Abstract
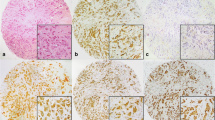
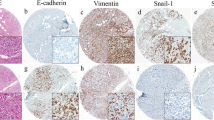
The aim of this study is to evaluate the biological role and clinical implications of silent mating type information regulation 2 homolog 1 (SIRT1) as a novel candidate for target therapy in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) for which there is no specific agent. 344 patients who received surgical resection for TNBC from January 2003 to December 2006 at Seoul National University Hospital were enrolled, and the role of SIRT1 protein was evaluated via immunohistochemistry on tissue samples. In vivo experiments to evaluate tumor invasiveness were carried out with three human TNBC cell lines following SIRT1-siRNA transfection. Expression of SIRT1 significantly correlated with lymph node metastasis (p = 0.008). In multivariate analysis, SIRT1 expression (p = 0.011), T stage (p = 0.014), and lymphatic invasion (p < 0.001) were revealed to be independent predictive factors for lymph node metastasis. Combination of these three parameters revealed predictive performance for lymph node metastasis with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.689 on receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curves analysis. SIRT1 expression correlated with shorter disease-free survival (P = 0.003) but not with overall survival. Inhibition of SIRT1 with small interfering RNA (siRNA) conspicuously suppressed the invasiveness of TNBC cell lines. This study reveals the role of SIRT1 on tumor invasiveness and unfavorable clinical outcomes, and we suggest its potential role as a prognostic indicator as well as a novel therapeutic target in TNBC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kojima K et al (2008) A role for SIRT1 in cell growth and chemoresistance in prostate cancer PC3 and DU145 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 373(3):423–428
Chen WY et al (2005) Tumor suppressor HIC1 directly regulates SIRT1 to modulate p53-dependent DNA-damage responses. Cell 123(3):437–448
Kobayashi Y et al (2005) SIRT1 is critical regulator of FOXO-mediated transcription in response to oxidative stress. Int J Mol Med 16(2):237–243
Yuan H, Su L, Chen WY (2013) The emerging and diverse roles of sirtuins in cancer: a clinical perspective. OncoTargets Ther 6:1399–1416
Deng CX (2009) SIRT1, is it a tumor promoter or tumor suppressor? Int J Biol Sci 5(2):147–152
Anders CK, Carey LA (2009) Biology, metastatic patterns, and treatment of patients with triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer 9(Suppl 2):S73–S81
Dent R et al (2007) Triple-negative breast cancer: clinical features and patterns of recurrence. Clin Cancer Res 13(15 Pt 1):4429–4434
Chung YR et al (2015) Distinctive role of SIRT1 expression on tumor invasion and metastasis in breast cancer by molecular subtype. Hum Pathol 46(7):1027–1035
Elston CW, Ellis IO (1991) Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology 19(5):403–410
Hammond ME et al (2010) American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer (unabridged version). Arch Pathol Lab Med 134(7):e48–e72
Wolff AC et al (2013) Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol 31(31):3997–4013
Rakha EA et al (2007) Breast carcinoma with basal differentiation: a proposal for pathology definition based on basal cytokeratin expression. Histopathology 50(4):434–438
Simic P et al (2013) SIRT1 suppresses the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis and organ fibrosis. Cell reports 3(4):1175–1186
Tomao F et al (2015) Triple-negative breast cancer: new perspectives for targeted therapies. OncoTargets Ther 8:177–193
Song NY, Surh YJ (2012) Janus-faced role of SIRT1 in tumorigenesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1271:10–19
Lin Z, Fang D (2013) The Roles of SIRT1 in Cancer. Genes Cancer 4(3–4):97–104
Wu M et al (2012) Expression of SIRT1 is associated with lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in both operable triple-negative and non-triple-negative breast cancer. Med Oncol (Northwood, Lond Engl) 29(5):3240–3249
Lee H et al (2011) Expression of DBC1 and SIRT1 is associated with poor prognosis for breast carcinoma. Hum Pathol 42(2):204–213
Clark-Knowles KV et al (2013) SIRT1 catalytic activity has little effect on tumor formation and metastases in a mouse model of breast cancer. PLoS ONE 8(11):e82106
Cao YW et al (2015) Clinicopathological and prognostic role of SIRT1 in breast cancer patients: a meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med 8(1):616–624
Sorlie T et al (2003) Repeated observation of breast tumor subtypes in independent gene expression data sets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(14):8418–8423
Thiery JP et al (2009) Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 139(5):871–890
Lehmann BD et al (2011) Identification of human triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for selection of targeted therapies. J Clin Investig 121(7):2750–2767
Ellsworth RE et al (2009) Molecular changes in primary breast tumors and the Nottingham Histologic Score. Pathol Oncol Res 15(4):541–547
Byles V et al (2012) SIRT1 induces EMT by cooperating with EMT transcription factors and enhances prostate cancer cell migration and metastasis. Oncogene 31(43):4619–4629
Xu J et al (2013) Up-regulation of MBD1 promotes pancreatic cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion by epigenetic down-regulation of E-cadherin. Curr Mol Med 13(3):387–400
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Dongnam Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences (DIRAMS) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (Grant No. 50608-2015) and by Grant No. 03-2014-0380 from Seoul National University Hospital Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Soo Young Chung and Yoon Yang Jung made equal contributions to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, S.Y., Jung, Y.Y., Park, I.A. et al. Oncogenic role of SIRT1 associated with tumor invasion, lymph node metastasis, and poor disease-free survival in triple negative breast cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis 33, 179–185 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-015-9767-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-015-9767-5