Zhang J andXiao G (2008) Parathyroid hormone increases activating transcription factor 4 expression and activity in osteoblasts: requirement for osteocalcin gene expression. Endocrinology 149: 1960–1968.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, HR., Jeong, SH., Im, YS. et al. Modulation of osteocalcin expression by purmorphamine derivatives. Genes & Genomics 31, 261–266 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03191198
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03191198