Abstract
Purpose
ORM1 is a plasma drug binding protein. Its polymorphism rs17650 (*S>*F) has been reported to be an important factor affecting the binding ability and effect of antiretroviral protease inhibitors. The aim of this study was to determine whether the ORM1 rs17650 polymorphism also influences warfarin therapy.
Methods
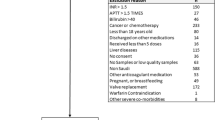
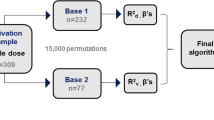
A total of 191 Chinese patients with steady-dose warfarin therapy were enrolled in this study. The patients were studied for warfarin maintenance dose, the ORM1 rs17650 polymorphism, and two polymorphisms previously demonstrated to affect warfarin response [CYP2C9 rs1057910 (*3) and VKORC1 rs7294 (−1639 G>A)].
Results
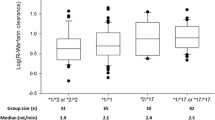
Warfarin dose was partially correlated with the VKORC1 rs7294, CYP2C9 rs1057910 and ORM1 rs17650 polymorphisms. Patients carrying the wild-type of these three genes (n = 96) took a mean dose of 3.0 ± 1.1 mg warfarin, which was significantly higher than that taken by the 52 *S patients (2.7 ± 0.7) and 11 *S*S patients (2.5 ± 0.6 mg) (p = 0.048).
Conclusion
We identified ORM1 as another polymorphic gene affecting warfarin dose requirements. ORM1 *S carriers require lower maintenance doses to achieve and maintain an optimal level of anticoagulation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perini JA, Struchiner CJ, Silva-Assuncao E, Santana IS, Rangel F, Ojopi EB, Dias-Neto E, Suarez-Kurtz G (2008) Pharmacogenetics of warfarin: development of a dosing algorithm for brazilian patients. Clin Pharmacol Ther 84:722–728
Lesko LJ (2008) The critical path of warfarin dosing: finding an optimal dosing strategy using pharmacogenetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 84:301–303
Klein TE, Altman RB, Eriksson N, Gage BF, Kimmel SE, Lee MT, Limdi NA, Page D, Roden DM, Wagner MJ, Caldwell MD, Johnson JA (2009) Estimation of the warfarin dose with clinical and pharmacogenetic data. N Engl J Med 360:753–764
Wen MS, Lee M, Chen JJ, Chuang HP, Lu LS, Chen CH, Lee TH, Kuo CT, Sun FM, Chang YJ, Kuan PL, Chen YF, Charng MJ, Ray CY, Wu JY, Chen YT (2008) Prospective study of warfarin dosage requirements based on CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genotypes. Clin Pharmacol Ther 84:83–89
Otagiri M (2009) Study on binding of drug to serum protein. Yakugaku Zasshi 129:413–425
Yuasa I, Umetsu K, Vogt U, Nakamura H, Nanba E, Tamaki N, Irizawa Y (1997) Human orosomucoid polymorphism: molecular basis of the three common ORM1 alleles, ORM1*F1, ORM1*F2, and ORM1*S. Hum Genet 99:393–398
Mastana SS, Jayasekara R, Fisher P, Sokol RJ, Papiha SS (1993) Genetic polymorphism of orosomucoid (ORM) in populations of the United Kingdom, Indian subcontinent, and Cambodia. Jpn J Hum Genet 38:289–296
Li JH, Xu JQ, Li Y, Zhuang YY, Gong JB (1999) Genetic polymorphisms of orosomucoid on the Han population in Nanjing of China. Clin Chim Acta 288:161–168
Li JH, Xu JQ, Cao XM, Ni L, Li Y, Zhuang YY, Gong JB (2002) Influence of the ORM1 phenotypes on serum unbound concentration and protein binding of quinidine. Clin Chim Acta 317:85–92
Tinguely D, Baumann P, Conti M, Jonzier-Perey M, Schopf J (1985) Interindividual differences in the binding of antidepressives to plasma proteins: the role of the variants of alpha 1-acid glycoprotein. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 27:661–666
Zhang C, Tu ZL, Wang QB, Cheng XL, Zhang PH (2007) Influence of ORM1 polymorphism on serum concentration of free nortriptyline. Yao Xue Xue Bao 42:843–848
Colombo S, Buclin T, Decosterd LA, Telenti A, Furrer H, Lee BL, Biollaz J, Eap CB (2006) Orosomucoid (alpha1-acid glycoprotein) plasma concentration and genetic variants: effects on human immunodeficiency virus protease inhibitor clearance and cellular accumulation. Clin Pharmacol Ther 80:307–318
Urien S, Albengres E, Zini R, Tillement JP (1982) Evidence for binding of certain acidic drugs to alpha1-acid glycoprotein. Biochem Pharmacol 31:3687–3689
Nakagawa T, Kishino S, Itoh S, Sugawara M, Miyazaki K (2003) Differential binding of disopyramide and warfarin enantiomers to human alpha(1)-acid glycoprotein variants. Br J Clin Pharmacol 56:664–669
Lee MT, Chen CH, Chou CH, Lu LS, Chuang HP, Chen YT, Saleem AN, Wen MS, Chen JJ, Wu JY, Chen YT (2009) Genetic determinants of warfarin dosing in the Han-Chinese population. Pharmacogenomics 10:1905–1913
Wang TL, Li HL, Tjong WY, Chen QS, Wu GS, Zhu HT, Hou ZS, Xu S, Ma SJ, Wu M, Tai S (2008) Genetic factors contribute to patient-specific warfarin dose for Han Chinese. Clin Chim Acta 396:76–79
Shil AB, Strohm MP (2009) Warfarin pharmacogenetics. N Engl J Med 360:2474-75, 2475
Garcia DA, Hylek E (2009) Warfarin pharmacogenetics. N Engl J Med 360:2474–2475
Takeuchi F, McGinnis R, Bourgeois S, Barnes C, Eriksson N, Soranzo N, Whittaker P, Ranganath V, Kumanduri V, McLaren W, Holm L, Lindh J, Rane A, Wadelius M, Deloukas P (2009) A genome-wide association study confirms VKORC1, CYP2C9, and CYP4F2 as principal genetic determinants of warfarin dose. PLoS Genet 5(3):e1000433
McDonald MG, Rieder MJ, Nakano M, Hsia CK, Rettie AE (2009) CYP4F2 is a vitamin K1 oxidase: an explanation for altered warfarin dose in carriers of the V433M variant. Mol Pharmacol 75(6):1337–1346
Caldwell MD, Awad T, Johnson JA, Gage BF, Falkowski M, Gardina P, Hubbard J, Turpaz Y, Langaee TY, Eby C, King CR, Brower A, Schmelzer JR, Glurich I, Vidaillet HJ, Yale SH, Qi Zhang K, Berg RL, Burmester JK (2008) CYP4F2 genetic variant alters required warfarin dose. Blood 111(8):4106–4112
Borgiani P, Ciccacci C, Forte V, Sirianni E, Novelli L, Bramanti P, Novelli G (2009) CYP4F2 genetic variant (rs2108622) significantly contributes to warfarin dosing variability in the Italian population. Pharmacogenomics 10(2):261–266
Pautas E, Moreau C, Gouin-Thibault I, Golmard JL, Mahé I, Legendre C, Taillandier-Hériche E, Durand-Gasselin B, Houllier AM, Verrier P, Beaune P, Loriot MA, Siguret V (2010) Genetic factors (VKORC1, CYP2C9, EPHX1, and CYP4F2) are predictor variables for warfarin response in very elderly, frail inpatients. Clin Pharmacol Ther 87(1):57–64
Bejarano-Achache I, Levy L, Mlynarsky L, Bialer M, Muszkat M, Caraco Y (2012) Effects of CYP4F2 polymorphism on response to warfarin during induction phase: a prospective, open-label. Observational Cohort Study. Clin Ther 34(4):811–23
Zhang JE, Jorgensen AL, Alfirevic A, Williamson PR, Toh CH, Park BK, Pirmohamed M (2009) Effects of CYP4F2 genetic polymorphisms and haplotypes on clinical outcomes in patients initiated on warfarin therapy. Pharmacogenet Genomics 19(10):781–789
Perini JA, Struchiner CJ, Silva-Assunção E, Suarez-Kurtz G (2010) Impact of CYP4F2 rs2108622 on the stable warfarin dose in an admixed patient cohort. Clin Pharmacol Ther 87(4):417–420
Liang R, Wang C, Zhao H, Huang J, Hu D, Sun Y (2012) Influence of CYP4F2 genotype on warfarin dose requirement—a systematic review and meta-analysis. Thromb Res 130(1):38–44
Wadelius M, Chen LY, Eriksson N, Bumpstead S, Ghori J, Wadelius C, Bentley D, McGinnis R, Deloukas P (2007) Association of warfarin dose with genes involved in its action and metabolism. Hum Genet 121:23–34
Krynetskiy E, McDonnell P (2007) Building individualized medicine: prevention of adverse reactions to warfarin therapy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 322:427–434
Wadelius M, Pirmohamed M (2007) Pharmacogenetics of warfarin: current status and future challenges. Pharmacogenomics J 7:99–111
Cooper GM, Johnson JA, Langaee TY, Feng H, Stanaway IB, Schwarz UI, Ritchie MD, Stein CM, Roden DM, Smith JD, Veenstra DL, Rettie AE, Rieder MJ (2008) A genome-wide scan for common genetic variants with a large influence on warfarin maintenance dose. Blood 112:1022–1027
Wadelius M, Chen LY, Lindh JD, Eriksson N, Ghori MJ, Bumpstead S, Holm L, McGinnis R, Rane A, Deloukas P (2009) The largest prospective warfarin-treated cohort supports genetic forecasting. Blood 113(4):784–792
Breckenridge A, Orme M (1973) Kinetics of warfarin absorption in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther 14:955–961
Porter RS, Sawyer WT (1992) Warfarin. In: Evans WE, Schentag JJ, Jusko WJ (eds) Applied pharmacokinetics. Applied Therapeutics, Inc, Vancouver, pp 31-1 to 31-46
Seller EM, Koch-Weser J (1971) Kinetics and clinical importance of displacement of warfarin from albumin by acidic drugs. Ann N Y Acad Sci 170:213–225
Zimmerman JJ, Raible DG, Harper DM, Matschke K, Speth JL (2008) Evaluation of a potential tigecycline–warfarin drug interaction. Pharmacotherapy 28(7):895–905
Nishi K, Ueno M, Murakami Y, Fukunaga N, Akuta T, Kadowaki D, Watanabe H, Suenaga A, Maruyama T, Otagiri M (2009) A site-directed mutagenesis study of drug-binding selectivity in genetic variants of human alpha(1)-acid glycoprotein. J Pharm Sci 98:4316–4326
Kishino S, Nomura A, Di ZS, Sugawara M, Iseki K, Kakinoki S, Kitabatake A, Miyazaki K (1995) Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein concentration and the protein binding of disopyramide in healthy subjects. J Clin Pharmacol 35:510–514
Eap CB, Cuendet C, Baumann P (1988) Binding of amitriptyline to alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and its variants. J Pharm Pharmacol 40:767–770
Li J, Li Y, Gong J, Zhuang K, Yiyi K, Xu J-Q (2009) Serum A1-Acid glycoprotein concentrations in 213 healthy male subjects and relative analysis with age. Acta Universitatis Medicinalis Nanjing 20(5):336–338
Yoon HW, Giraldo EA, Wijdicks EF (2011) Valproic acid and warfarin: an underrecognized drug interaction. Neurocrit Care 15(1):182–185
Guthrie SK, Stoysich AM, Bader G, Hilleman DE (1995) Hypothesized interaction between valproic acid and warfarin. J Clin Psychopharmacol 15(2):138–139
Hughes CA, Freitas A, Miedzinski LJ (2007) Interaction between lopinavir/ritonavir and warfarin. Can Med Assoc J 177:357–359
Gatti G, Alessandrini A, Camera M, Di Biagio A, Bassetti M, Rizzo F (1998) Influence of indinavir and ritonavir on warfarin anticoagulant activity. Aids 12:825–826
Knoell KR, Young TM, Cousins ES (1998) Potential interaction involving warfarin and ritonavir. Ann Pharmacother 32:1299–1302
Funding
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China grant 81072707, 81173134 and 81070902.
Competing interests
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L.S., Shang, J.J., Shi, S.Y. et al. Influence of ORM1 polymorphisms on the maintenance stable warfarin dosage. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 69, 1113–1120 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-012-1448-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-012-1448-6