Abstract
Two uplift episodes have recently been recorded at Phlegraean Fields, a volcanic region near Naples (south-central Italy). The first episode occurred in 1970 and lasted up to 1972; the second has begun at the end of 1982 and is still in progress.
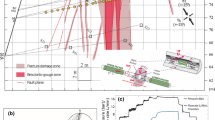
An attempt to model the ground deformations which occurred during the 1970–1972 event is made in this paper. The source has been assumed to be a two-dimensional fluid-filled fracture, similar to a sill. A good fit with experimental data has been obtained for a short (1–2 km long) shallow (3 km deep) source and a driving pressure ranging from 60 to 210 bars. Rigidity values have been fixed at 3.5–4.0 × 1010 c.g.s., with Poisson ratio equal to 0.3.
This solution which differs from previous approaches byMogi (1958) andWalsh andDecker (1971) is non-unique, but the present results are in good agreement with observed horizontal and vertical displacements. Notwithstanding the oversimplification made in assuming a homogeneous elastic semi-infinite medium, the predicted stress field seems to be in agreement with the fault-plane solutions and the pattern of epicenters determined for the uplift-seismic swarm episode that is still in progress.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbarella, M., Gubellini, A. andRusso, P., 1983,Rilievo ed analisi dei recenti movimenti orizzontali del suolo nell'area flegrea. Atti II Convegno Naz. G.N.G.T.S., CNR, Roma (in press).
Bodvarsson, G., 1976,Thermoelastic Phenomena in Geothermal Systems. In« Proceedings of the 2nd Symposium on the Development and Use of Geothermal Resources », San Francisco, California, United Nations, New York,2, p. 903–907.
Bruni, P., Sbrana, A. andSilvano, A., 1981, Risultati geologici preliminari dell'eplorazione geotermica dei Campi Flegrei. Rend. Soc. Geol. It.,4, p. 231–236.
Caputo, M., 1979,Two-thousand Years of Geodetic and Geophysical Observation in the Phlegraean Fields near Naples, Geophys. J.R. astr. Soc.,56, p. 319–328.
Corrado, G. Guerra, I., Lo Bascio, A., Luongo, G. andRampoldi, R., 1977,Inflation and Microearthquake Activity of Phlegraean Fields, Italy. Bull. Volcanol.,40, p. 1–20.
Davis, P.M., 1983,Surface Deformation Associated with a Dipping Hydrofracture. J. Geophys. Res.,88, p. 5826–5834.
De Michelis, A. M., Dequal, S. andFolloni, G., 1978,Geodetic Surveying of Soil Movements in the Phlegraean Area. Rivista del Catasto e dei Servizi Tecnici Erariali,XXXIII, 1, p. 11–26.
Dequal, S., 1972,Rilievo degli spostamenti planimetrici di punti nella zona di Pozzuoli. Quaderni della Ricerca Scientifica, CNR, Roma, p. 231–262.
Dieterich, J.H. andDecker, R.W., 1975,Finite Element Modeling of Surface Formation Associated with Volcanism. J. Geophys. Res.,80, p. 4094–4102.
Goodier, J.N., 1937,On the Integration of the Thermoelastic Equations. Phil. Mag.,7, p. 1017–1032.
Kisslinger, C., 1975,Processes during the Matsushiro Earthquake Swarm as Revealed by Levelling, Gravity and Spring-flow Observations. Geology,3, p. 217–221.
Lyell, C., 1872,Principles of Geology. Appleton and Co., New York,II, 621 pp.
Mogi, K., 1958,Relations between the Eruptions of Various Volcanoes and the Deformations of the Ground Surfaces around Them. Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst., Tokyo Univ.,36, p. 99–134.
Nur, A., 1974,The Matsushiro, Japan, Earthquake Swarm: Confirmation of the Dilatancy-Fluid Diffusion Model. Geology,2, p. 217–221.
Pollard, D.D. andHolzhausen, G., 1979,On the Mechanical Interaction between a Fluid-filled Fracture and the Earth's Surface. Tectonophysics,53, p. 27–57.
Ryan, M.P., Blevius, J.Y.K., Okamura, A.T. andKoyanagi, R.Y., 1983,Magma Reservoir Subsidence Mechanics: Theoretical Summary and Application to Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii. J. Geophys. Res.,88, p. 4147–4181.
Sneddon, I.N., 1946,The Distribution of Stress in the Neighbourhood of a Crack in an Elastic Solid. Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A,A187, p. 229–260.
Sun, R.J., 1969,Theoretical Size of Hydraulically Induced Horizontal Fractures and Corresponding Surface Uplift in an Idealized Medium. J. Geophys. Res.,74, p. 5995–6011.
Tsumura, K., 1978,Anomalous Crustal Activity in the Izu Peninsula, Central Honshu. In« Earthquake Precursors»,Kisslinger C. andSuzuki Z. (eds.), Center for Academic Publ., Japan, p. 51–68.
Versino, L. (ed.), 1972,Relazione sui rilievi effettuati nell'area flegrea nel 1970–71. Quaderni Ricerca Scientifica, n. 83, CNR, Rome.
Walsh, J.B. andDecker, R.W., 1971,Surface Deformation Associated with Volcanism. J. Geophys. Res.,76, p. 3291–3302.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonasia, V., Pingue, F. & Scarpa, R. A fluid-filled fracture as possible mechanism of ground deformation at Phlegraean Fields, Italy. Bull Volcanol 47, 313–320 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01961562
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01961562