Abstract
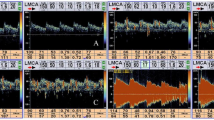
Right-to-left shunt through a patent foramen ovale was searched for in 80 patients with acute ischemic stroke by simultaneously performing transthoracic two-dimensional echocardiography and transcranial Doppler during agitated saline injection. A patent foramen ovale was detected by echocardiography in 14 patients (17.5%). Transcranial Doppler correctly identified all 14 patients, and 7 more patients in whom echocardiographic findings were indeterminate. Prevalence of patent foramen ovale by transcranial Doppler was therefore 26.3% (21 of 80 patients). Concordance between the two tests was 91.3% (73 of 80 patients). The delivery of contrast material to cerebral vessels is therefore demonstrable by transcranial Doppler in all patients diagnosed by contrast echocardiography, suggesting that paradoxical embolization through a patent foramen ovale may be more frequent than previously thought. Transcranial Doppler with contrast injection is a valid alternative in case of poor echocardiographic image quality.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jones HR, Caplan LR, Come PC, Swinton LW, Breslin DJ. Cerebral emboli of paradoxical origin. Ann Neurol 1983; 13: 14–19.
Harvey JR, Teague SM, Anderson JL, Voyles WF, Thadani U. Clinically silent atrial septal defects with evidence for cerebral embolization. Ann Intern Med 1986; 105: 695–97.
Biller J, Johnson MR, Adams HP. Further observations on cerebral or retinal ischemia in patients with right-left intracardiac shunts. Arch Neurol 1987; 44: 740–43.
Webster MWI, Chancellor AM, Smith HJ, Swift DL, Sharpe DN, Bass NM et al. Patent foramen ovale in young stroke patients. Lancet 1988; 2: 11–12.
Lechat P, Mas JL, Lascault G, Loron P, Theard M, Klimczac M et al. Prevalence of patent foramen ovale in patients with stroke. N Engl J Med 1988; 18: 1148–52.
Falk RH. PFO or UFO? The role of a patent foramen ovale in cryptogenic stroke. Am Heart J 1991; 121: 1264–66.
Shub C, Dimopoulos DN, Seward JB, Callahan JR, Tancredi RG, Schattenberg TT et al. Sensitivity of two-dimensional echocardiography in the direct visualization of atrial septal defect utilizing the subcostal approach: experience with 154 patients. J Am Coll Cardiol 1983; 2: 127–35.
Di Tullio M, Sacco RL, Gopal A, Mohr JP, Homma S. Patent foramen ovale as a risk factor for cryptogenic stroke. Ann Intern Med 1992; (in press) 117: 461–65.
Teague SM, Sharma MK. Detection of paradoxical cerebral echo contrast embolization by transcranial Doppler ultrasound. Stroke 1991; 22: 740–45.
Hagen PT, Scholz DG, Edwards WD. Incidence and size of patent foramen ovale during the first 10 decades of life: an autopsy study of 965 normal hearts. Mayo Clin Proc 1984; 59: 17–20.
Nemec JJ, Marwick TH, Long RJ, Davison MB, Chimowitz MI, Litowitz H, Salcedo EE. Comparison of transcranial Doppler ultrasound and transesophageal contrast echocardiography in the detection of interatrial right-to-left shunts. Am J Cardiol 1991; 68: 1498–502.
Karnik R, Stollberger C, Valentin A, Winkler WB, Slany J. Detection of patent foramen ovale by transcranial contrast Doppler ultrasound. Am J Cardiol 1992; 69: 560–62.
Mohr JP. Cryptogenic stroke. N Engl J Med 1988; 318: 1197–98.
Rocchini AP. Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect: past, present and future. Circulation 1990; 82: 751–58.
Borow KM, Karp R. Atrial septal defect: lessons from the past, directions for the future. N Engl J Med 1990; 323: 1698–700.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di Tullio, M., Sacco, R.L., Massaro, A. et al. Transcranial Doppler with contrast injection for the detection of patent foramen ovale in stroke patients. Int J Cardiac Imag 9, 1–5 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01142927
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01142927