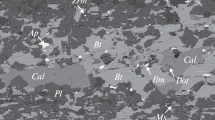
Abstract
Reactions and partial melting of peraluminous rocks in the presence of H2O-CO2–salt fluids under parameters of granulite-facies metamorphism were modeled in experiments on interaction between orthopyroxene–cordierite–biotite–plagioclase–quartz metapelite with H2O, H2O-CO2, H2O-CO2-NaCl, and H2O-CO2-KCl fluids at 600 MPa and 850°C. Rock melting in the presence of H2O and equimolar H2O-CO2 fluids generates peraluminous (A/CNK1 > 1.1) melts whose composition corresponds to magnesian calcic or calc–alkaline S-type granitoids. The melts are associated with peritectic phases: magnesian spinel and orthopyroxene containing up to 9 wt % Al2O3. In the presence of H2O-CO2-NaCl fluid, cordierite and orthopyroxene are replaced by the association of K-Na biotite, Na-bearing gedrite, spinel, and albite. The Na2O concentrations in the biotite and gedrite are functions of the NaCl concentrations in the starting fluid. Fluids of the composition H2O-CO2-KCl induce cordierite replacement by biotite with corundum and spinel and by these phases in association with potassium feldspar at X KCl = 0.02 in the fluid. When replaced by these phases, cordierite is excluded from the melting reactions, and the overall melting of the metapelite is controlled by peritectic reactions of biotite and orthopyroxene with plagioclase and quartz. These reactions produce such minerals atypical of metapelites as Ca-Na amphibole and clinopyroxene. The compositions of melts derived in the presence of salt-bearing fluids are shifted toward the region with A/CNK < 1.1, as is typical of so-called peraluminous granites of type I. An increase in the concentrations of salts in the fluids leads to depletion of the melts in Al2O3 and CaO and enrichment in alkalis. These relations suggest that the protoliths of I-type peraluminous granites might have been metapelites that were melted when interacting with H2O-CO2-salt fluids. The compositions of the melts can evolve from those with A/CNK > 1.1 (typical of S-type granites) toward those with A/CNK = 1.0–1.1 in response to an increase in the concentrations of alkali salts in the fluids within a few mole percent. Our experiments demonstrate that the origin of new mineral assemblages in metapelite in equilibrium with H2O-CO2-salt fluids is controlled by the activities of alkaline components, while the H2O and CO2 activities play subordinate roles. This conclusion is consistent with the results obtained by simulating metapelite mineral assemblages by Gibbs free energy minimization (using the PERPE_X software), as shown in log(\({a_{{H_2}O}}\))–log(\({a_{N{a_2}O}}\)) and log(\({a_{{H_2}O}}\))–log(\({a_{{K_2}O}}\)) diagrams.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta-Vigil, A., London, D., and Morgan, G.B., Experiments on the kinetics of partial melting of a leucogranite at 200 MPa H2O and 690–800°C: compositional variability of melts during the onset of H2O-saturated crustal anatexis, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 2006, vol. 151, pp. 539–551.
Aranovich, L.Y. and Safonov, O.G., Halogens in highgrade metamorphism, in The role of halogens in Terrestrial and Extraterrestrial Geochemical Processes, Harlov, D.E. and Aranovich, L.Y., Eds., 2017 (in press).
Aranovich, L.Ya., Zakirov, I.V., Sretenskaya, N.G., and Gerya, T.V., Ternary system H2O-CO2-NaCl at high T–P parameters: an empirical mixing model, Geochem. Int., 2010, vol. 48, no. 5, pp. 446–455.
Aranovich, L.Y., Shmulovich, K.I., and Fed’kin, V.V., The H2O and CO2 regime in regional metamorphism, Int. Geol. Rev., 1987, vol. 29, pp. 1379–1401.
Aranovich, L.Y. and Newton, R.C., H2O activity in concentrated KCl and KCl-NaCl solutions at high temperatures and pressures measured by the brucite–periclase equilibrium, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 1997, vol. 127, pp. 261–271.
Aranovich, L.Y., Newton, R.C., and Manning, C.E., Brine-assisted anatexis: experimental melting in the system haplogranite–H2O-NaCl-KCl at deep-crustal conditions, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2013, vol. 374, pp. 111–120.
Aranovich, L.Y., Makhluf, A.R., Manning, C.E., and Newton, R.C., Dehydration melting and the relationship between granites and granulites, Precambrian Res., 2014, vol. 253, pp. 26–37.
Beard, J. and Lofgren, G., Dehydration melting and watersaturated melting of basaltic and andesitic greenstones and amphibolites at 1, 3 and 6.9 kb, J. Petrol., 1991, vol. 32, pp. 365–402.
Bose, S., Fukuoka, M., Sengupta, P., and Dasgupta, S., Evolution of high-Mg–Al granulites from Sunkarametta, Eastern Ghats, India: evidence for a lower crustal heating–cooling trajectory, J. Metamorph. Geol., 2000, vol. 18, pp. 223–240.
Chappell, B.W., Aluminium saturation in I- and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites, Lithos, 1999, vol. 46, pp. 535–551.
Chappell, B.W. and White, A.J.R., Two contrasting granite types: 25 years later, Austral. J. Earth Sci., 2001, vol. 48, pp. 489–499.
Chappell, B.W., Bryant, C.J., and Wyborn, D., Peraluminous I-type granites, Lithos, 2012, vol. 153, pp. 142–153.
Clemens, J.D., Stevens, G., and Farina, F., The enigmatic source of I-type granites: the peritectic connexion, Lithos, 2011, vol. 126, pp. 174–181.
Connolly, J.A.D., Computation of phase equilibria by linear programming: a tool for geodynamic modeling and its application to subduction zone decarbonation, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2005, vol. 236, pp. 524–541.
Dasgupta, S., Sengupta, P., Sengupta, Pr., et al., Petrology of gedrite-bearing rocks in mid-crustal ductile shear zones from the Eastern Ghats Belt, India, J. Metamorph. Geol., 1999, vol. 17, pp. 765–778.
Franz, L. and Harlov, D.E., High-grade K-feldspar veining in granulites from the Ivrea–Verbano zone, northern Italy: fluid flow in the lower crust and implications for granulite facies genesis, J. Geol., 1998, vol. 106, pp. 455–472.
Frost, B.R., Barnes, C.G., Collins, W.J., et al., A geochemical classification for granitic rocks, J. Petrol., 2001, vol. 42, pp. 2033–2048.
Gardien, V., Thompson, A.B., and Ulmer, P., Melting of biotite + plagioclase + quartz gneisses: the role of H2O in the stability of amphibole, J. Petrol., 2000, vol. 41, pp. 651–666.
Gilbert, F., Guillaume, D., and Laporte, D., Importance of fluid immiscibility in the H2O-NaCl-CO2 system and selective CO2 entrapment in granulites: experimental phase diagram at 5–7 kbar, 900°C and wetting textures, Eur. J. Mineral., 1998, vol. 10, pp. 1109–1123.
Grew, E.S., Herd, R.K., and Marquez, N., Boron-bearing kornerupine from fiskenaesset, west Greenland: a reexamination of specimens from the type locality, Mineral. Mag., 1987, vol. 51, p. 695.
Hansen, E., Ahmed, K., and Harlov, D.E., Rb depletion in biotites and whole rocks across an amphibolite to granulite facies transition zone, Tamil Nadu, South India, Lithos, 2002, vol. 64, pp. 29–47.
Harlov, D.E., Fluid induced dehydration of mafic lower crust from amphibolite to granulite facies: nature and experiment, Amer. Geophys. Union, Fall Meeting 2004, vol. 85, p. 47.
Harlov, D.E., Petrological and experimental application of REE- and actinide-bearing accessory minerals to the study of Precambrian high-grade gneiss terranes, Origin and Evolution of Precambrian High-Grade Terrains, with Special Emphasis on the Limpopo Complex in Southern Africa, Van Reenen D.D., Kramers J.D., McCourt S., Perchuk L.L., Eds., Geol. Soc. Am. Mem., 2011, vol. 207, pp. 13–24.
Harlov, D.E. and Förster, H.-J., High-grade fluid metasomatism on both a local and regional scale: the Seward Peninsula, Alaska and the Val Strona di Omegna, Ivrea-Verbano zone, northern Italy. Part I: petrography and silicate mineral chemistry, J. Petrol., 2002, vol. 43, pp. 769–799.
Harlov, D.E. and Melzer, S., Experimental partitioning of Rb and K between phlogopite and concentrated (K, Rb)Cl brine: implication for the role of concentrated KCl brines in the depletion of Rb in phlogopite and the stability of phlogopite during charnockite genesis, Lithos, 2002, vol. 64, pp. 15–28.
Harlov, D.E., Hansen, E.C., and Bigler, C., Petrologic evidence for K-feldspar metasomatism in granulite facies rocks, Chem. Geol., 1998, vol. 151, pp. 373–386.
Harlov, D.E., Van den Kerkhof, A., and Johansson, L., Localized, solid-state dehydration associated with the Varberg charnockite intrusion, SW Sweden, Precambrian Res., 2014, vol. 253, pp. 50–62.
Hawthorne, F.C., Schindler, M., Abdu, Y., et al., The crystal chemistry of the gedrite-group amphiboles. II. Stereochemistry and chemical relations, Mineral. Mag., 2008, vol. 72, pp. 731–745.
Heinrich, W., Fluid immiscibility in metamorphic rocks, Rev. Mineral. Geochem., 2007, vol. 65, pp. 389–430.
Holland, T.J.B. and Powell, R., An improved and extended internally consistent thermodynamic dataset for phases of petrological interest, involving a new equation of state for solids, J. Metamorph. Geol., 2011, vol. 29, pp. 333–383.
Johannes, W., Melting of plagioclase–quartz assemblages at 2 kbar water pressure, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 1989, vol. 103, pp. 270–276.
Johnson, E.L., Experimentally determined limits for H2O–CO2–NaCl immiscibility in granulites, Geology, 1991, vol. 19, pp. 925–928.
Kanazawa, T., Tsunogae, T., Sato, K., and Santosh, M., The stability and origin of sodic gedrite in ultrahigh-temperature Mg–Al granulites: a case study from the Gondwana suture in southern India, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 2009, vol. 157, pp. 95–110.
Kelsey, D.E. and Hand, M., On ultrahigh temperature crustal metamorphism: phase equilibria, trace element thermometry, bulk composition, heat sources, timescales and tectonic settings, Geosci. Front., 2015, vol. 6, pp. 311–356.
Khodorevskaya L.I. Granitization of Amphibolites: 2. Characterization of Physical and Chemical Phenomena Related to Fluid Filtration through a Rock, Petrology, 2004, vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 282–295.
Khodorevskaya, L.I. and Aranovich, L.Ya., Experimental study of amphibole interaction with H2O–NaCl fluid at 900°C, 500 MPa: toward granulite facies melting and mass transfer, Petrology, 2016, vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 215–233.
Kilink, I.A. and Burnham, C.W., Partitioning of chloride between a silicate melt and coexisting aqueous phase from 2 to 8 kilobars, Econ. Geol., 1972, vol. 67, pp. 231–235.
Koester, E., Pawley, A.R., Fernandes, L.A., et al., Experimental melting of cordierite gneiss and the petrogenesis of syntranscurrent peraluminous granites in southern brazil, J. Petrol., 2002, vol. 43, pp. 1595–1616.
Koizumi, T., Tsunogae, T., and van Reenen, D.D., Fluid evolution of partially retrogressed pelitic granulite from the southern marginal zone of the Neoarchean Limpopo Complex, South Africa: evidence from phase equilibrium modeling, Precambrian Res., 2014, vol. 253, pp. 146–156.
Korikovsky, S.P. and Aranovich, L.Ya., Charnockitization and enderbitization of mafic granulites in the Porya Bay Area, Lapland Granulite Belt, southern Kola Peninsula: I. Petrology and geothermobarometry, Petrology, 2010, vol. 18, no. 4, pp. 320–349.
Korikovsky, S.P. and Aranovich, L.Ya., Charnockitization of feldspar-free orthopyroxene–clinopyroxene–phlogopite metaultramafite in the Lapland Granulite Belt, southern Kola Peninsula: compositional trends of rocks and minerals, P–T parameters, and fluid regime, Petrology, 2015, vol. 23, no. 3, pp. 189–226.
Korzhinskii, D.S., Role of alkalinity in the formation of charnockite gneisses, Tr. Vostochno-Sibirsk. Inst. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser. Geol., 1962, vol. 5, pp. 50–61.
Larikova, T.L. and Zaraisky, G.P., Experimental modeling of corona textures, J. Metamorph. Geol., 2009, vol. 27, pp. 139–151.
Manning, C.E., Thermodynamic modeling of fluid-rock interaction at mid-crustal and upper-mantle conditions, Rev. Mineral. Geochem., 2013, vol. 76, pp. 135–164.
Manning, C.E. and Aranovich, L.Y., Brines at high pressure and temperature: thermodynamic, petrological and geochemical effects, Precambrian Res., 2014, vol. 253, pp. 6–16.
Markl, G. and Bucher, K., Composition of fluids in the lower crust inferred from metamorphic salt in lower crustal rocks, Nature, 1998, vol. 391, pp. 781–783.
Newton, R.C., Simple-system mineral reactions and highgrade metamorphic fluids, Eur. J. Mineral., 1995, vol. 7, pp. 861–881.
Newton, R.C. and Manning, C.A., Role of saline fluids in deep-crustal and upper-mantle metasomatism: insights from experimental studies, Geofluids, 2010, vol. 10, pp. 58–72.
Newton, R.C., Smith, J.V., and Windley, B.F., Carbonic metamorphism, granulites and crustal growth, Nature, 1980, vol. 288, pp. 45–50.
Newton, R.C., Aranovich, L.Y., Hansen, E.C., and Vandenheuvel, B.A., Hypersaline fluids in Precambrian deepcrustal metamorphism, Precambrian Res., 1995, vol. 91, pp. 41–63.
Newton, R.C., Touret, J.L.R., and Aranovich, L.Y., Fluids and H2O activity at the onset of granulite facies metamorphism, Precambrian Res., 2014, vol. 253, pp. 17–25.
Nijland, T.G., Touret, J.L., and Visser, D., Anomalously low temperature orthopyroxene, spinel, and sapphirine occurrences in metasediments from the Bamble amphibolite-to-granulite facies transition zone (South Norway): possible evidence for localized action of saline fluids, J. Geol., 1998, vol. 106, pp. 575–590.
Patino Douce, A.E. and Harris, N., Experimental constraints on Himalayan anatexis, J. Petrol., 1998, vol. 39, pp. 689–710.
Patino Douce, A.E. and Johnston, A.D., Phase equilibria and melt productivity in the pelitic system: implications for the origin of peraluminous granitoids and aluminous granulites, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 1991, vol. 107, pp. 202–218.
Perchuk, L.L. and Gerya, T.V., Fluid control of charnockitization, Chem. Geol., 1993, vol. 175–186.
Perchuk L.L., Gerya T.V., and Korsman, K., Model of charnokitization of gneiss complexes, Petrologiya, 1994, vol. 2, no. 5, pp. 451–480.
Perchuk, L.L., Safonov, O.G., Gerya, T.V., et al., Mobility of components in metasomatic transformation and partial melting of gneisses: an example from Sri-Lanka, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 2000, vol. 140, pp. 212–232.
Pickering, J.M. and Johnston, D.A., Fluid-absent melting behavior of a two-mica metapelite: experimental constraints on the origin of Black Hills granite, J. Petrol., 1998, vol. 39, pp. 1787–1804.
Rajesh, H.M., Belyanin, G.A., Safonov, O.G., et al., Fluid-induced dehydration of the Paleoarchean Sand River biotite-hornblende gneiss, Central Zone, Limpopo Complex, South Africa, J. Petrol., 2013, vol. 54, pp. 41–74.
Ravindra-Kumar, G.R., Mechanism of arrested charnockite formation at Nemmara, Palghat region, southern India, Lithos, 2004, vol. 75, pp. 331–358.
Ryabchikov, I.D. and Hamilton, D.L., Possibility of separation of concentrated chloride solutions during crystallization of felsic magmas, Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1971, vol. 197, pp. 933–937.
Safonov, O.G., The role of alkalis in the formation of coronitic textures in metamangerites and metaanorthosites from the Adirondack Complex, United States, Petrology, 1998, vol. 6, no. 6, pp. 583–602.
Safonov, O.G. and Aranovich, L.Y., Alkali control of highgrade metamorphism and granitization, Geosci. Front., 2014, vol. 5, pp. 711–727.
Safonov, O.G., Kosova, S.A., and van Reenen, D.D., Interaction of biotite-amphibole gneiss with H2O–CO2-(K, Na)Cl fluids at 550 MPa and 750 and 800°C: experimental study and applications to dehydration and partial melting in the middle crust, J. Petrol., 2014a, vol. 55, pp. 2419–2456.
Safonov, O.G., Kovaleva, E.I., Kosova, S.A., et al., Experimental and petrological constraints on local-scale interaction of biotite–amphibole gneiss with H2O–CO2–(K, Na)Cl fluids at middle-crustal conditions: example from the Limpopo Complex, South Africa, Geosci. Front., 2012, vol. 3, pp. 829–841.
Safonov, O.G., Tatarinova, D.S., van Reenen, D.D., et al., Fluid-assisted interaction of peraluminous metapelites with trondhjemitic magma within the Petronella shear-zone, Limpopo Complex, South Africa, Precambrian Res., 2014, vol. 253, pp. 114–145.
Santosh, M., Carbonic metamorphism of charnockites in the southwestern Indian Shield: a fluid inclusion study, Lithos, 1986, vol. 19, pp. 1–10.
Shmulovich, K.I. and Graham, C.M., Melting of albite and dehydration of brucite in H2O–NaCl fluids to 9 kbars and 700–900°C: implications for partial melting and water activities during high pressure metamorphism, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 1996, vol. 124, pp. 370–382.
Shmulovich, K.I. and Graham, C.M., An experimental study of phase equilibria in the systems H2O-CO2–CaCl2 and H2O–CO2–NaCl at high pressures and temperatures (500–800°C, 0.5–0.9 GPa): geological and geophysical applications, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 2004, vol. 146, pp. 450–462.
Sisson, T.W., Ratajeski, K., Hankins, W.B., and Glazner, A.F., Voluminous granitic magmas from common basaltic sources, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 2005, vol. 148, pp. 635–661.
Skjerlie, K.P. and Douce, A.P., Anatexis of interlayered amphibolite and pelite at 10 kbar: effect of diffusion of major components on phase relations and melt fraction, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 1995, vol. 122, pp. 62–78.
Srikantappa, C. and Zargar, S.A., First report on the halitebearing fluid inclusions in the Precambrian granulites around Halaguru, Dharwar Craton, India, Ind. Mineral., 2009, vol. 43, pp. 77–80.
Touret, J.L.R., Fluid regime in southern Norway: the record of inclusions, The Deep Proterozoic Crust in the North Atlantic Provinces, Proc. NATO Adv. Study Inst. Ser., 1985, vol. C158, pp. 517–549.
Touret, J.L.R. and Huizenga, J.M., Fluids in granulites, Origin and Evolution of Precambrian high-grade terrans, with special emphasis on the Limpopo Complex in Southern Africa, Van Reenen D.D., Kramers J.D., McCourt S., and Perchuk L.L., Eds., Geol. Soc. Am. Mem., 2011, vol. 207, pp. 25–37.
Touret, J.L.R. and Nijland, T.G., Prograde, peak and retrograde metamorphic fluids and associated metasomatism in upper amphibolite to granulite facies transition zones, in Metasomatism and the Chemical Transformation of Rock, Berlin–Heidelberg: Springer, 2013, pp. 415–469.
Tropper, P., Manning, C.E., and Harlov, D.E., and Y transport during high-grade metamorphism, Chem. Geol., 2011, vol. 282, pp. 58–66.
Tropper, P., Manning, C.E., and Harlov, D.E., Experimental determination of CePO4 and YPO4 solubilities in H2O–NaF at 800°C and 1 GPa: implications for rare earth element transport in high-grade metamorphic fluids, Geofluids, 2013, vol. 13, pp. 372–380.
Tsunogae, T., Santosh, M., and Shimpo, M., Sodic gedrite in ultrahigh-temperature Mg–Al-rich rocks from the Palghat–Cauvery shear zone system, southern India, J. Mineral. Petrol. Sci., 2007, vol. 102, pp. 39–43.
van Reenen, D.D., Hydration of cordierite and hypersthene and a description of the retrograde orthoamphibole isograd in the Limpopo Belt, South Africa, Am. Mineral., 1986, vol. 71, pp. 900–915.
van Reenen, D.D., Smit, C.A., Perchuk, L.L., et al., Thrust exhumation of the Neoarchean ultrahigh-temperature southern marginal zone, Limpopo Complex: convergence of decompression–cooling paths in the hanging wall and prograde P-T paths in the footwall, Geol. Soc. Am. Mem., 2011, vol. 207, pp. 189–212.
Vielzeuf, D. and Montel, J.M., Partial melting of metagreywackes. Part I. Fluid-absent experiments and phase relationships, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 1994, vol. 117, pp. 375–393.
Visser, D., Nijland, T.G., Lieftink, D.J., and Maijer, C., The occurrence of preiswerkite in a tourmaline–biotite–scapolite rock from Blengsvatn, Norway, Am. Mineral., 1999, vol. 84, pp. 977–982.
Watson, E.B. and Brenan, J.M., Fluids in the lithosphere, 1. Experimentally determined wetting characteristics of CO2–H2O fluids and their implications for fluid transport, host-rock physical properties, and fluid inclusion formation, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1987, vol. 85, pp. 594–615.
Webster, J.D., Exsolution of magmatic volatile phases from Cl-enriched mineralizing granitic magmas and applications for ore metal transport, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1997, vol. 61, pp. 1017–1029.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © O.G. Safonov, S.A. Kosova, 2017, published in Petrologiya, 2017, Vol. 25, No. 5, pp. 461–490.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Safonov, O.G., Kosova, S.A. Fluid–mineral reactions and melting of orthopyroxene–cordierite–biotite gneiss in the presence of H2O-CO2-NaCl and H2O-CO2-KCl fluids under parameters of granulite-facies metamorphism. Petrology 25, 458–485 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S086959111705006X
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S086959111705006X