Abstract
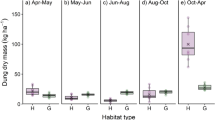
Increases in the deposition of nitrogen affect biodiversity and the composition of natural vegetation. A significant amount of this nitrogen may originate not only from intensive agricultural and livestock farming, but also from wild ungulates whose abundance and area of distribution are currently increasing in the Iberian Peninsula. In this study we have estimated the abundance of two species of wild ungulates (red deer and wild boar) and the amount of nitrogen contained in their droppings and in the grass. We have also recorded the herbaceous community. The results show that the density of these ungulates is positively correlated to an increase in the grass nitrogen, which adversely affects the percentage of leguminosae in pastures. These results suggest that high densities of ungulates may be affecting plant communities by increasing the amount of nitrogen as a result the deposition of droppings. The current system of big game management should therefore be reviewed to make it compatible with the conservation of plant communities and small herbivore species that may be negatively affected by changes in pasture quality and quantity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acevedo P, Vicente J, Hofle U, Cassinello J, Ruiz-Fons F, Gortázar C (2007) Estimation of European wild boar relative abundance and aggregation: a novel method in epidemiological risk assessment. Epidemiol Infect 135(3):519–527
Acevedo P, Ruiz-Fons F, Vicente J, Reyes-Garcia AR, Alzaga V, Gortazar C (2008) Estimating red deer abundance in a wide range of management situations in Mediterranean habitats. J Zool 276(1):37–47
Acevedo P, Santos JP, Real R, Vicente J (2011) Evaluación del estado de la población de cabra montés de los montes de toledo: relaciones con el ciervo. Pirineos. Rev de Ecol de Mon 166:29–49
Adler P, Raff D, Lauenroth W (2001) The effect of grazing on the spatial heterogeneity of vegetation. Oecologia 128(4):465–479
Adler PB, Milchunas DG, Sala OE, Burke IC, Lauenroth WK (2005) Plant traits and ecosystem grazing effects: comparison of US sagebrush steppe and Patagonian steppe. Ecol Appl 15(2):774–792
Affleck DL, Gregoire TG, Valentine HT (2005) Design unbiased estimation in line intersect sampling using segmented transects. Environ Ecol Stat 12(2):139–154
Bakker ES, Ritchie ME, Olff H, Milchunas DG, Knops JM (2006) Herbivore impact on grassland plant diversity depends on habitat productivity and herbivore size. Ecol Lett 9(7):780–788
Barabesi L (2007) Some comments on design-based line-intersect sampling with segmented transects. Environ Ecol Stat 14(4):483–494
Barrio IC, Bueno CG, Tortosa FS (2010) Alternative food and rabbit damage in vineyards of southern Spain. Agric Ecosyst Environ 138(1):51–54
Barrio IC, Bueno CG, Villafuerte R, Tortosa FS (2013) Rabbits, weeds and crops: can agricultural intensification promote wildlife conflicts in semiarid agro-ecosystems? J Arid Environ 90:1–4
Bodelier PLE, Laanbroek HJ (2004) Nitrogen as a regulatory factor of methane oxidation in soils and sediments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 47(3):265–277
Bosch J, Peris S, Fonseca C, Martínez M, De La Torre A, Iglesias I, Muñoz MJ (2012) Distribution, abundance and density of the wild boar on the Iberian Peninsula, based on the CORINE program and hunting statistics. Folia Zool 61(2):138–151
Bowman WD, Conant RT (1994) Shoot growth dynamics and photosynthetic response to increased nitrogen availability in the alpine willow Salix glauca. Oecologia 97(1):93–99
Buckland ST, Anderson DR, Burnham KP, Laake JL, Borchers DL, Thomas L (2004) Introduction to distance sampling: estimating abundance of biological population. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Bueno CG, Alados CL, Gómez-García D, Barrio IC, García-González R (2009) Understanding the main factors in the extent and distribution of wild boar rooting on alpine grasslands. J Zool 279(2):195–202
Carpio AJ, Guerrero-Casado J, Ruiz-Aizpurua L, Tortosa FS, Vicente J (2014a) Is high abundance of wild ungulates in a Mediterranean region compatible with the European rabbit? Wildl Biol 20(3):161–166
Carpio AJ, Guerrero-Casado J, Tortosa FS, Vicente J (2014b) Predation of simulated red-legged partridge nests in big game estates from South Central Spain. Eur J Wildl Res 60(2):391–394
Côté SD, Rooney TP, Trembley JP, Dussault C, Waller DM (2004) Ecological impacts of deer overabundance. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 35(1):113–147
Cuevas MF, Novillo A, Campos C, Dacar MA, Ojeda RA (2010) Food habits and impact of rooting behaviour of the invasive wild boar, Sus scrofa, in a protected area of the Monte Desert Argentina. J Arid Environ 74(11):1582–1585
Danell K, Bergstrom R, Edenius L, Ericsson G (2003) Ungulates as drivers of tree population dynamics at module and genet levels. For Ecol Manag 181(1–2):67–76
Fernández-Olalla M, Muñoz-Igualada J, Martínez-Jauregui M, Rodríguez-Vigal C, Miguel-Ayanz AS (2006) Selección de especies y efecto del ciervo (Cervus elaphus L.) sobre arbustedos y matorrales de los Montes de Toledo, España central. Invest Agrar: Sist Recur For 15(3):329–338
Forrester TD, Wittmer HU (2013) A review of the population dynamics of mule deer and black-tailed deer Odocoileus hemionus in North America. Mammal Rev 43(4):292–308
Garbarino M, Lingua E, Subira MM, Motta R (2011) The larch wood pasture: structure and dynamics of a cultural landscape. Eur J For Res 130(4):491–502
García D, Rodríguez-Cabal MA, Amico GC (2009) Seed dispersal by a frugivorous marsupial shapes the spatial scale of a mistletoe population. J Ecol 97(2):217–229
González-Hernández MP, Starkey EE, Karchesy J (2000) Tannins in plants of Galician forests (NW Spain). Implications in pasture ecosystems management. Pastagens e Forrag 21:683–688
Gregoire TG, Valentine HT (2003) Line intersect sampling: ell-shaped transects and multiple intersections. Environ Ecol Stat 10(2):263–279
Hamel S, Garel M, Festa-Bianchet M, Gaillard JM, Côté SD (2009) Spring Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) predicts annual variation in timing of peak faecal crude protein in mountain ungulates. J Appl Ecol 46(3):582–589
Hornung M, Sutton MA (1995) Impacts of nitrogen deposition in terrestrial ecosystems. Atmos Environ 29:3395–3396
Horsley SB, Stout SL, DeCalesta DS (2003) White-tailed deer impact on the vegetation dynamics of a northern hardwood forest. Ecol Appl 13(1):98–118
Howe HF, Brown JS, Zorn‐Arnold B (2002) A rodent plague on prairie diversity. Ecol Lett 5(1):30–36
Hristov AN, Hanigan M, Cole A, Todd R, McAllister TA, Ndegwa PM, Rotz A (2011) Ammonia emissions from dairy farms and beef feedlots. Can J Anim Sci 91(1):1–35
Kariuki IW, Norton BW (2008) The digestion of dietary protein bound by condensed tannins in the gastro-intestinal tract of sheep. Anim Feed Sci Tech 142(3–4):197–209
Knapp AK, Hoover DL, Blair JM, Buis G, Burkepile DE, Chamberlain A, Zinn A (2012) A test of two mechanisms proposed to optimize grassland aboveground primary productivity in response to grazing. J. Plant Ecol. doi:10.1093/jpe/rts020
Knight TM (2003) Effects of herbivory and its timing across populations of Trillium grandiflorum (Liliaceae). Am J Bot 90(8):1207–1214
Kuijper DPJ (2011) Lack of natural control mechanisms increases wildlife-forestry conflict in managed temperate European forest systems. Eur J For Res 130:895–909
Kuijper DPJ, Cromsigt J, Churski M, Adam B, Jedrzejewska B, Jedrzejewski W (2009) Do ungulates preferentially feed in forest gaps in European temperate forest? For Ecol Manag 258(7):1528–1535
Lawton JH (1994) What do species do in ecosystems? Oikos 71:367–374
Lazo A, Delecourt C, Soriguer RC (1992) Evaluation of hare abundance allowed by their use of attraction points. Z Saugetierkd 57:373–379
Massey BN, Weckerly FW, Vaughn CE, McCullough DR (1994) Correlations between faecal nitrogen and diet composition in free-ranging black-tailed deer. Southwest Nat 39(2):165–170
Mohr D, Cohnstaedt LW, Topp W (2005) Wild boar and red deer affect soil nutrients and soil biota in steep oak stands of the Eifel. Soil Biol Biochem 37(4):693–700
Monzón A, da Silva SV, Manso FT (2012) Integrating the deer (Cervus elaphus) in the Portuguese forests: impacts and new challenges for forest certification. For Ecol Manag 267:1–6
Moreno G, Pulido FJ (2009) The functioning, management and persistence of dehesas. In: Rigueiro-Rodríguez A, McAdam J, Mosquera-Losada MR (eds) Agroforestry in Europe. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 127–160
Nelson F, Kerasote T, King RJH, Bateson P, Eves HE, Wolf CM, Yaich SC (2005) The ethics of hunting. Front Ecol Environ 3(7):392–397
Olff H, Ritchie ME (1998) Effects of herbivores on grassland plant diversity. Trends Ecol Evol 13(7):2611–2651
Palacio S, Bueno CG, Azorín J, Maestro M, Gómez-García D (2013) Wild-boar disturbance increases nutrient and C stores of geophytes in subalpine grasslands. Am J Bot 100(9):1790–1799
Pastor J, Naiman RJ (1992) Selective foraging and ecosystem processes in boreal forests. Am Nat 139(4):690–705
Peco B, Sánchez AM, Azcárate F (2006) Abandonment in grazing systems: consequences for vegetation and soil. Agric Ecosyst Environ 113(1–4):284–294
Perea R, Gil L (2014) Tree regeneration under high levels of wild ungulates: the use of chemically vs. physically-defended shrubs. For Ecol Manag 312:47–54
Pitcairn CER, Leith ID, Sheppard LJ, Sutton MA, Fowler D, Munro RC, Tang S, Wilson D (1998) The relationship between nitrogen deposition, species composition and foliar nitrogen concentrations in woodland flora in the vicinity of livestock farms. Environ Pollut 102(1):41–48
Powlson DS (2000) Tackling nitrate from agriculture. Soil Use Manag 16:141–141
Ritchie ME, Tilman D (1995) Responses of legumes to herbivores and nutrients during succession on a nitrogen-poor soil. Ecology 76:2648–2655
Ritchie ME, Tilman D, Knops JMH (1998) Herbivore effects on plant and nitrogen dynamics in oak savanna. Ecology 79:165–177
Rodríguez-Hidalgo P, Gortazar C, Tortosa FS, Rodriguez-Vigal C, Fierro Y, Vicente J (2010) Effects of density, climate, and supplementary forage on body mass and pregnancy rates of female red deer in Spain. Oecologia 164(2):389–398
Seagle SW, Liang SY (2001) Application of a forest gap model for prediction of browsing effects on riparian forest succession. Ecol Model 144(2–3):213–229
Simonne AH, Simonne EH, Eitenmiller RR, Mills HA, Cresman CP (1997) Could the dumas method replace the Kjeldahl digestion for nitrogen and crude protein determinations in foods? J Sci Food Agric 73(1):39–45
Spanish Enviromental Ministery (2002) Plan forestal español (spanish forest planning). Secretaría General de Medio Ambiente, Ministerio de Medio Ambiente, Madrid
Tilman D (1988) Plant strategies and the dynamics and structure of plant communities. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Torres-Porras J (2009) El ciervo ibérico (Cervus elaphus hipanicus) en ecosistemas Mediterráneos: ecología y gestión cinegética. Universidad de Córdoba, Cordoba
Vaieretti MV, Cingolani AM, Harguindeguy NP, Cabido M (2013) Effects of differential grazing on decomposition rate and nitrogen availability in a productive mountain grassland. Plant Soil 371(1–2):675–691
Van Den Bos J, Bakker JP (1990) The development of vegetation patterns by cattle grazing at low stocking density in the Netherlands. Biol Conserv 51(4):263–272
Wu H, Dannenmann M, Fanselow N, Wolf B, Yao Z, Wu X, Brüggemann N, Zheng X, Han X, Dittert K, Butterbach-Bahl K (2011) Feedback of grazing on gross rates of N mineralization and inorganic N partitioning in steppe soils of Inner Mongolia. Plant Soil 340(1–2):127–139
Yates CO, Norton DA, Hobbs RJ (2000) Grazing effects on plant cover, soil and microclimate in fragmented woodlands in South Western Australia: implication for relation. Austral Ecol 25(1):36–47
Zaragoza-Castells J, Sánchez-Gómez D, Hartley IP, Matesanz S, Valladares F, Lloyd J, Atkin OK (2008) Climate-dependent variations in leaf respiration in a dry-land, low productivity Mediterranean forest: the importance of acclimation in both high-light and shaded habitats. Funct Ecol 22:172–184
Zuur AF, Ieno EN, Walker NJ, Saveliev AA, Smith GM (2009) Mixed effects models and extensions in ecology with R. Springer, New York
Acknowledgments
We should like to thank E. López and the students Oscar, David and Macarena for their help in collecting field data. We are also grateful to the estate keepers for their hospitality and assistance in the field work, and to the Andalucía Autonomous Government’s Environmental Council for financing this work via a project to improve the habitat of the black vulture in Córdoba province, thanks to which we have been able to carry out this work. Our thanks are also due to the editor and the anonymous reviewers for their thorough suggestions and comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carpio, A.J., Oteros, J., Lora, Á. et al. Effects of the overabundance of wild ungulates on natural grassland in Southern Spain. Agroforest Syst 89, 637–644 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-015-9801-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-015-9801-2